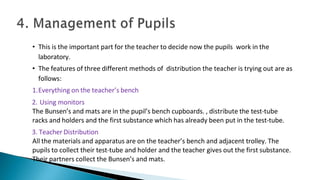
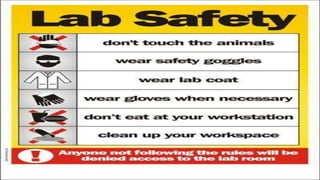
This document discusses several aspects of science laboratory design and management including:
1. It defines what a science laboratory is and discusses key components of laboratory design such as storage, equipment, and facilities.
2. It outlines best practices for teaching laboratory classes including pre-lab preparation, conducting experiments safely and effectively during class, and following up after labs.
3. It emphasizes the importance of science education and hands-on learning for developing student skills like problem solving and engaging their interest in STEM subjects.