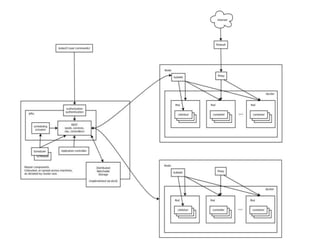
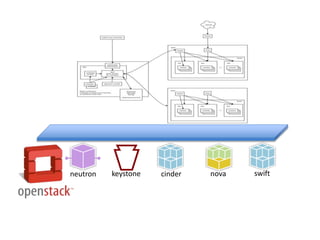
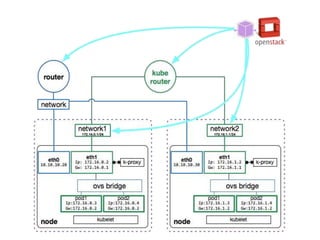
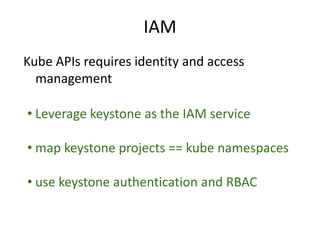
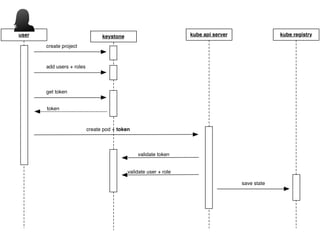
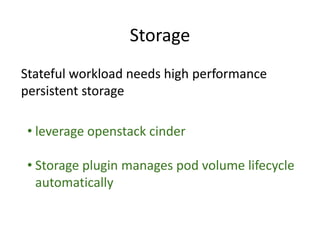
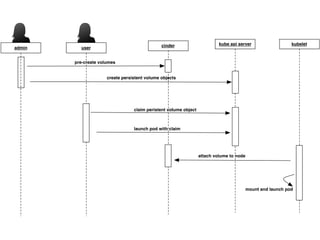
This document summarizes how Kubernetes can be used on OpenStack. It discusses integrating Kubernetes with OpenStack services for networking (Neutron), identity and access management (Keystone), storage (Cinder and Swift), cluster setup/management, and container registry. For each area, it provides an overview of the current integration and potential future enhancements.