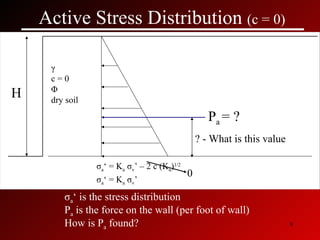
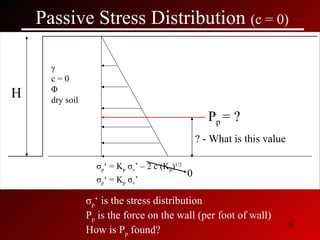
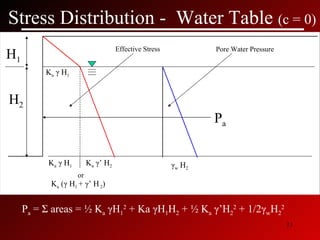
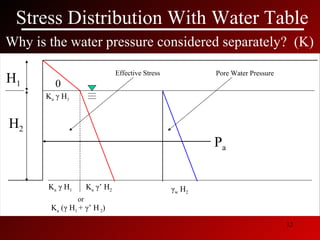
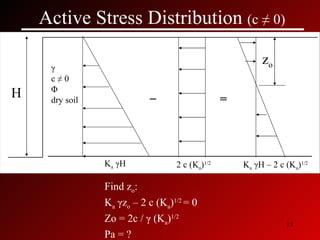
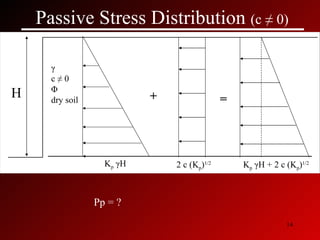
This document discusses lateral earth pressures and methods for calculating active, passive, and at-rest pressure coefficients (Ka, Kp, Ko). It provides equations for calculating the pressure coefficients based on soil properties. It also describes how to calculate the stress distribution under a retaining wall, accounting for factors like the water table, cohesion, and surcharge loads.
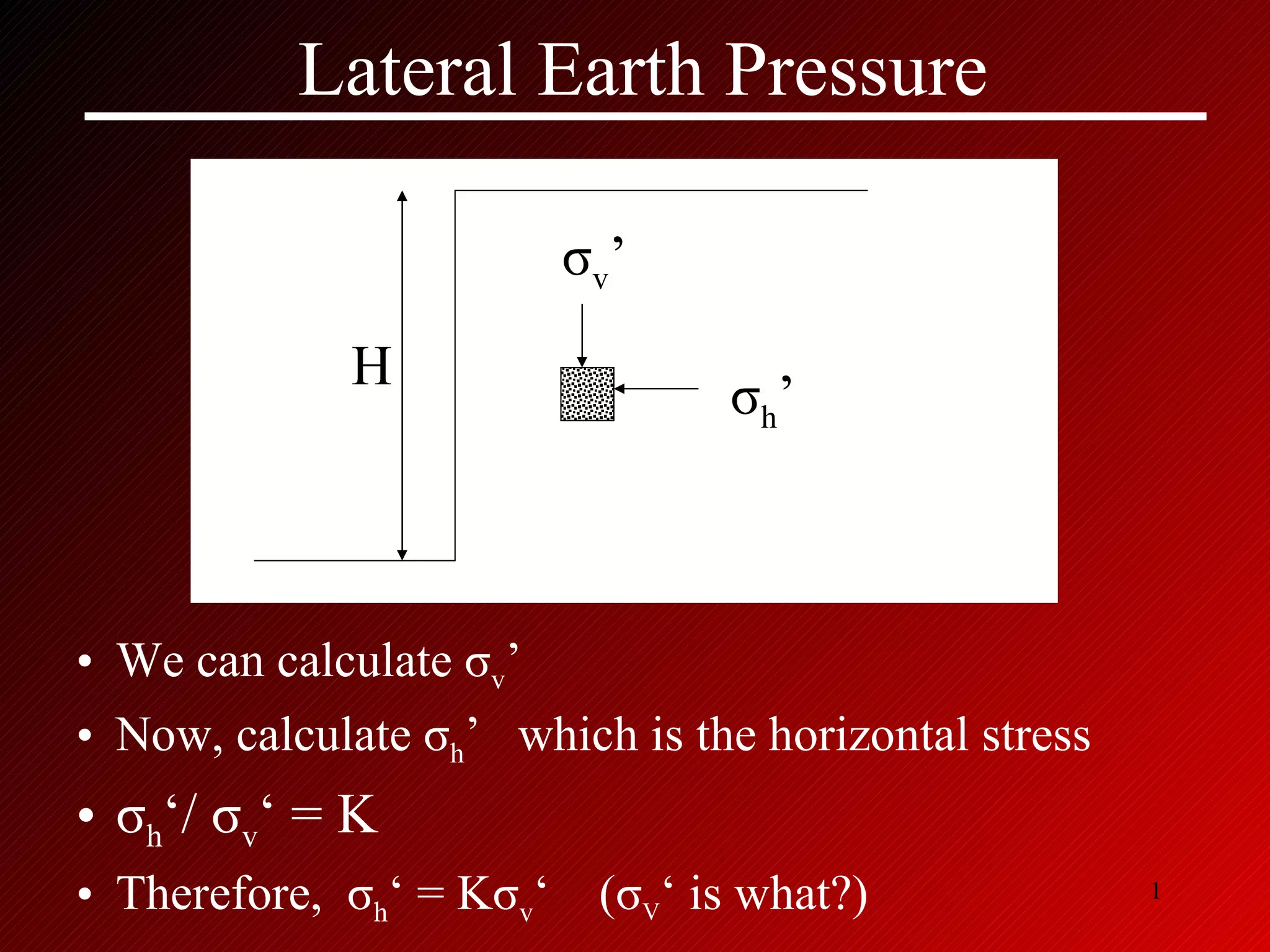

![At Rest Earth Pressure At rest earth pressure occur when there is no wall rotation such as in a braced wall (basement wall for example) K o can be calculated as follows: K o = 1 – sin φ for coarse grained soils K o = .44 + .42 [PI / 100] for NC soils K o (oc) = K o (NC) (OCR) 1/2 for OC soils σ v σ h z H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lateralearthpressurec-110930105824-phpapp02/85/Lateral-earth-pressure-3-320.jpg)