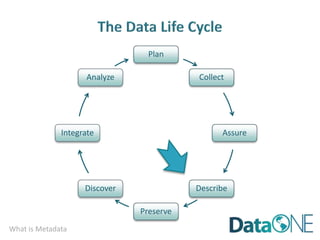
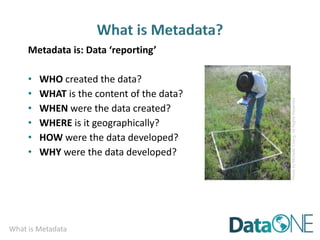
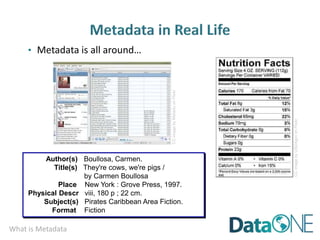
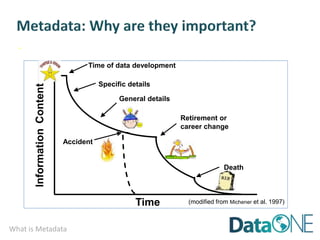
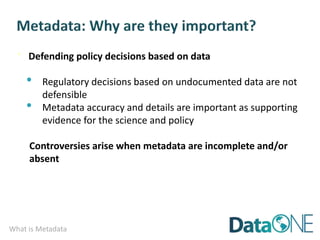
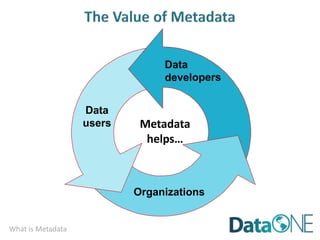
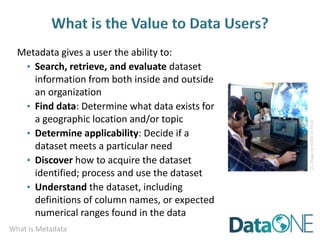
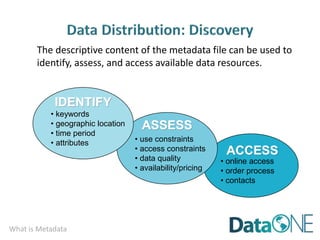
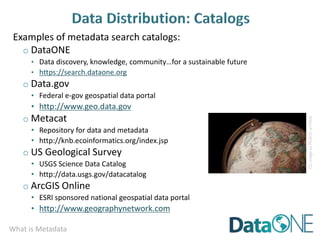
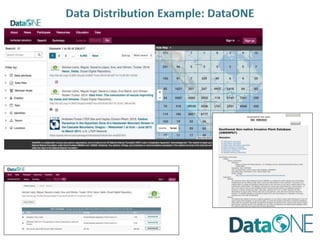
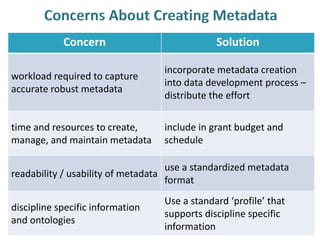
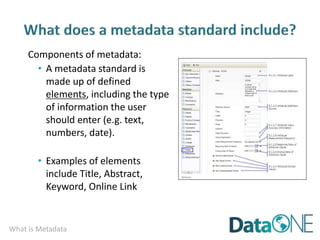
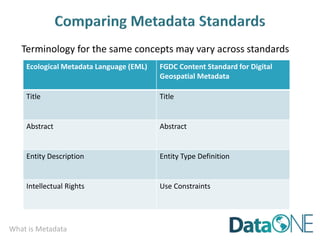
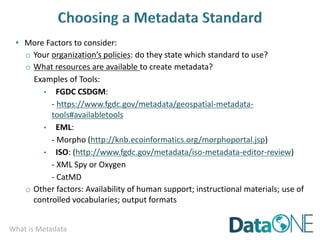
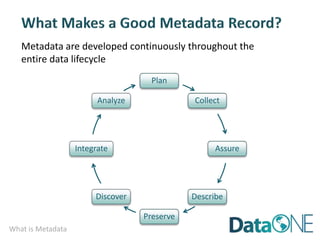
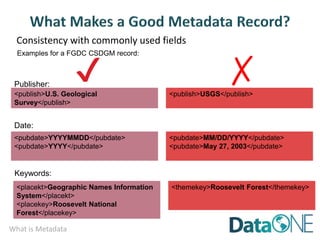
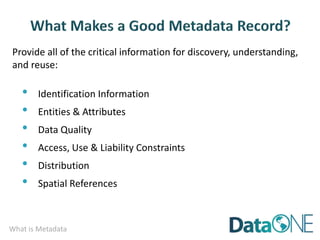
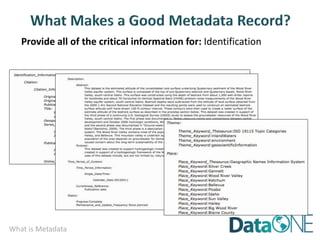
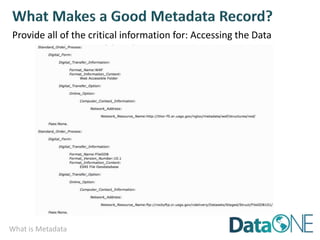
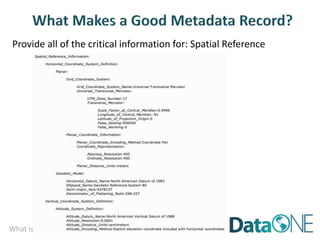
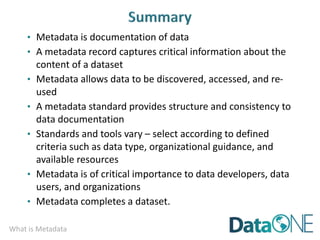
This document discusses metadata, which is data that describes other data. It explains that metadata captures information about data content, time, location, how it was collected and why. Good metadata allows data to be discovered, accessed, and understood. Key elements in a metadata record are identified and standards like FGDC and ISO are examined. The value of metadata for data users, providers and organizations is outlined. Tips for writing clear, complete and computer-readable metadata are provided.