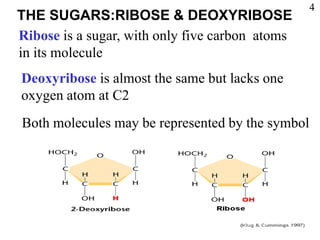
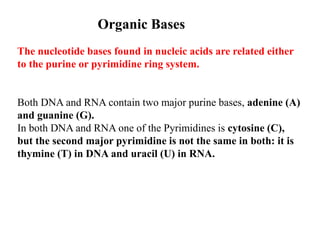
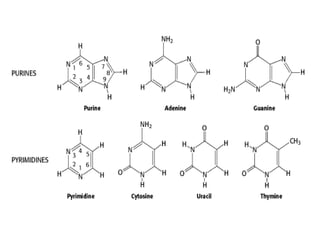
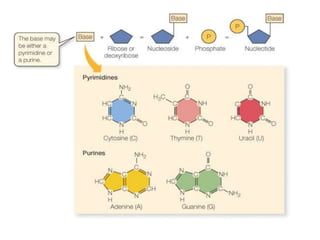
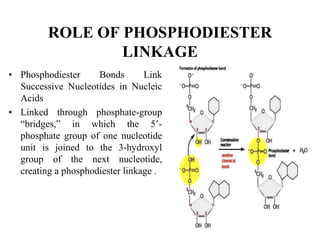
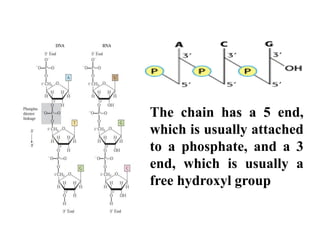
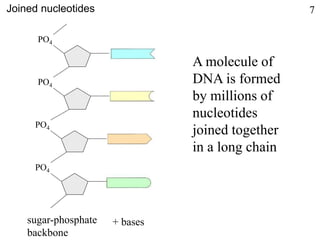
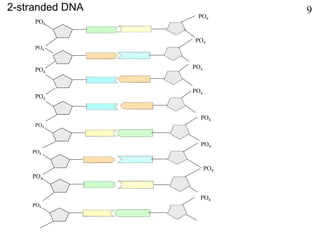
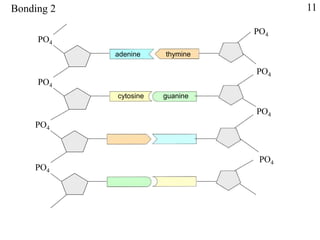
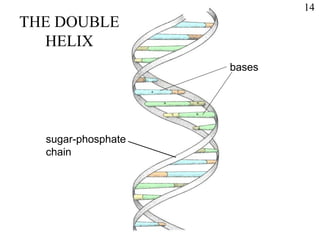
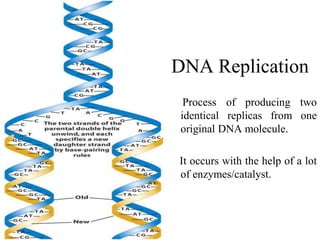
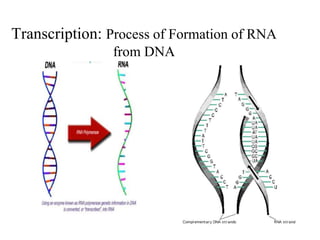
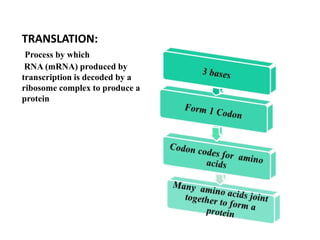
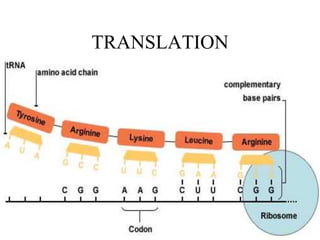
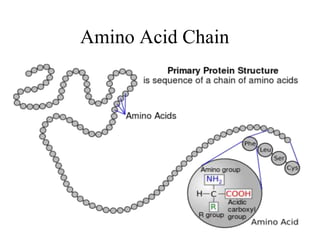
This document discusses nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It notes that nucleic acids were discovered by Friedrich Miescher in 1869 and are essential for life. DNA controls chemical changes in cells and determines cell and organism type. DNA is made up of nucleotides containing a sugar, phosphate group, and organic base. The nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds to form long chains coiled into the famous double helix structure. The central dogma explains how DNA information is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.