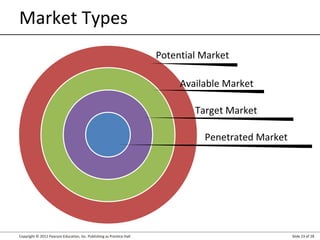
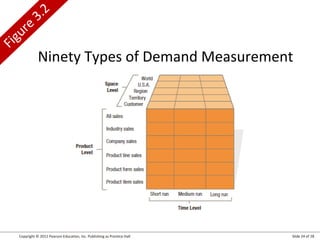
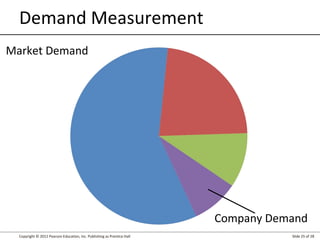
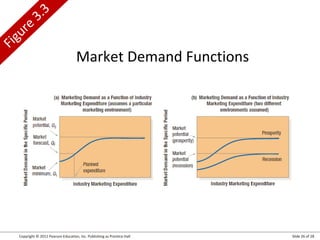
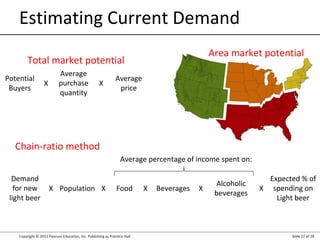
This document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of the marketing textbook "Marketing Management" by Kotler and Keller. It discusses the components of a modern marketing information system including collecting internal records and external information on customers, competitors, and factors. It also covers marketing intelligence, analyzing the macroenvironment, measuring and forecasting demand.