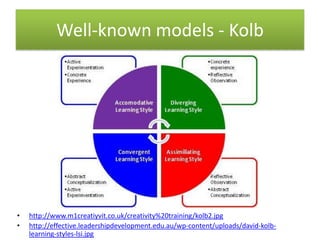
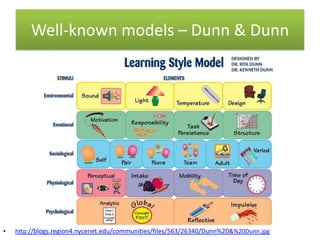
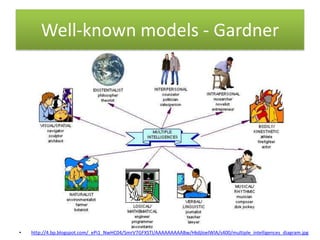
The document provides information and activities for visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners to help with pre-writing tasks. It discusses learning styles and defines them. Example activities are presented that incorporate different learning styles, such as using a voice recorder for auditory learners or forming groups to move around for kinesthetic learners. The document aims to show the connection between pre-writing activities and accommodating different learning styles.