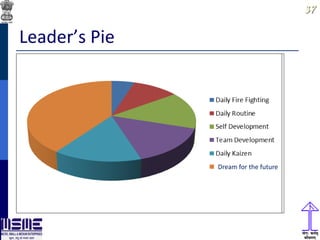
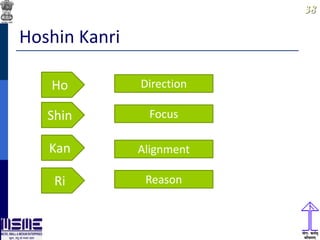
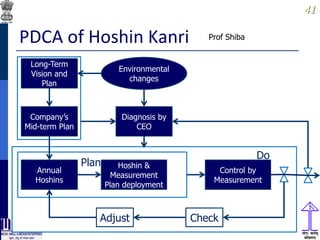
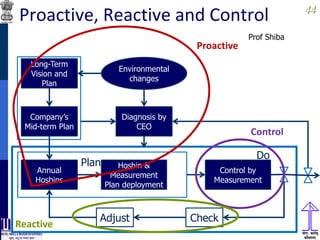
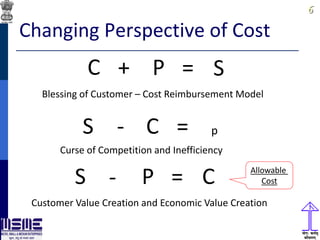
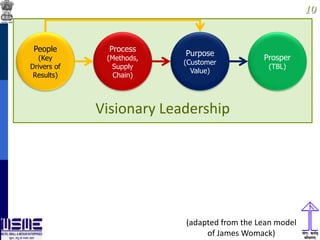
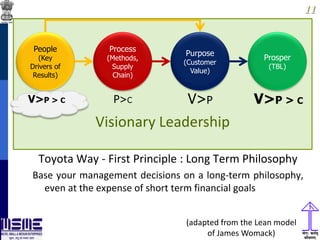
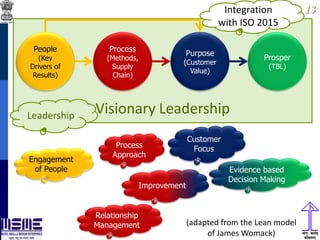
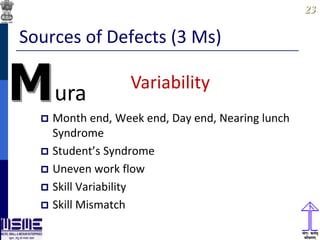
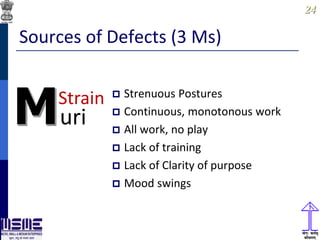
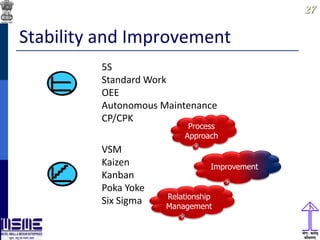
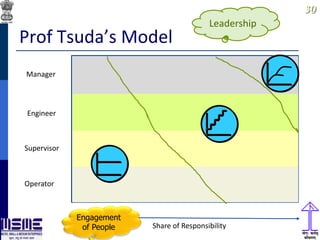
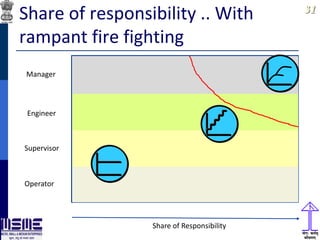
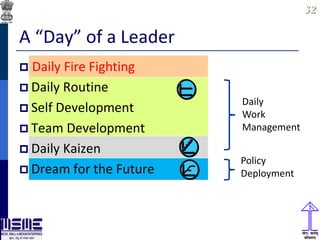
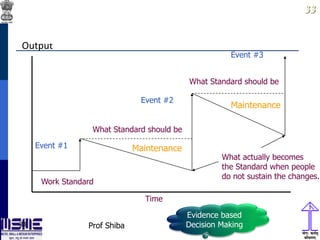
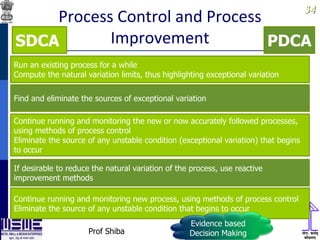
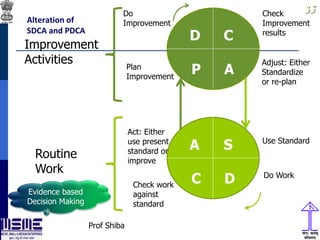
This document discusses lean thinking and leadership. It covers topics like changing cost perspectives in lean from focusing on costs to customer value. It emphasizes sustaining inequality between customer value and costs. The document presents models for lean thinking alignment with aspects like purpose, process, people and prosperity. It discusses integrating lean with quality management standards. Other topics covered include identifying types of waste, using tools like 5S, standard work and visual management. The document emphasizes leadership aspects such as engaging people, evidence-based decision making and developing a long term philosophy. It presents models for process control and improvement as well as aligning activities through hoshin kanri for business breakthroughs.


















![3636Building
Blocks of
DWM™
Standard Work
Visual
Manage-
ment
SDCA/
PDCA
Cycle
Daily
Kaizen
Defined Zonal Ownership
MP/CP Aligned with KPIs
Communication
KPIs Aligned with Policy Deployment
DWM aligned to
Customer Value
[ Control ] [ Improvement ]
Evidence based
Decision Making
Customer
Focus
Leadership Engagement
of People
Process
Approach
Improvement
Relationship
Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leanthinkingthrudwm-160311142029/85/Lean-Thinking-and-Daily-Work-Management-36-320.jpg)