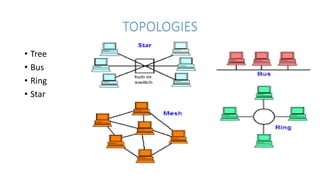
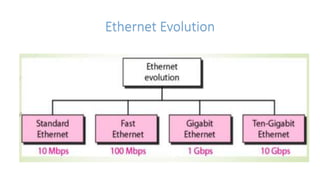
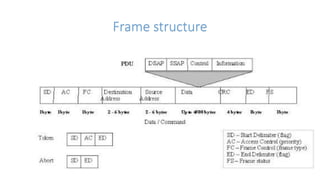
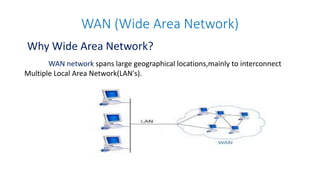
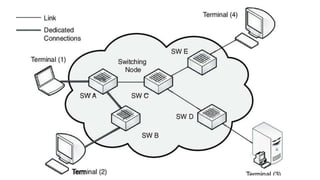
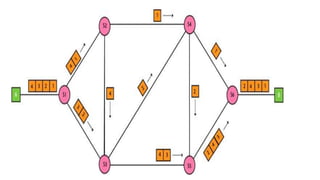
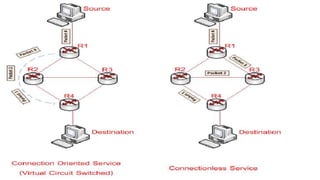
Local area networks (LANs) connect devices over small areas like offices and buildings. Common LAN types include star, bus, ring, and tree topologies. Essential LAN components are network interface cards, hubs, switches, routers, and gateways. While many LAN technologies existed, Ethernet is now dominant using protocols to enable communication between devices over cables. Token ring was another standard using a ring topology and token passing for transmission. Wide area networks (WANs) span larger geographical areas, connecting multiple LANs. WANs use routers, switches, and modems along with technologies like point-to-point, circuit switching, and packet switching to relay data over long distances.