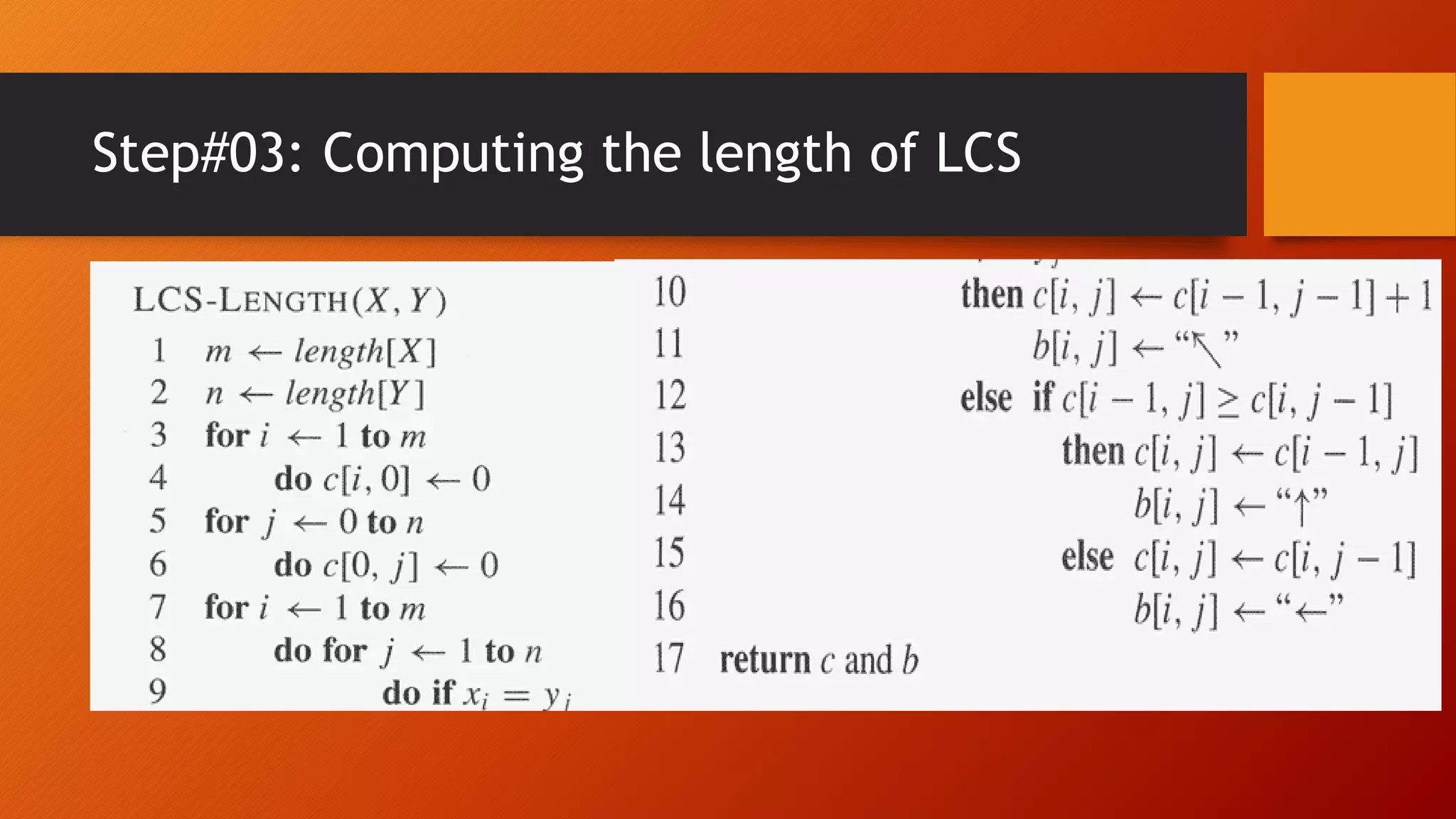
The document discusses the Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) concept, which is a significant application of dynamic programming used to determine common patterns in sequences. It outlines the process for calculating LCS using brute force and dynamic programming techniques, highlighting its relevance in areas like bioinformatics and software tools for comparison. Key steps include characterizing the LCS, defining the recursive relationship, and computing its length effectively.