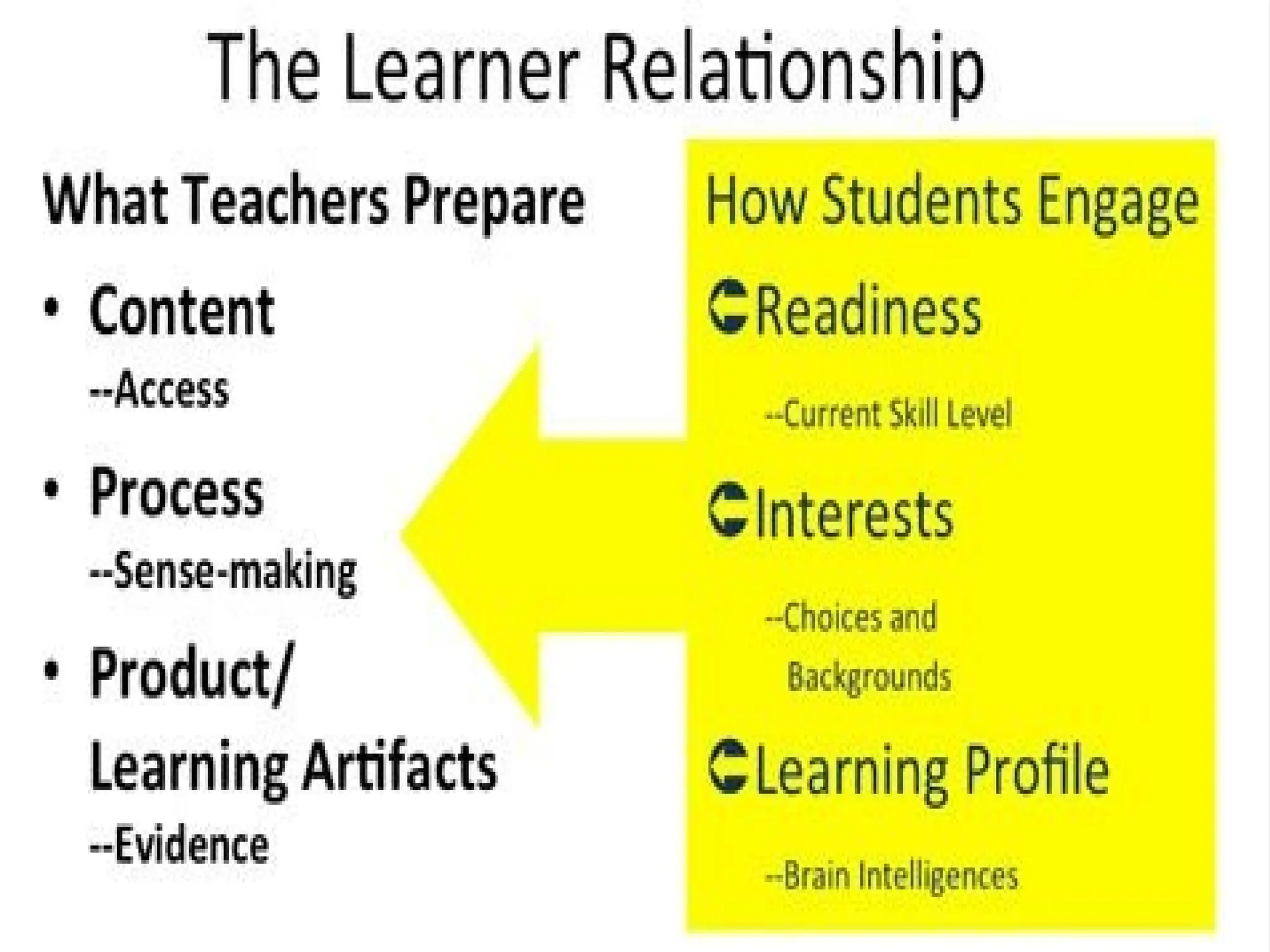
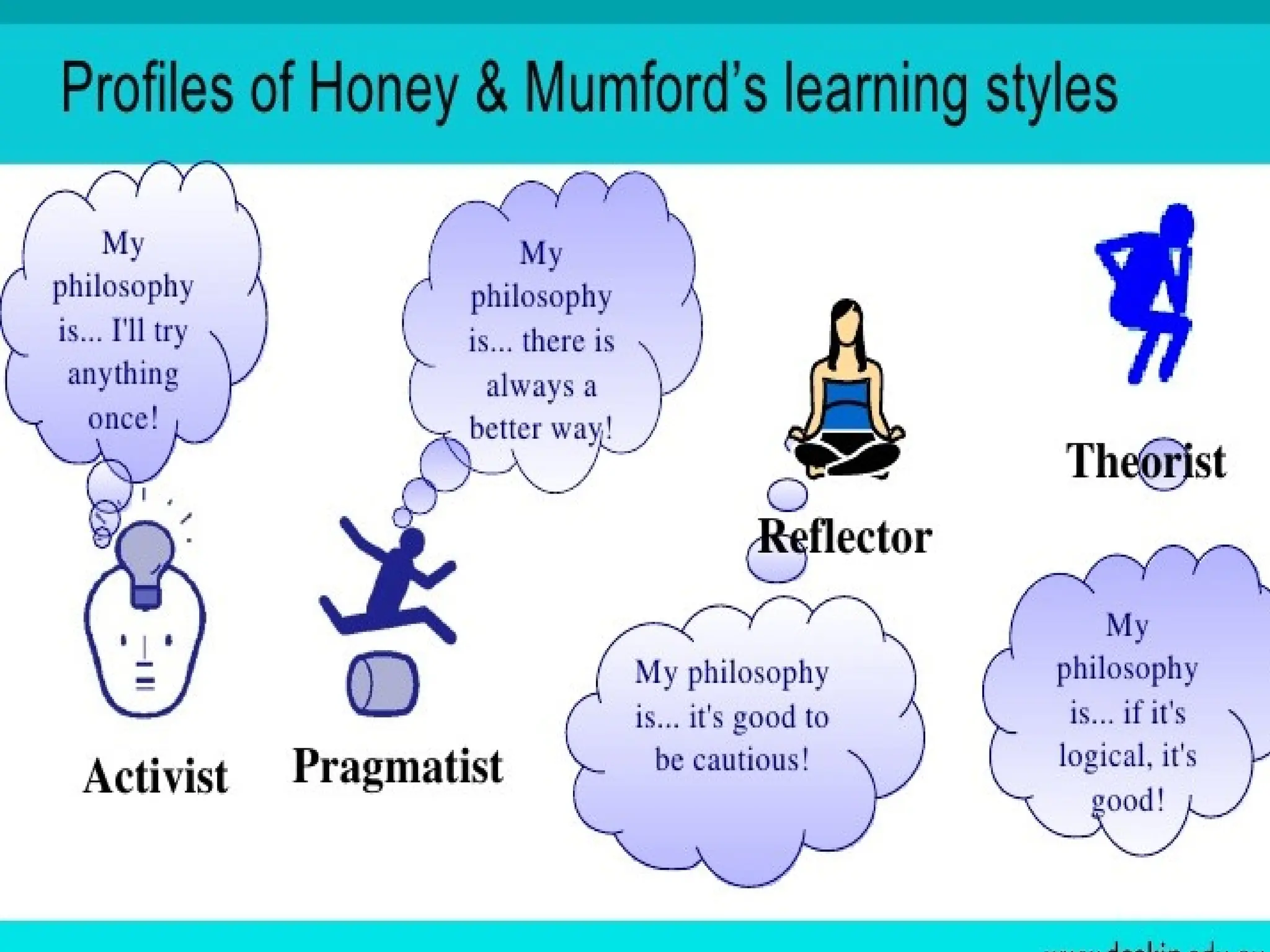
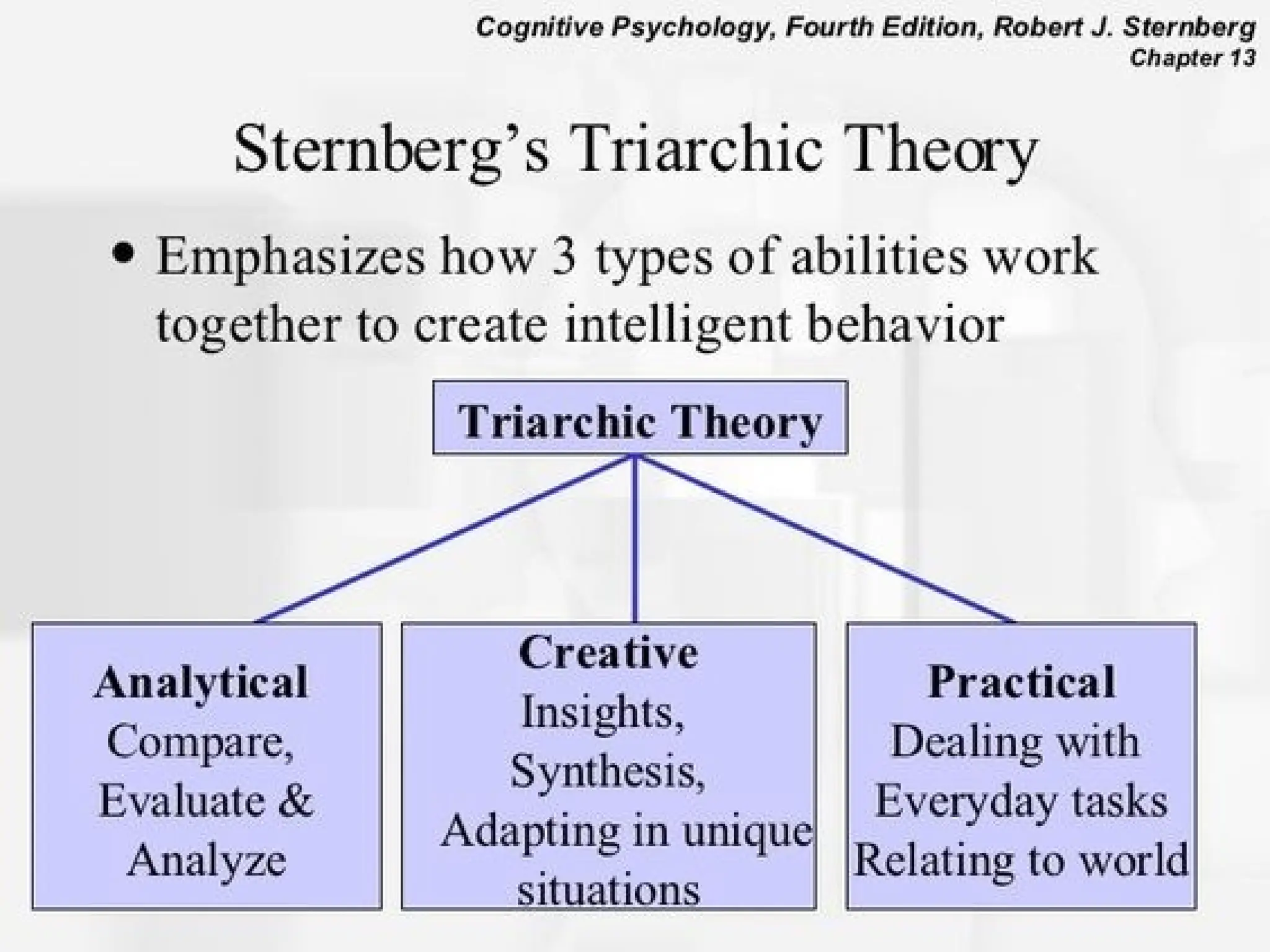
