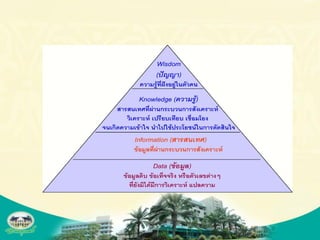
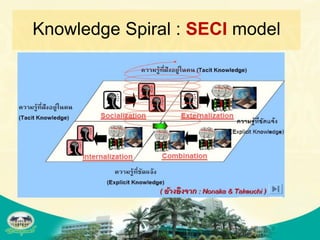
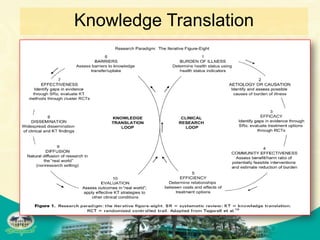
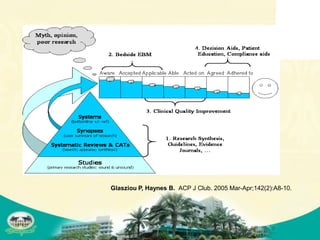
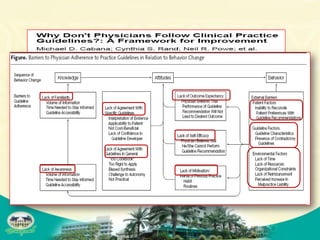
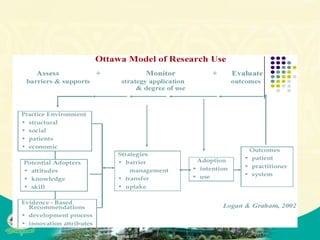
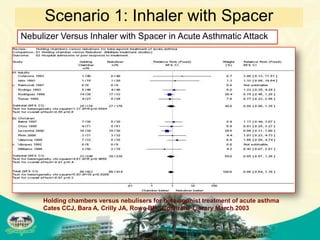
The document discusses knowledge management and knowledge translation in emergency medicine. It defines knowledge management as connecting people to information and each other to create new knowledge. The document also explains that knowledge translation is the process of applying research findings to improve healthcare practices and close the gap between what is known and what is done in clinical practice. It provides examples of how knowledge management and translation strategies like multifaceted interventions, education, reminders, and audit and feedback can be applied to implement guidelines and improve processes in an emergency department.