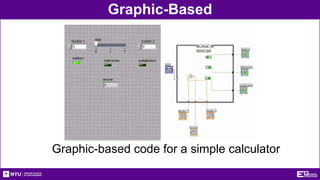
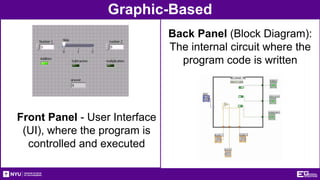
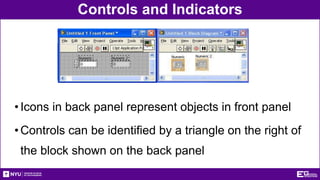
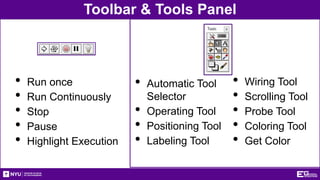
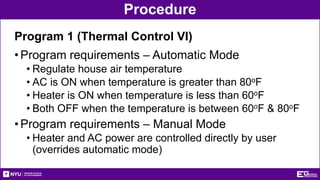
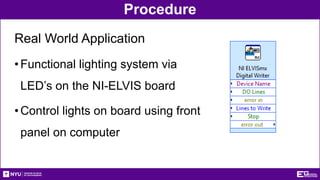
This document provides an introduction and overview of LabVIEW, a graphical programming language used for data acquisition, instrument control, and signal processing. It outlines the objectives of becoming familiar with graphical programming and using LabVIEW to obtain data from simulated instruments to create programs. LabVIEW programs called "Virtual Instruments" (VIs) resemble physical instruments with a front panel user interface and a block diagram where the program code is written. The document describes LabVIEW's tools, functions, and how to use an NI-ELVIS board to interface with the real world. It provides procedures for creating VIs to control temperature and lighting systems, including requirements and steps to program the front panel, back panel, and interface with real devices. A report