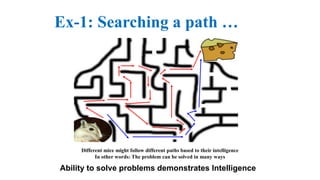
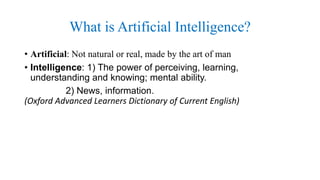
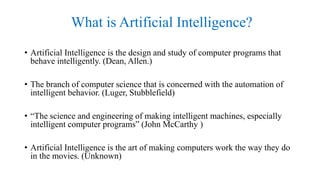
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), covering its definition, historical evolution, and foundational concepts such as knowledge representation and learning. It explores the characteristics that demonstrate intelligence, both in humans and machines, and discusses various applications of AI in fields like medicine and robotics. Furthermore, it addresses the goals of AI, including creating expert systems that mimic human thought and decision-making processes.





![What is Artificial Intelligence?
Systems that THINK Like Humans
• “[The automation of] activities that we associate with human thinking,
activities such as decision making, problem solving, learning …”
(Bellman, 1978)
• “The exciting new effort to make computers think … machines with
minds, in the full and literal sense” (Haugeland, 1985)
• “The study of computation that make it possible to perceive, reason
and act” (Winston 1992)
• “The study of mental faculties through the use of computational
models” (Charniak and McDermott)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-1introduction-190709154127/85/Lec-1-introduction-10-320.jpg)