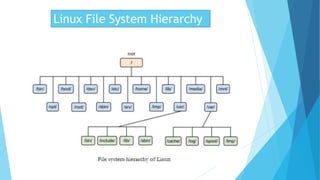
The document discusses the Linux file system hierarchy. It begins by explaining that all files on a Linux system are organized into a single tree of directories with the root directory "/" at the top. It then provides descriptions of the standard directories that make up the hierarchy, including /bin, /boot, /dev, /etc, /home, /lib, /media, /mnt, /opt, /root, /sbin, /srv, /tmp, /usr, and /var. It notes that these directories contain essential files and programs used for booting, configuration, user home directories, libraries, removable media, mounting other file systems, software packages, system administration tools, server data, temporary files, and data written by