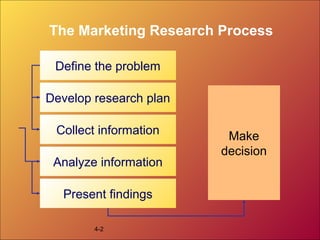
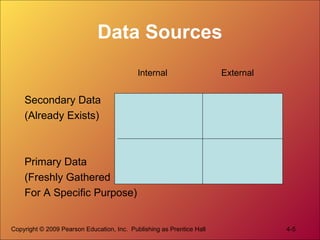
Marketing research is the process of defining problems, developing research plans, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings to make business decisions. It involves secondary and primary data sources. Common research methods include surveys, focus groups, observation, and experiments. Researchers use various question types in questionnaires and qualitative measures to collect information. Sampling plans and contact methods must be developed. Findings are then analyzed and presented to decision makers.