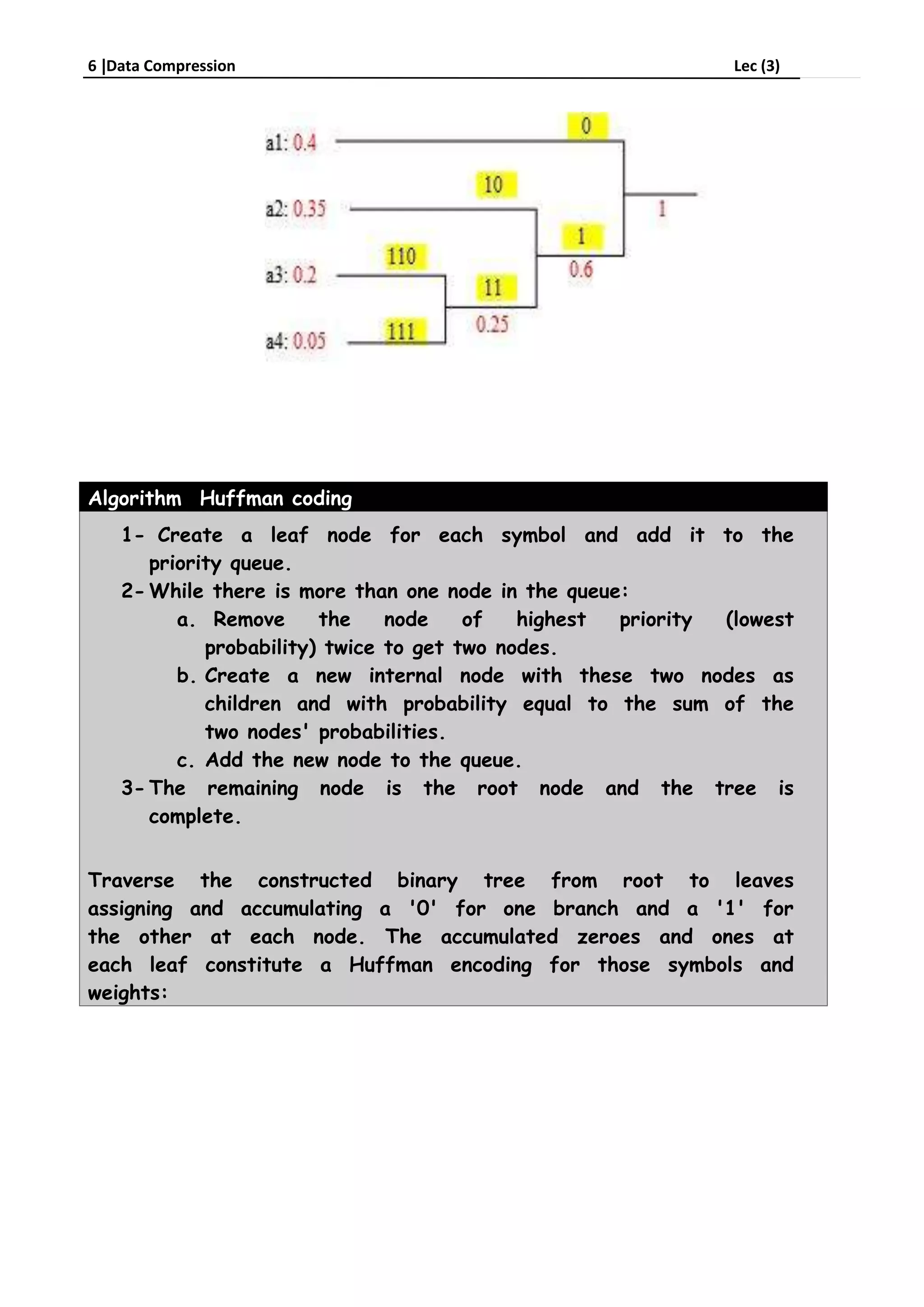
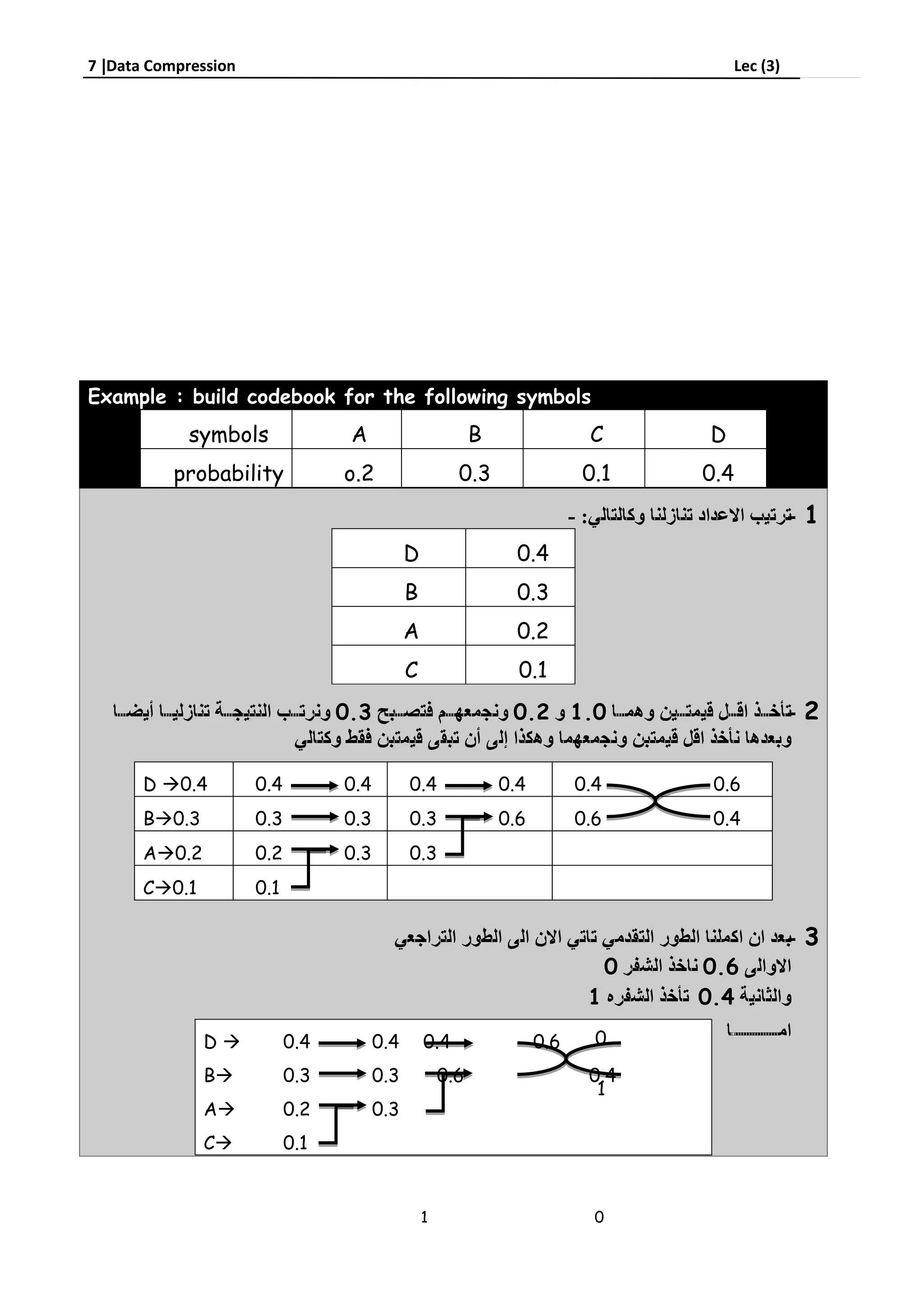
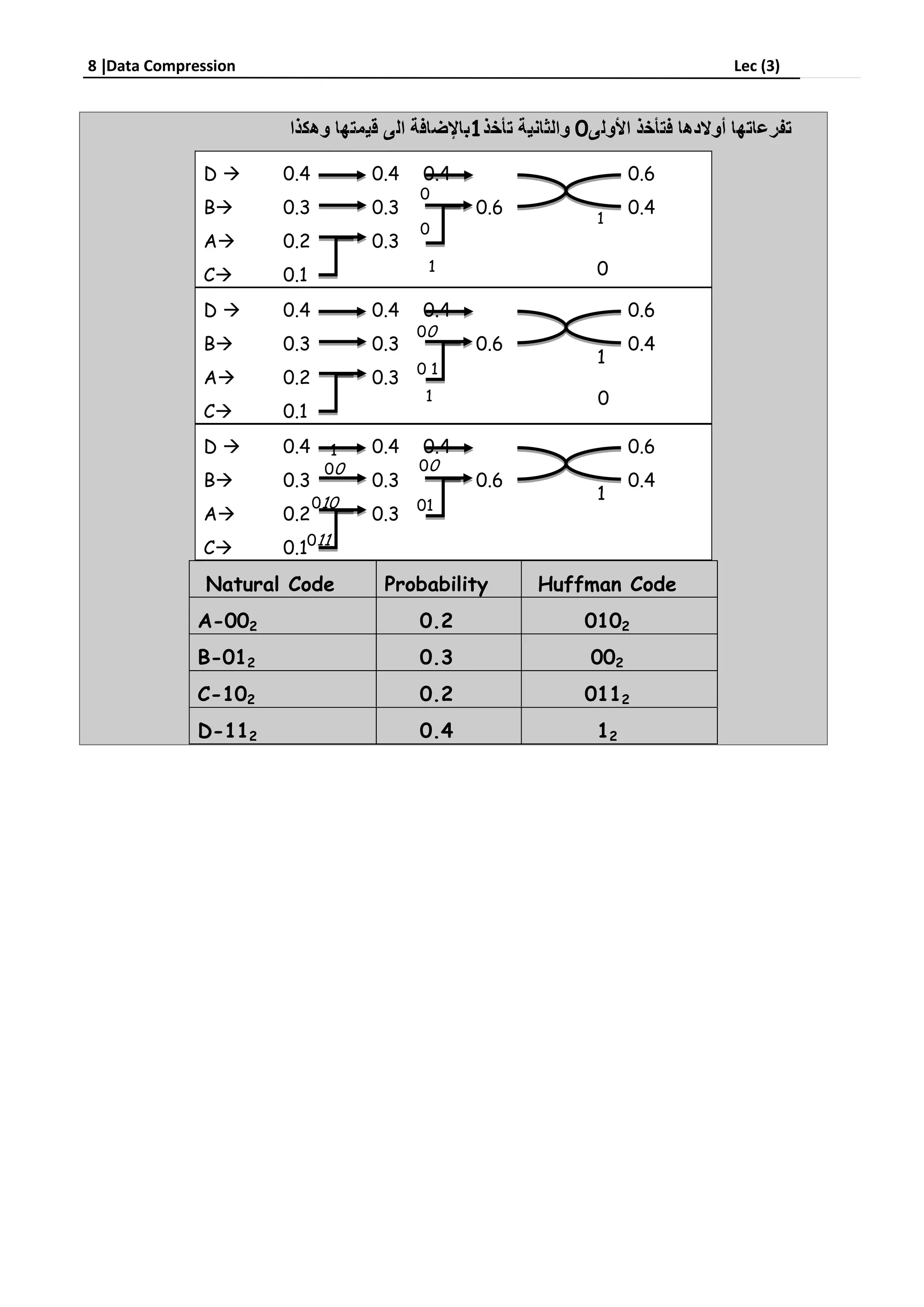
Run-length encoding is a data compression technique that replaces consecutive repeating characters with the character and number of repeats. It can be used to compress text by replacing strings like "aabbcc" with "a2b2c2". For images, runs of pixels with the same intensity value are encoded as a pair of the run length and pixel value. Huffman coding assigns variable-length binary codes to symbols based on their frequency, with more common symbols getting shorter codes to compress data more efficiently than fixed-length codes.