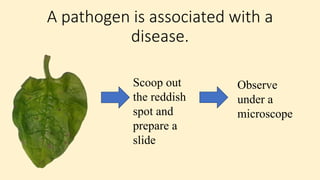
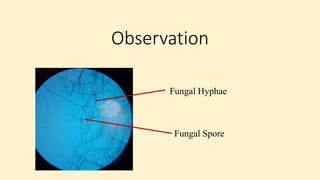
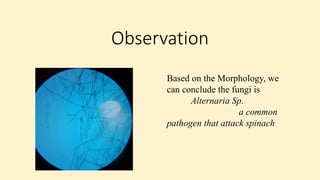
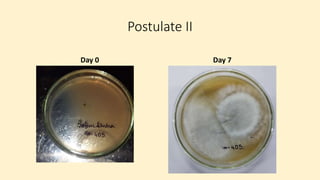
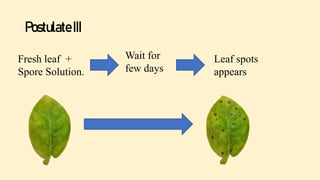
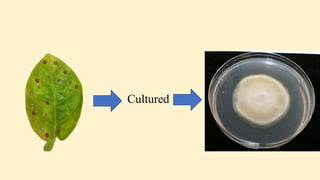
Robert Koch established a set of postulates to determine if a microorganism is the cause of a specific disease. The postulates require that (1) the pathogen must be found in all cases of the disease, (2) the pathogen can be isolated and grown in pure culture, (3) the pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when introduced into a healthy host, and (4) the pathogen must be re-isolated from the new host and found to be the same as the original pathogen. Koch's postulates provided a rigorous scientific framework for establishing causation between a microbe and a disease and advanced the field of microbiology. However, the postulates have limitations and do not apply to all disease situations