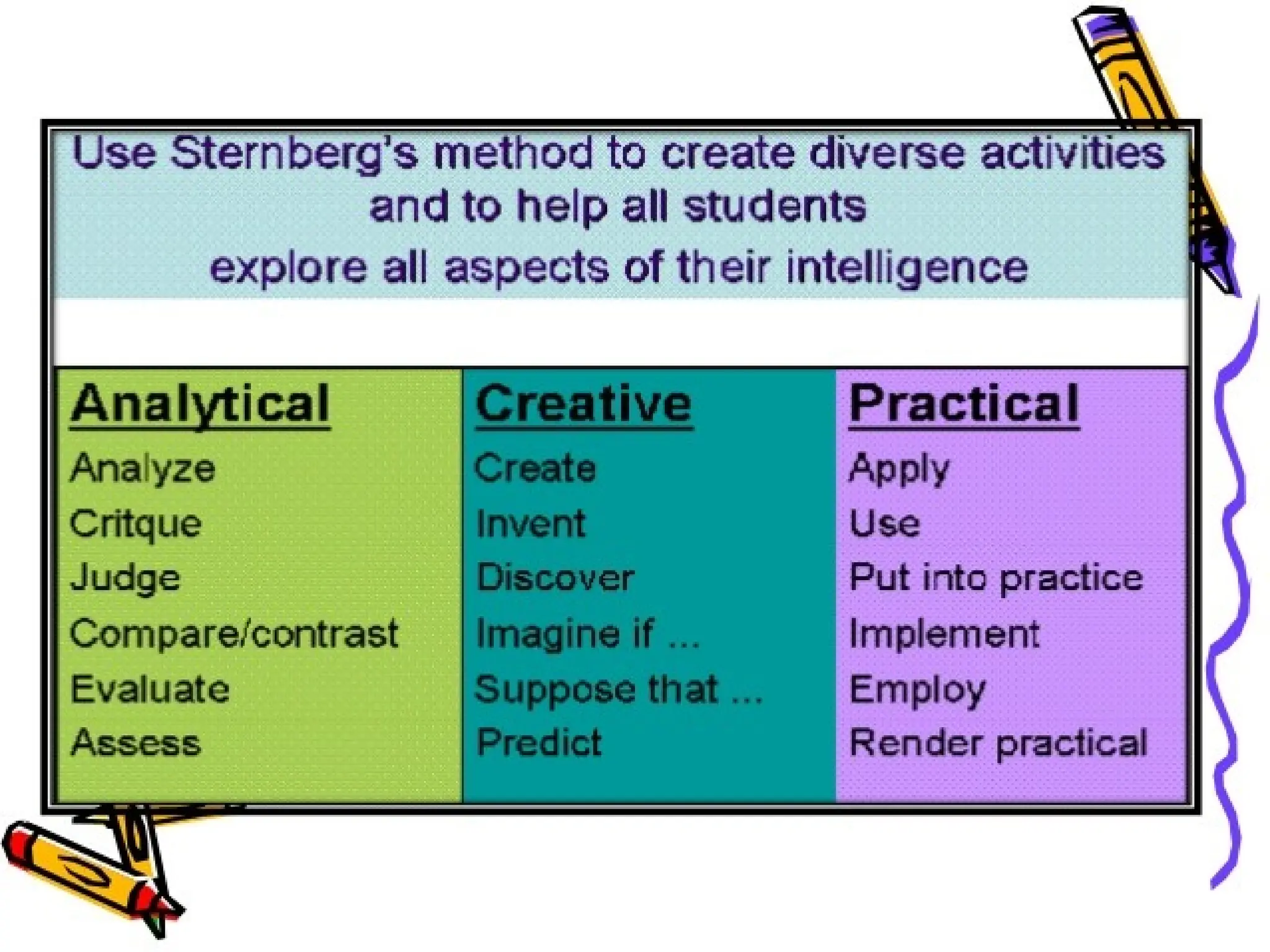
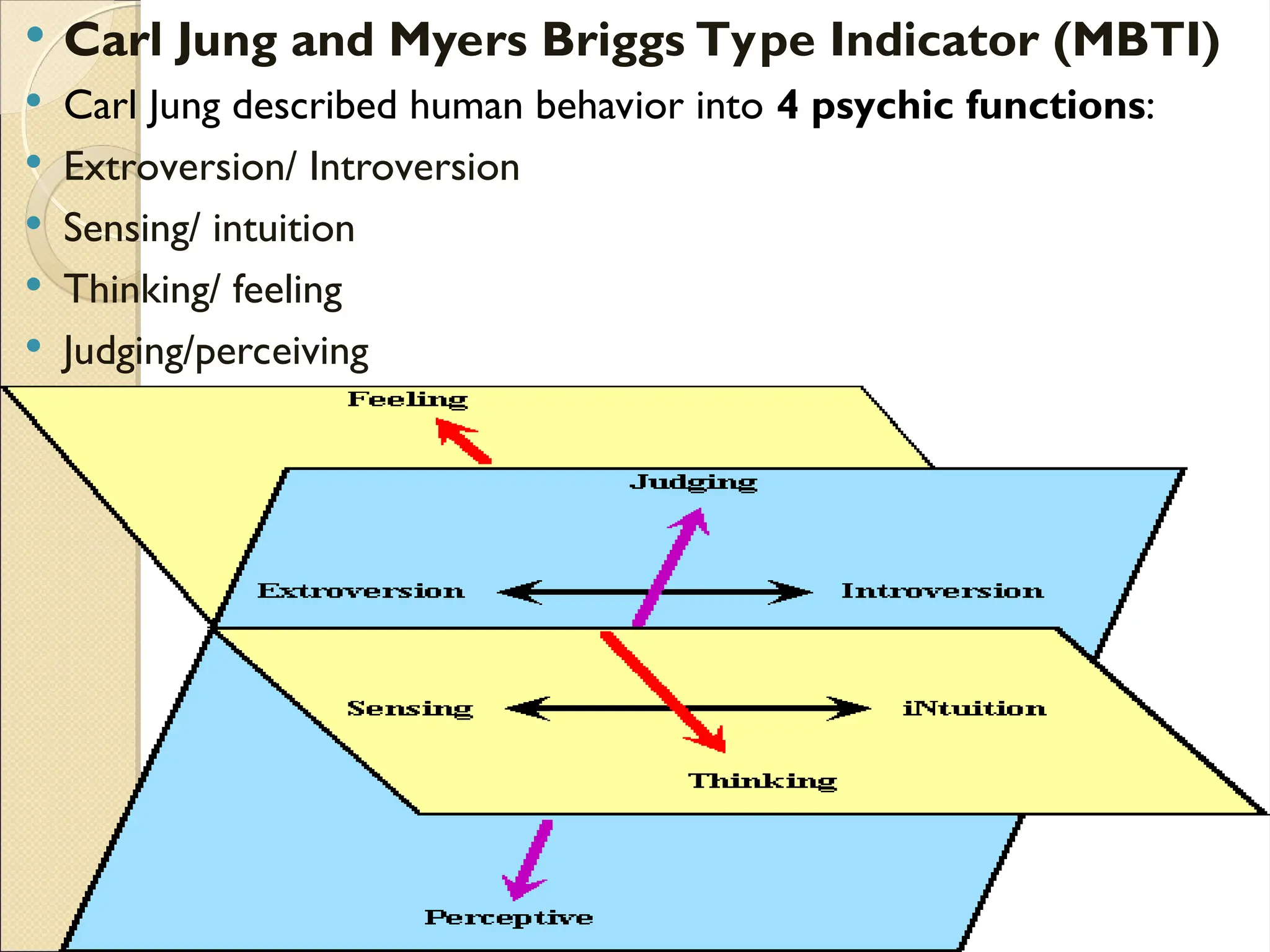
