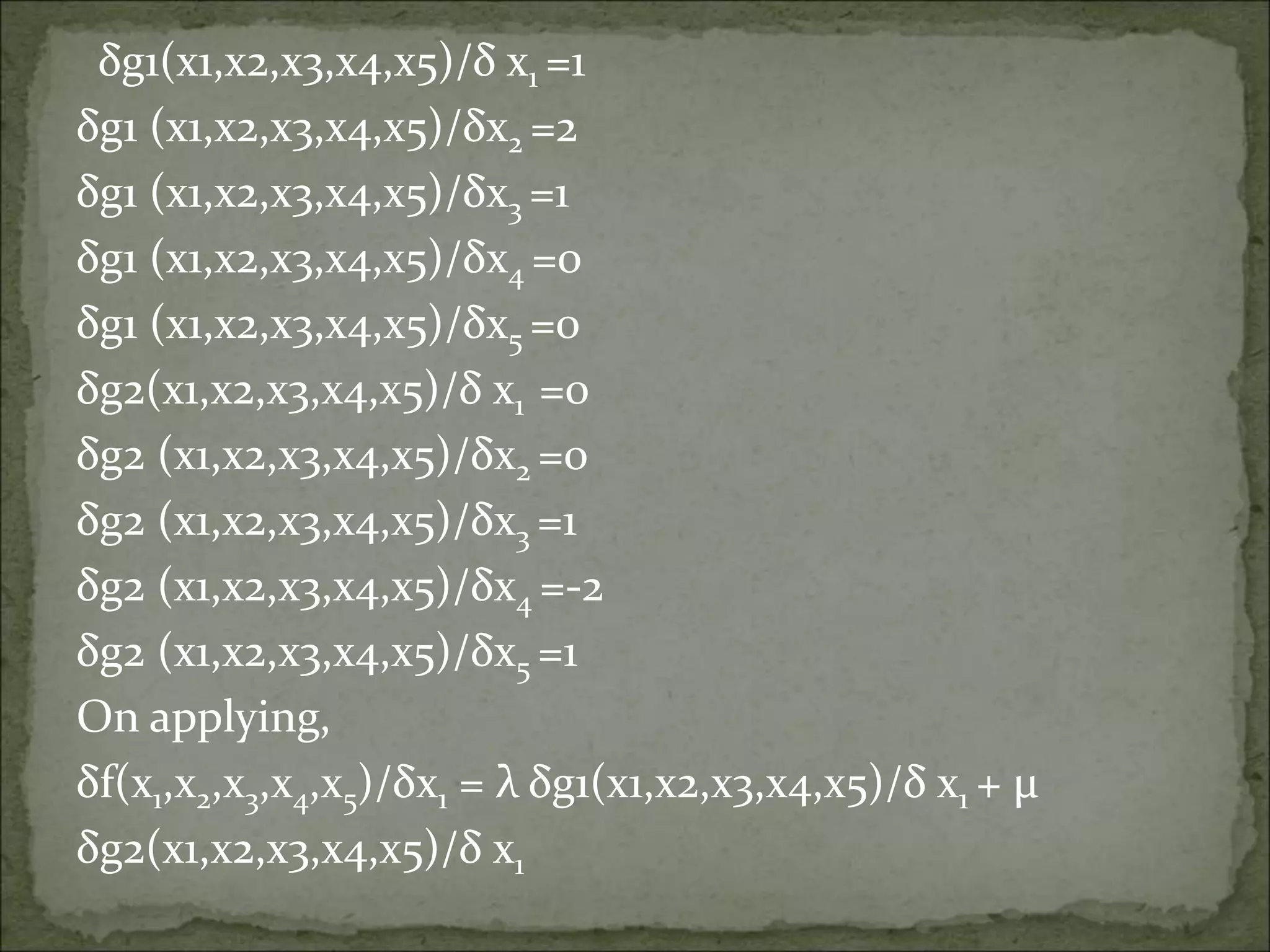The Lagrange multiplier method provides a strategy for finding the maxima and minima of a function subject to constraints. It involves setting up a system of equations involving the function, its derivatives, and the constraints and their derivatives. Solving this system of equations yields candidate maxima/minima points, which are then checked in the original function to determine if they are actually maxima or minima. The document provides examples of applying the Lagrange multiplier method to problems with single and multiple constraints.