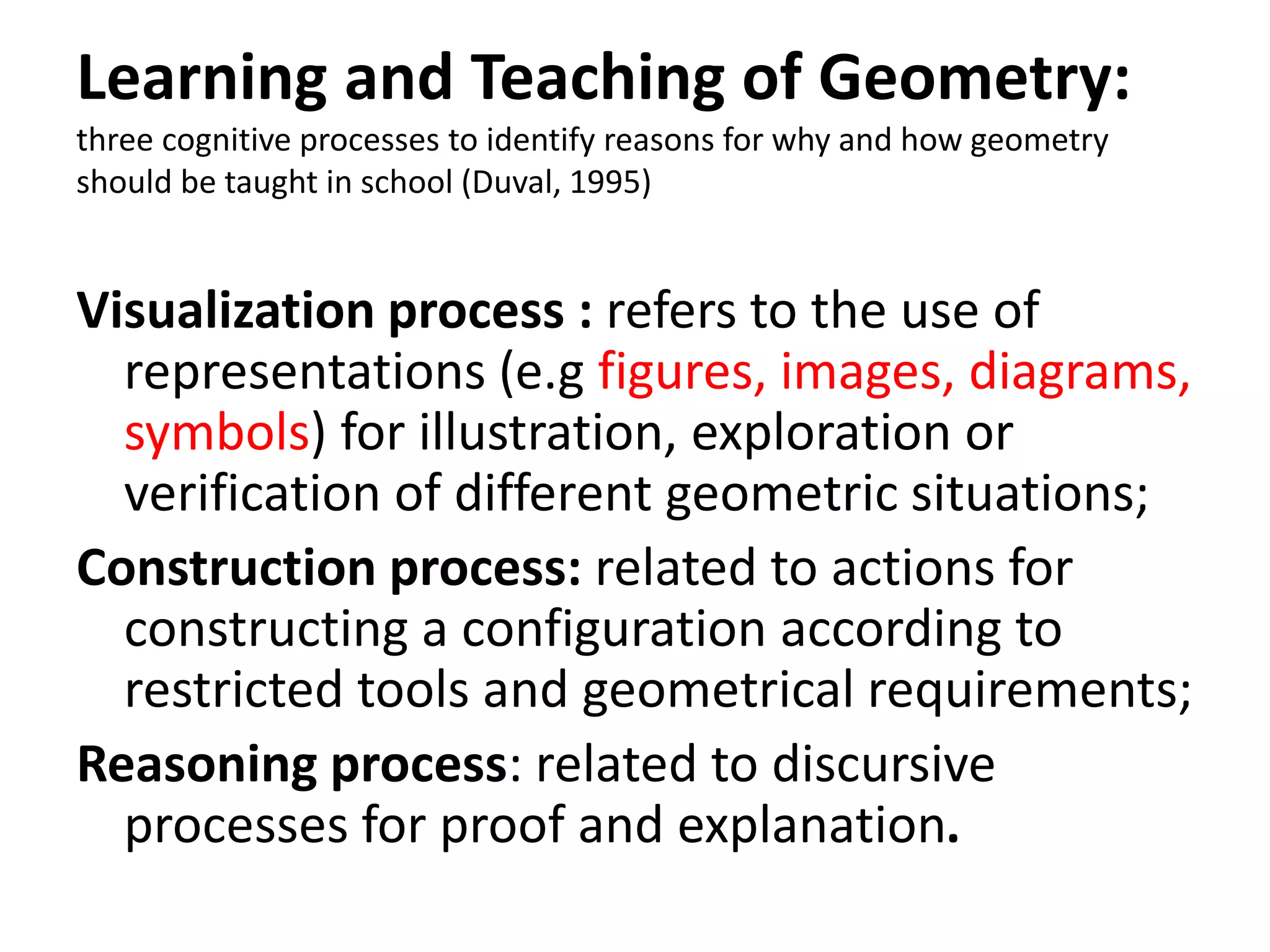
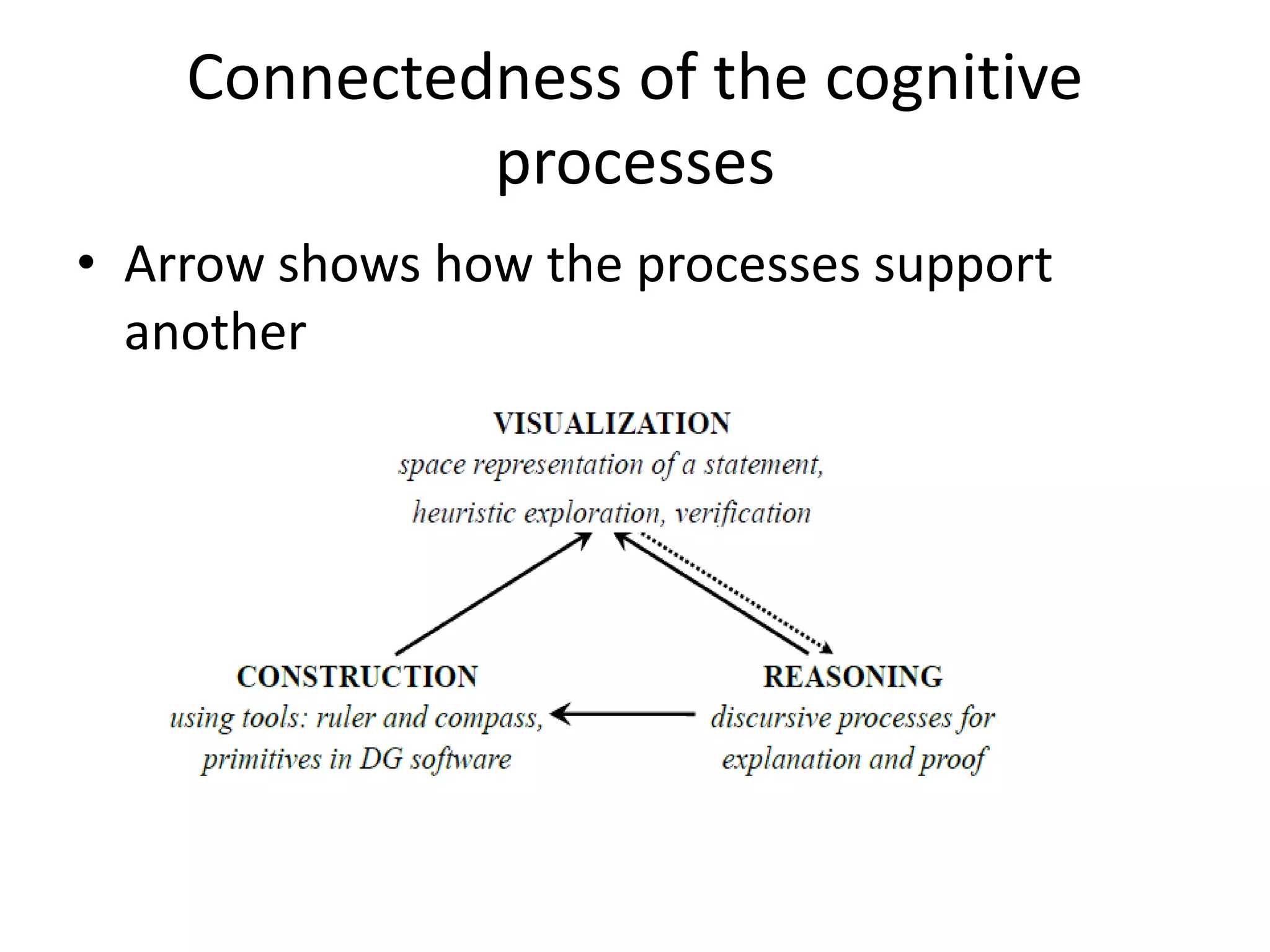
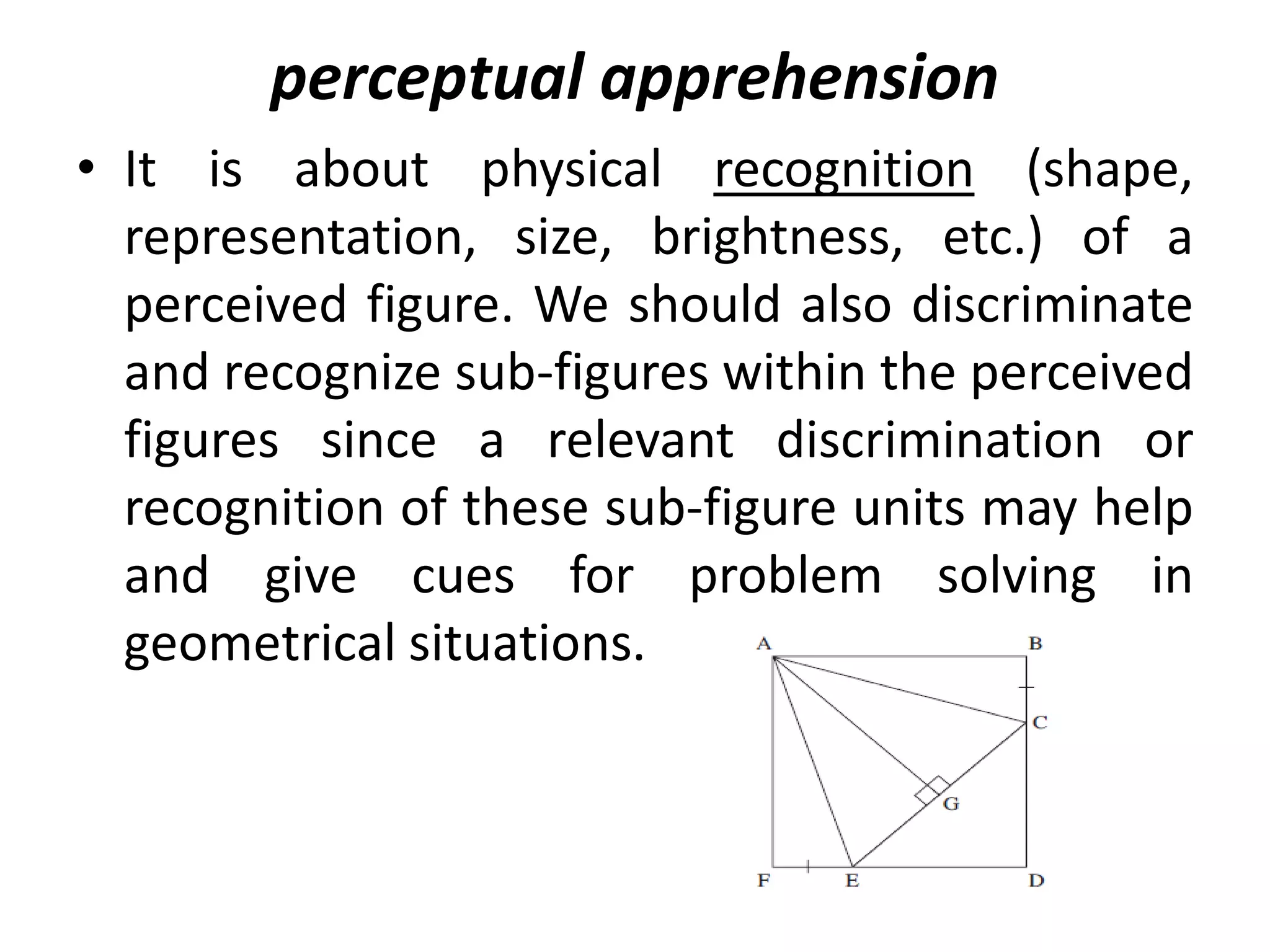
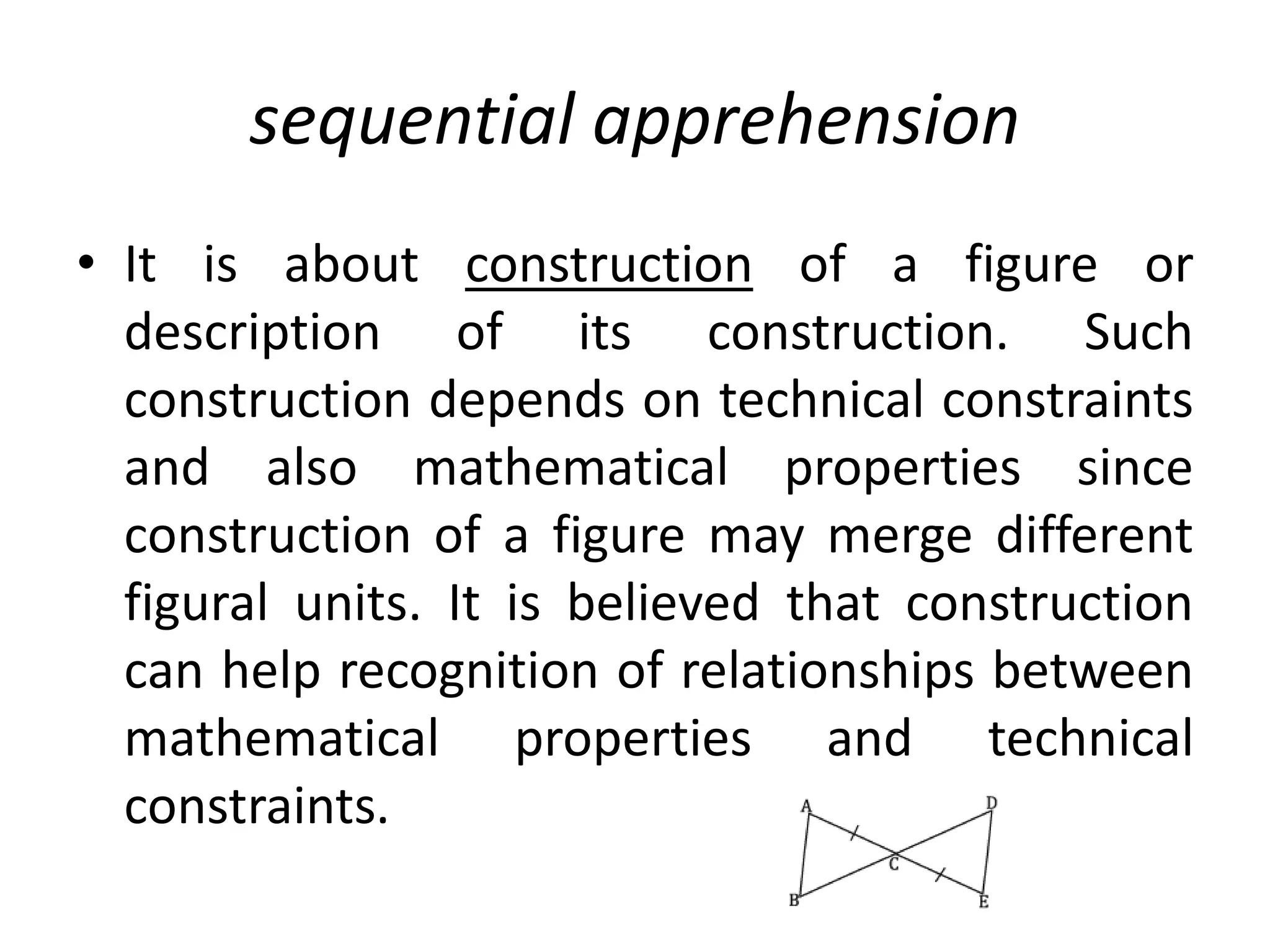
The document discusses the rationale for teaching geometry in schools. It outlines several key reasons: geometry teaches deductive reasoning skills, helps students develop spatial reasoning abilities, and provides a context for quantifying measurements of real-world objects. The document also reviews Duval's cognitive model of geometric reasoning, which identifies three processes - visualization, construction, and reasoning - that students use to understand geometric concepts. Duval's model examines how students apprehend geometric figures through perceptual, sequential, discursive, and operative processes in order to solve problems.