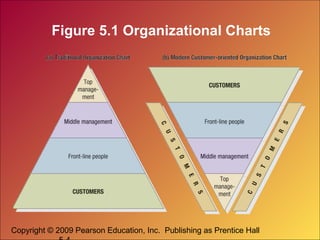
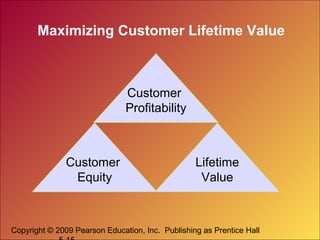
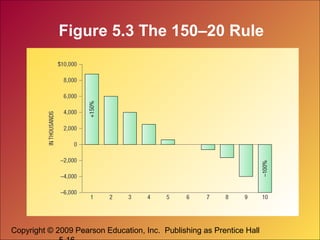
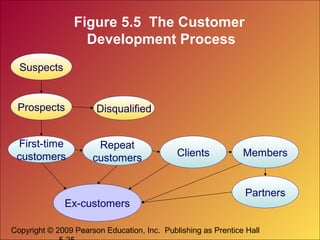
The document discusses how companies can create value, satisfaction, and loyalty for customers. It defines concepts like customer perceived value, quality, satisfaction, and lifetime value. It also discusses how companies can implement customer relationship management strategies to maximize customer retention, acquisition, and profitability through databases and targeted communications.