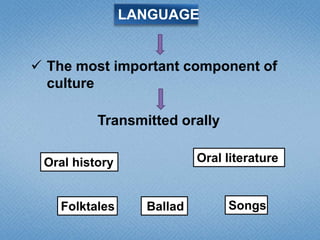
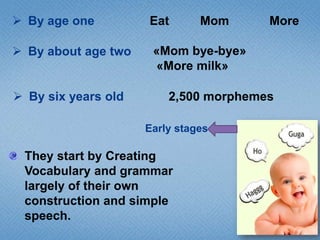
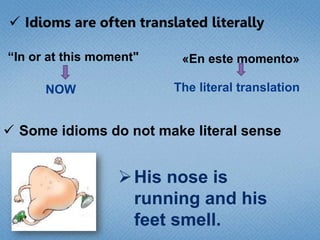
Children learn language through listening to adults and trying to communicate. By age 1 they can say single words, by age 2 they can say simple phrases, and by age 6 they have a vocabulary of around 2,500 words. They learn the sounds, words, and basic rules of their native language through positive reinforcement from parents as they imitate speech. Learning a second language is easier in early childhood when immersed with native speakers rather than in a classroom. While taking classes helps focus learning, immersion in a culture allows more natural psychological development similar to a child's first language acquisition.