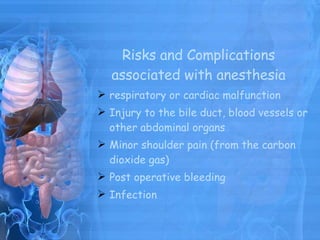
A laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder through several small incisions in the abdomen. During the procedure, carbon dioxide is used to inflate the abdomen so instruments can be inserted to tie off the cystic duct and artery before removing the gallbladder. It is usually performed to treat gallstones, gallbladder polyps, or cholecystitis. Compared to open surgery, laparoscopic cholecystectomy results in less pain, shorter hospital stays, and better cosmetic outcomes, though there are risks such as injury to other organs or postoperative bleeding.