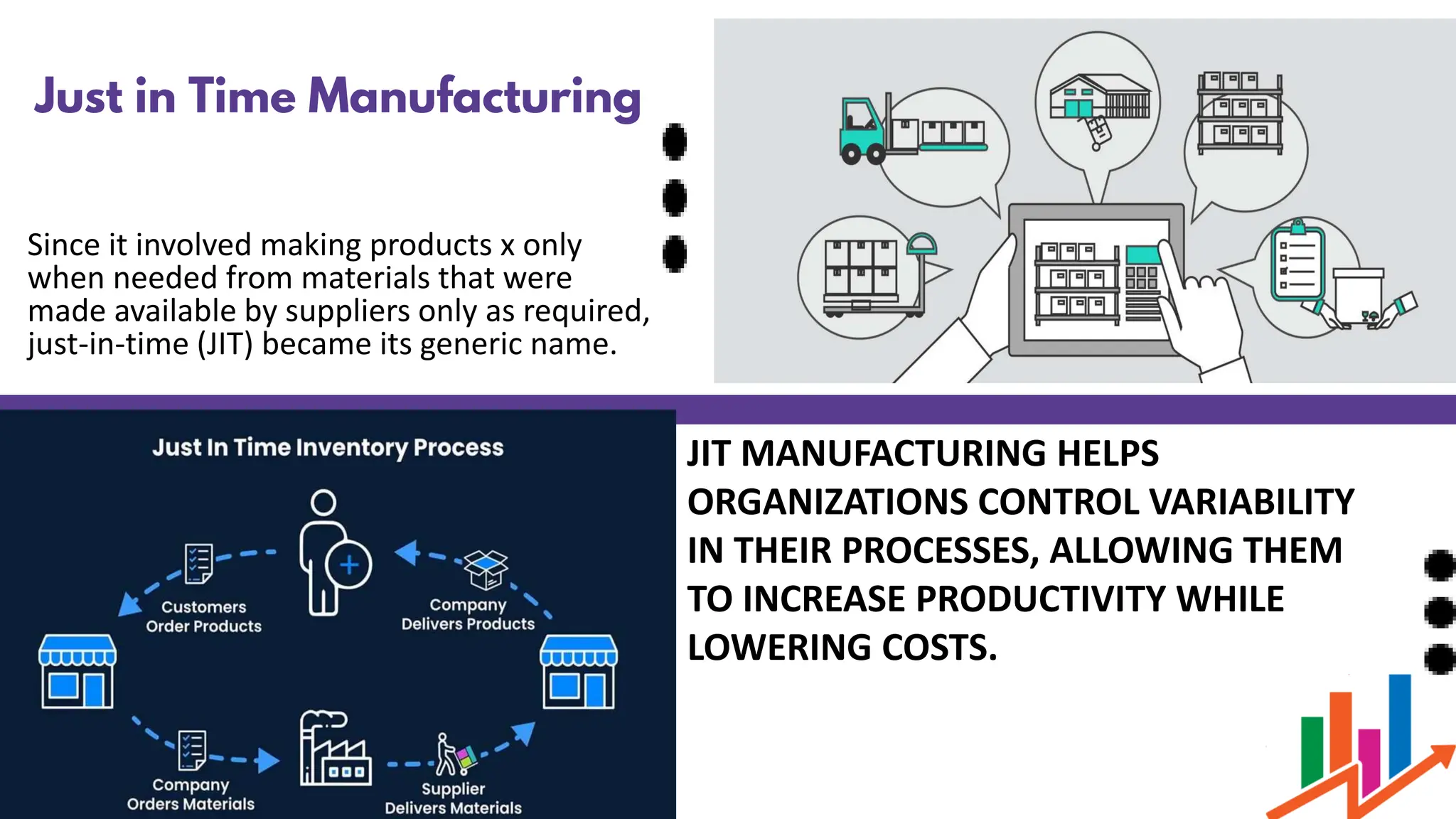
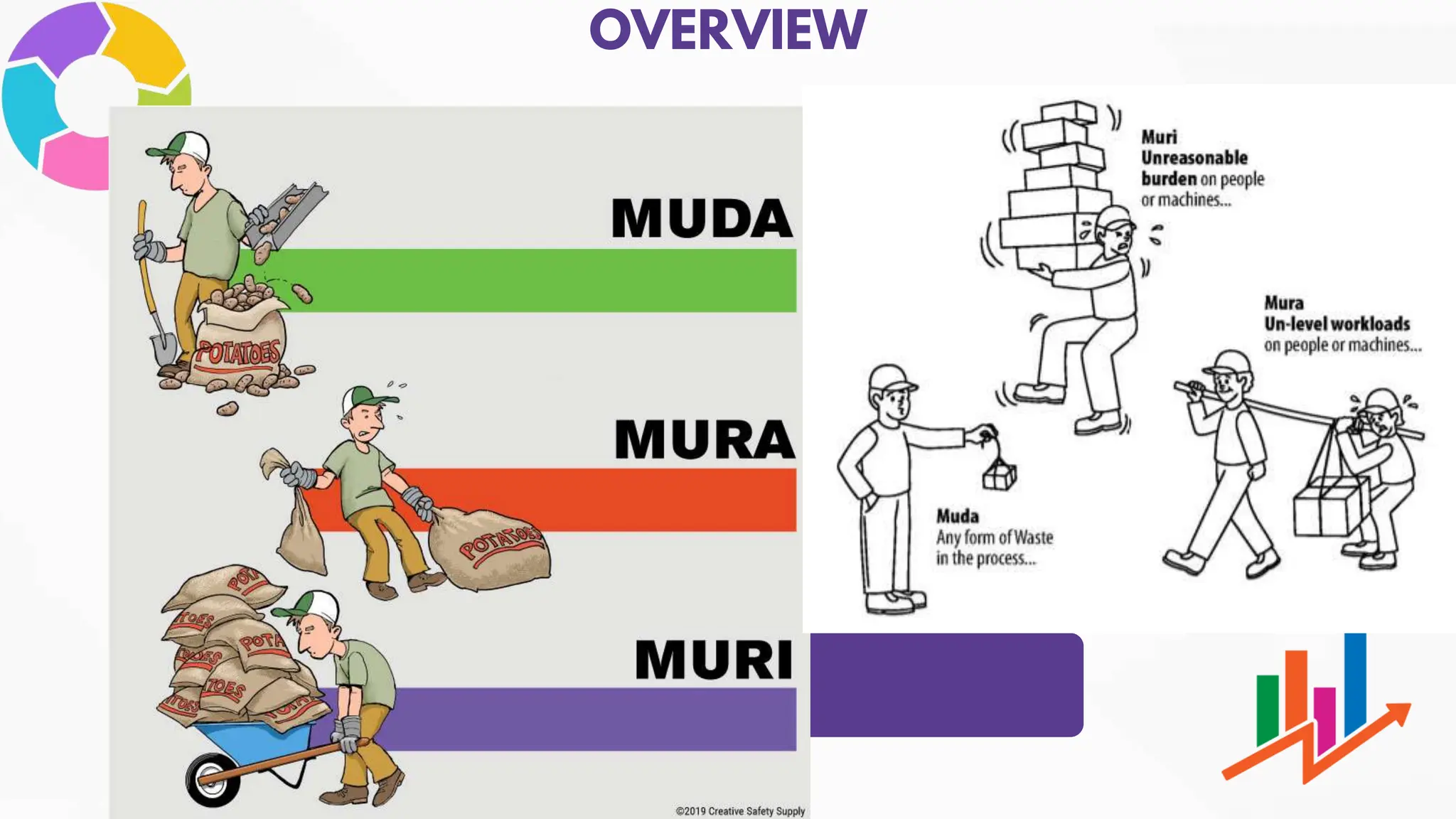
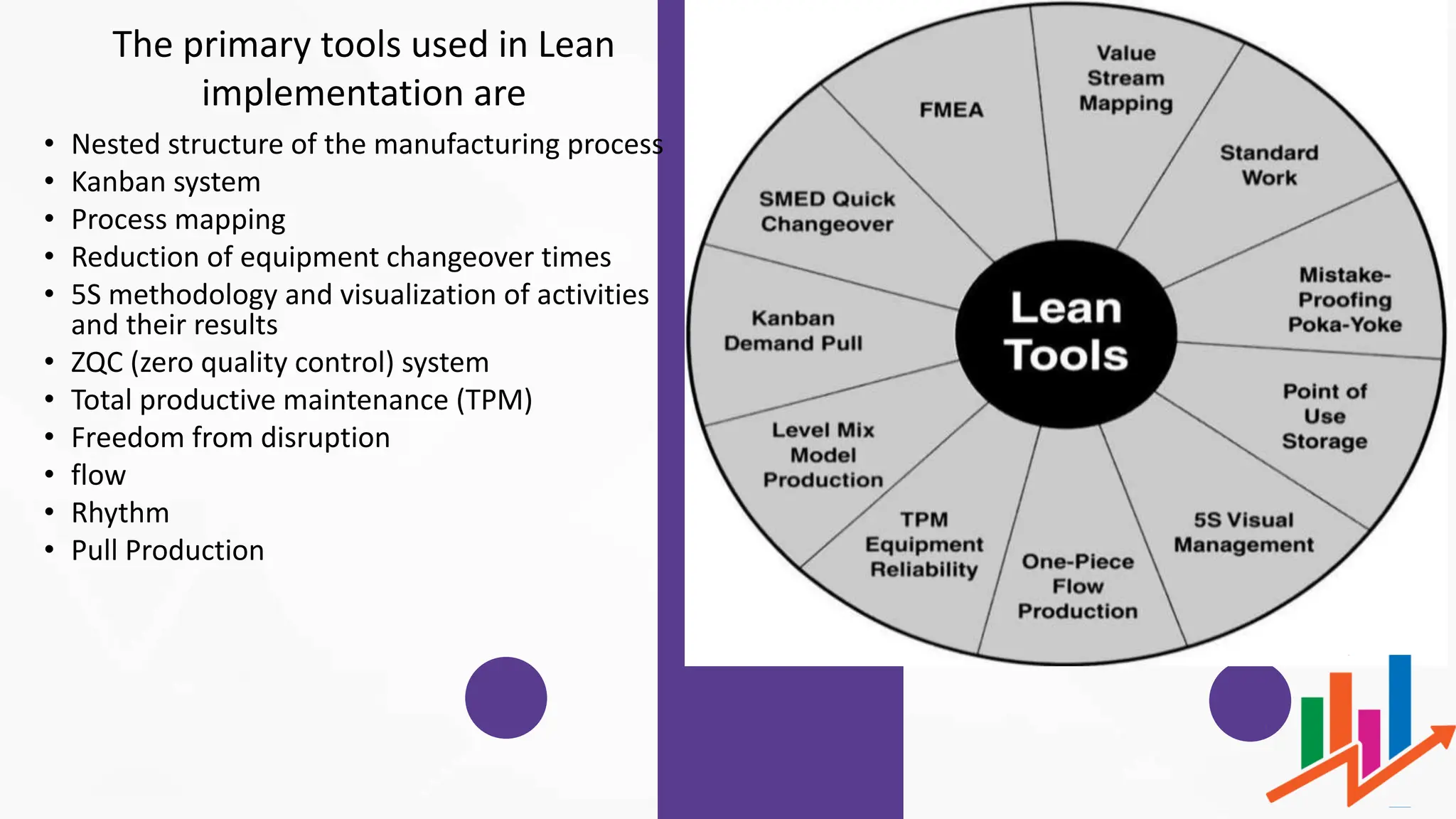
Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach focused on eliminating waste, enhancing productivity, and reducing costs, originally developed by Taiichi Ohno in the 1950s. It employs principles such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production, the 3M's of waste (muda, mura, muri), and continuous improvement (kaizen) to streamline processes. The benefits include cost reduction, improved quality, increased customer satisfaction, and enhanced employee morale.


![Genesis of Lean
Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing
• “Perfection is not attainable. But if
we chase perfection, we can catch
excellence.” Vince Lombardi
• Lean manufacturing or lean
production are reasonably new terms that
can be traced to Jim Womack, Daniel Jones
and Daniel Roos’ book, The Machine that
changed the world [1991]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aleanmanufacturingmc-240319143646-8c00a606/75/Lean-Manufacturing-5S-3M-Advantages-of-Lean-Manufacturingng-3-2048.jpg)