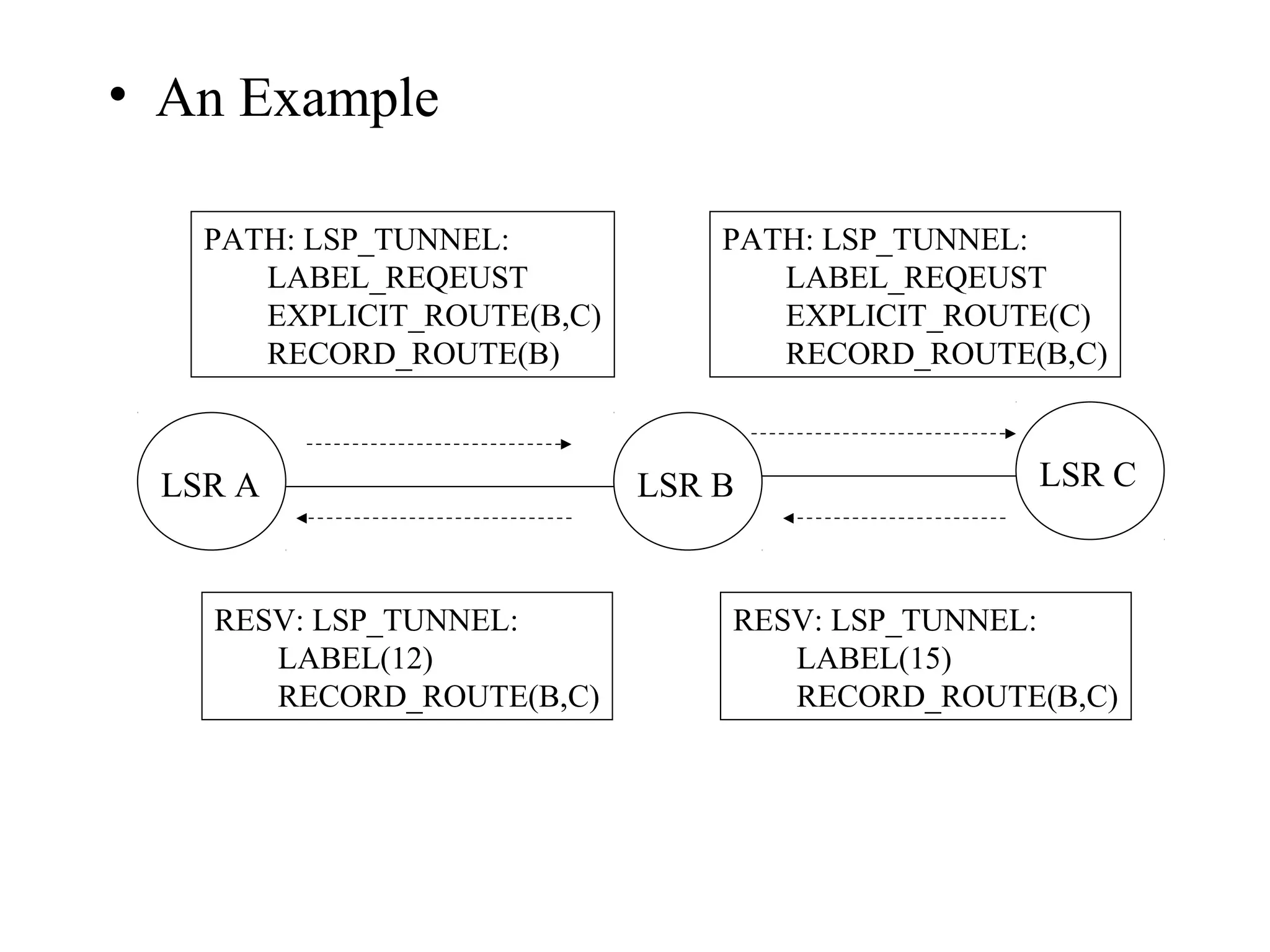
This document summarizes label distribution protocols, including LDP, RSVP-TE, and CR-LDP. LDP uses hop-by-hop routing to exchange label mappings between LDP peers using four types of messages over TCP or UDP. RSVP-TE establishes explicit routes for traffic engineering using RSVP with additional objects for label distribution, explicit routing, and bandwidth reservation. CR-LDP was another explicit routing protocol that is no longer in development.