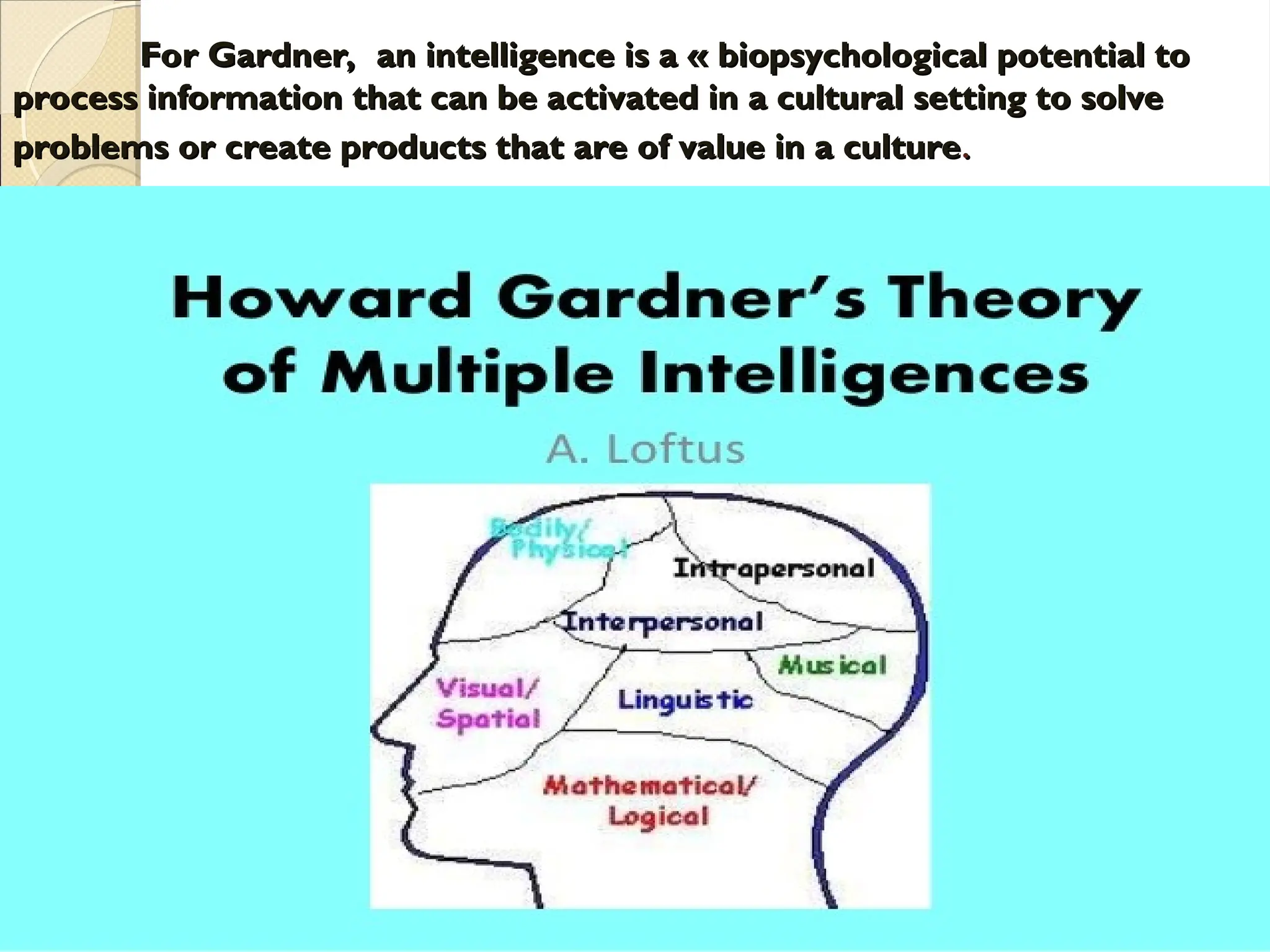
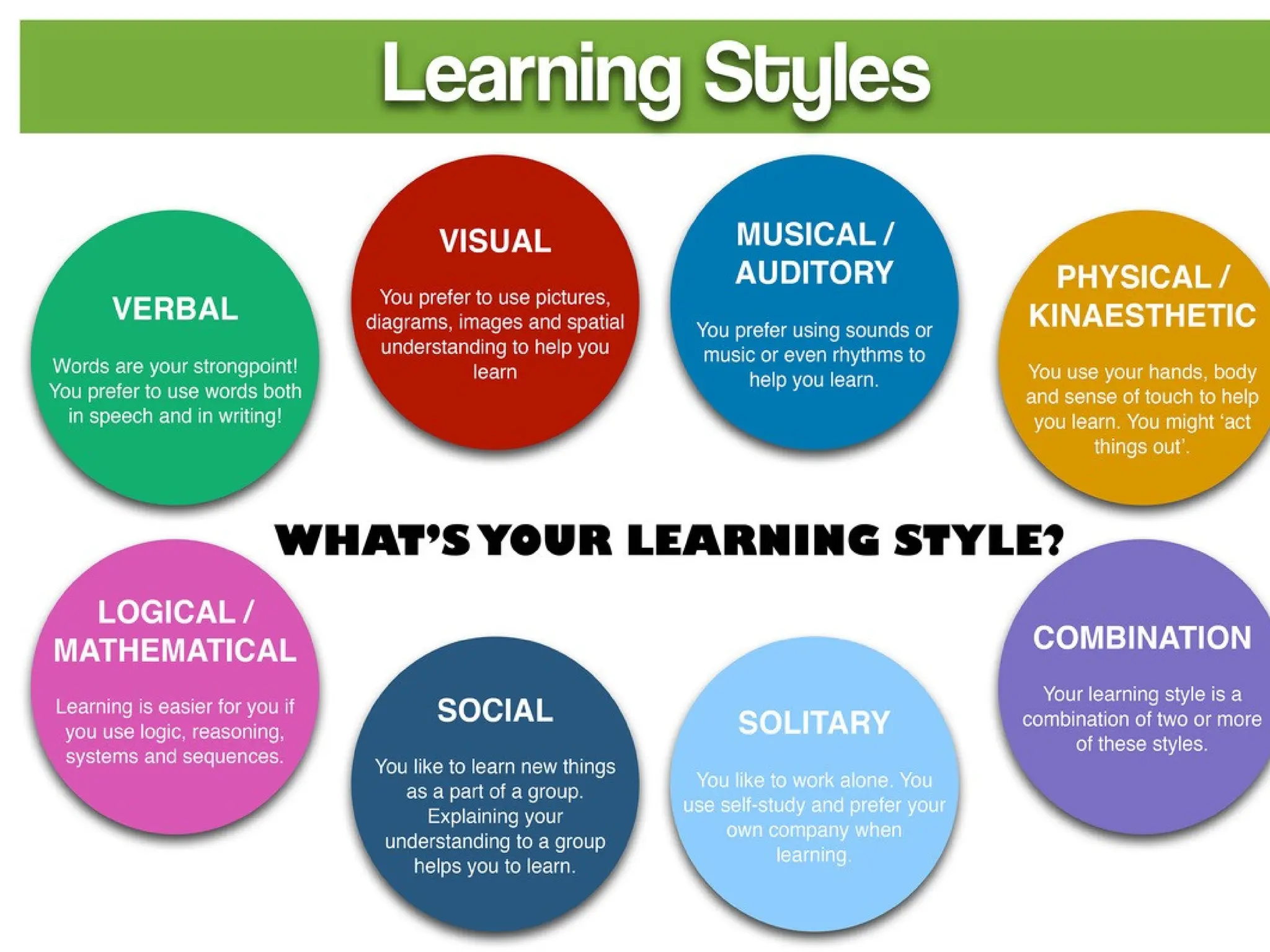
The document discusses various learning styles, emphasizing that no single approach fits all students due to their diverse backgrounds, abilities, and interests. It categorizes learners into four types: activists, reflectors, theorists, and pragmatists, each with distinct preferences for learning. Additionally, it references psychological frameworks like Carl Jung's and the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator to further understand individual differences in learning.