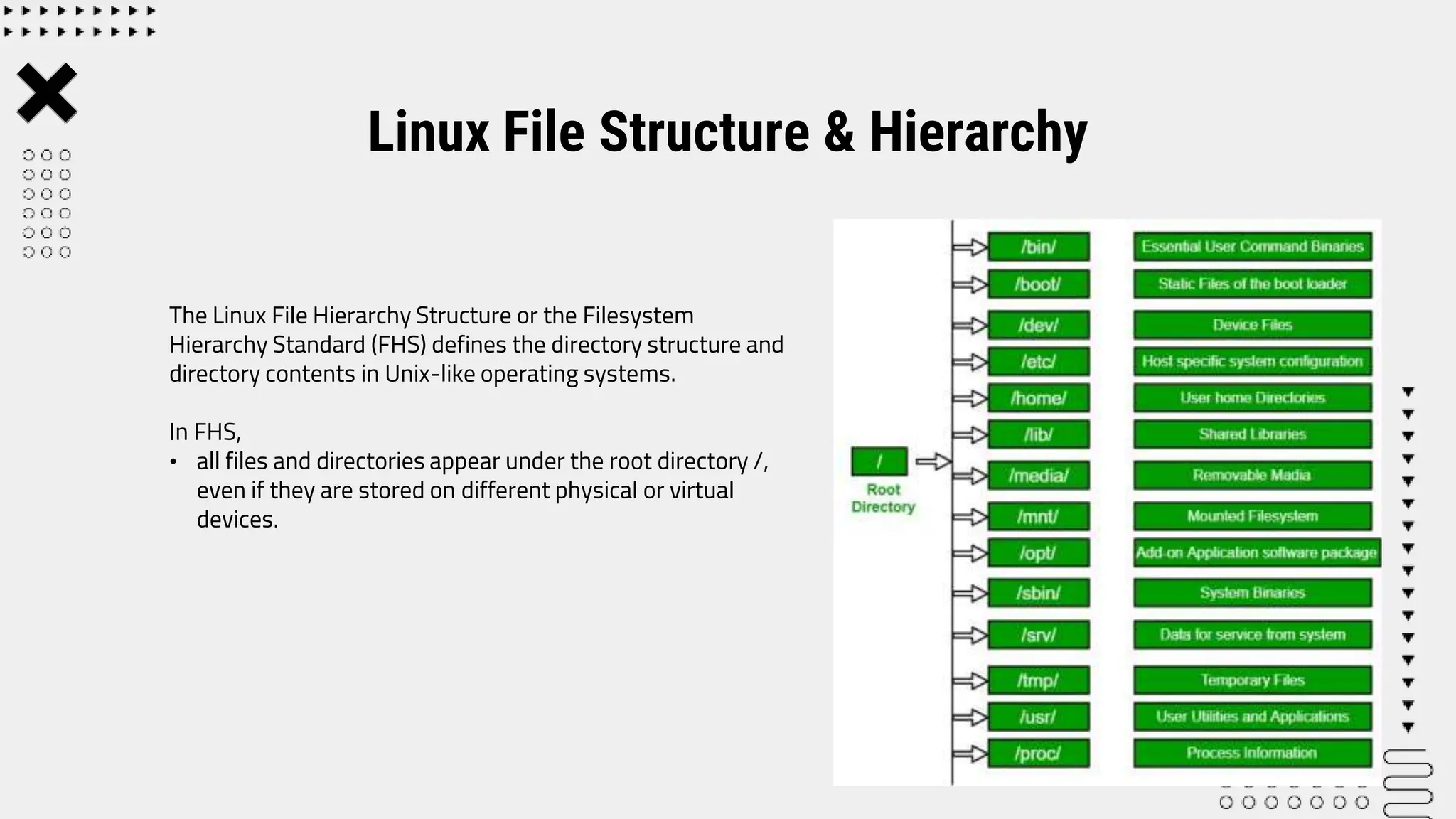
The Linux file system hierarchy defines the directory structure and contents of files and directories in Unix-like operating systems. It establishes that all files and directories appear under the root directory /. Some of the key directories in the hierarchy include /bin, which contains essential command binaries, /boot for boot loader files, /dev for device files, and /etc for system-wide configuration files. User home directories are located in /home, while temporary files are stored in /tmp. The hierarchy also includes directories like /lib for essential libraries, /opt for optional application software, /sbin for essential system binaries, and /usr for secondary hierarchy of read-only user data and utilities.