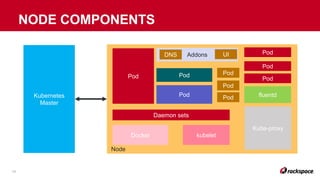
The document explores the integration of Kubernetes with OpenStack, detailing the history and components of both technologies. It discusses the advantages of using containers and Kubernetes for application deployment, including scalability and management challenges. Additionally, it highlights Rackspace's managed Kubernetes solution, focusing on its features such as security, ease of use, and support options.