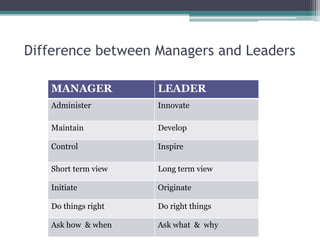
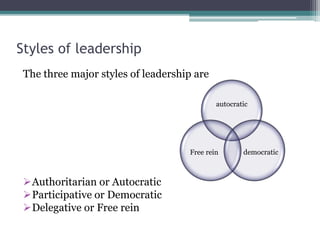
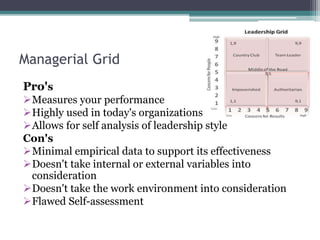
This document provides information about leadership and organizational behavior. It defines leadership, discusses the differences between managers and leaders, and outlines various leadership styles including autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. It also summarizes several theories of leadership such as trait theory, behavioral theory, and contingency theory. The document concludes by profiling Konosuke Matsushita, the founder of Panasonic, and outlining five lessons learned from his vision and management philosophy.