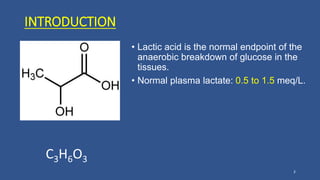
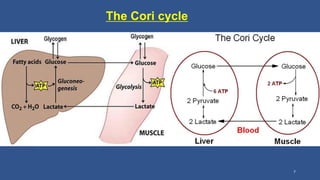
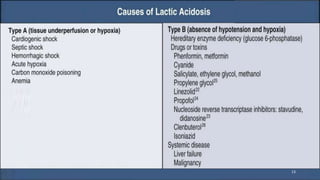
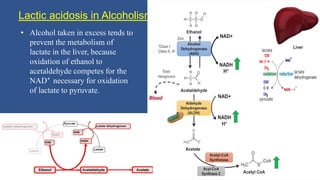
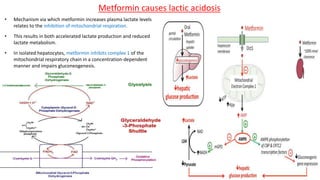
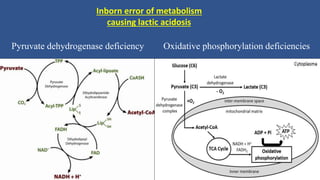
Lactic acidosis is defined as a serum lactate level >5mmol/L with a low blood pH (<7.35). It occurs when lactate production exceeds clearance, and there are two main types - type A from tissue hypoxia and type B from underlying metabolic disorders. Symptoms include breathing difficulties, muscle pains, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves measuring blood lactate and pH levels. Treatment focuses on resolving the underlying cause, avoiding sodium bicarbonate, and potentially using hemodialysis in severe cases to restore acid-base balance.