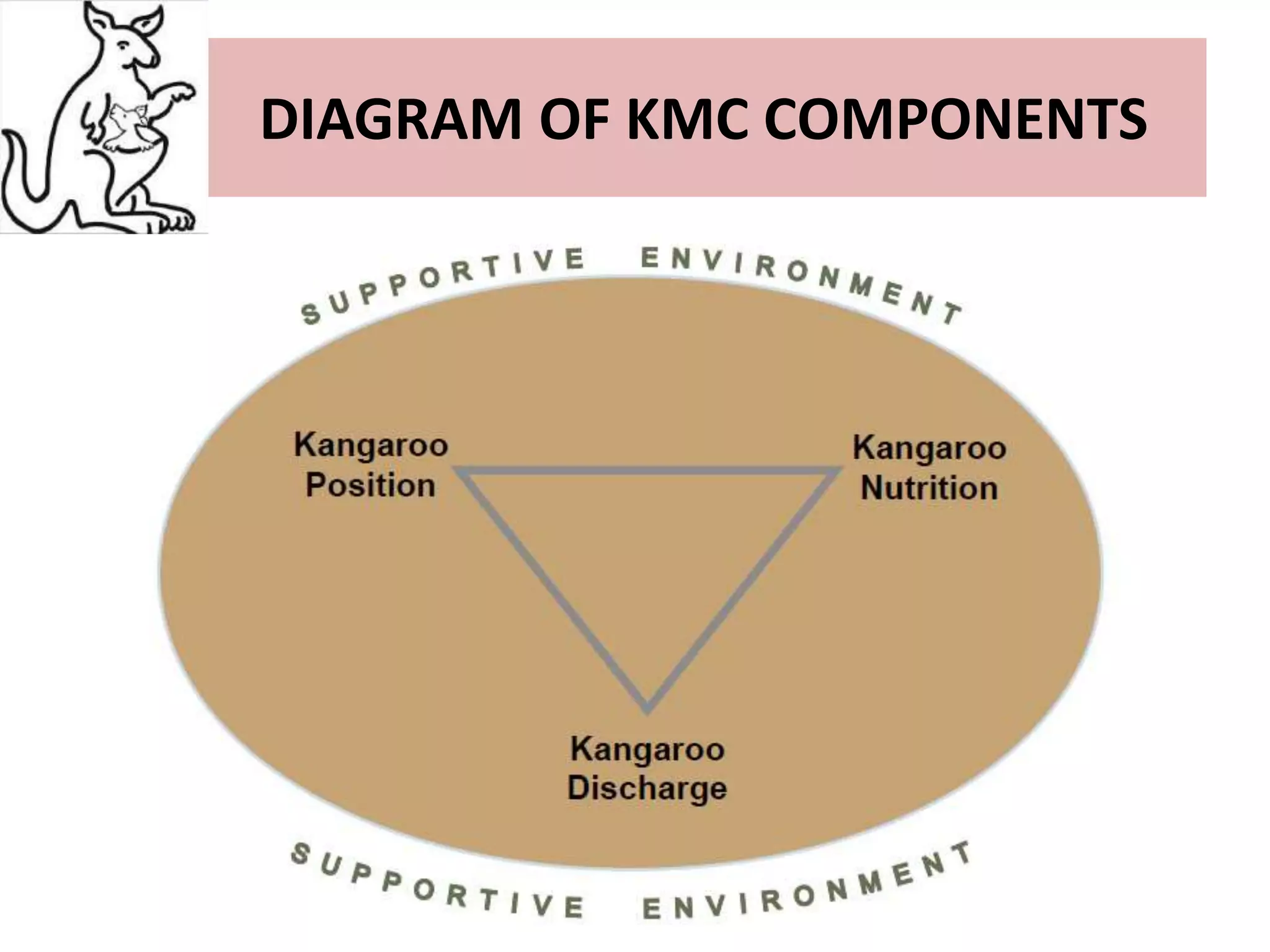
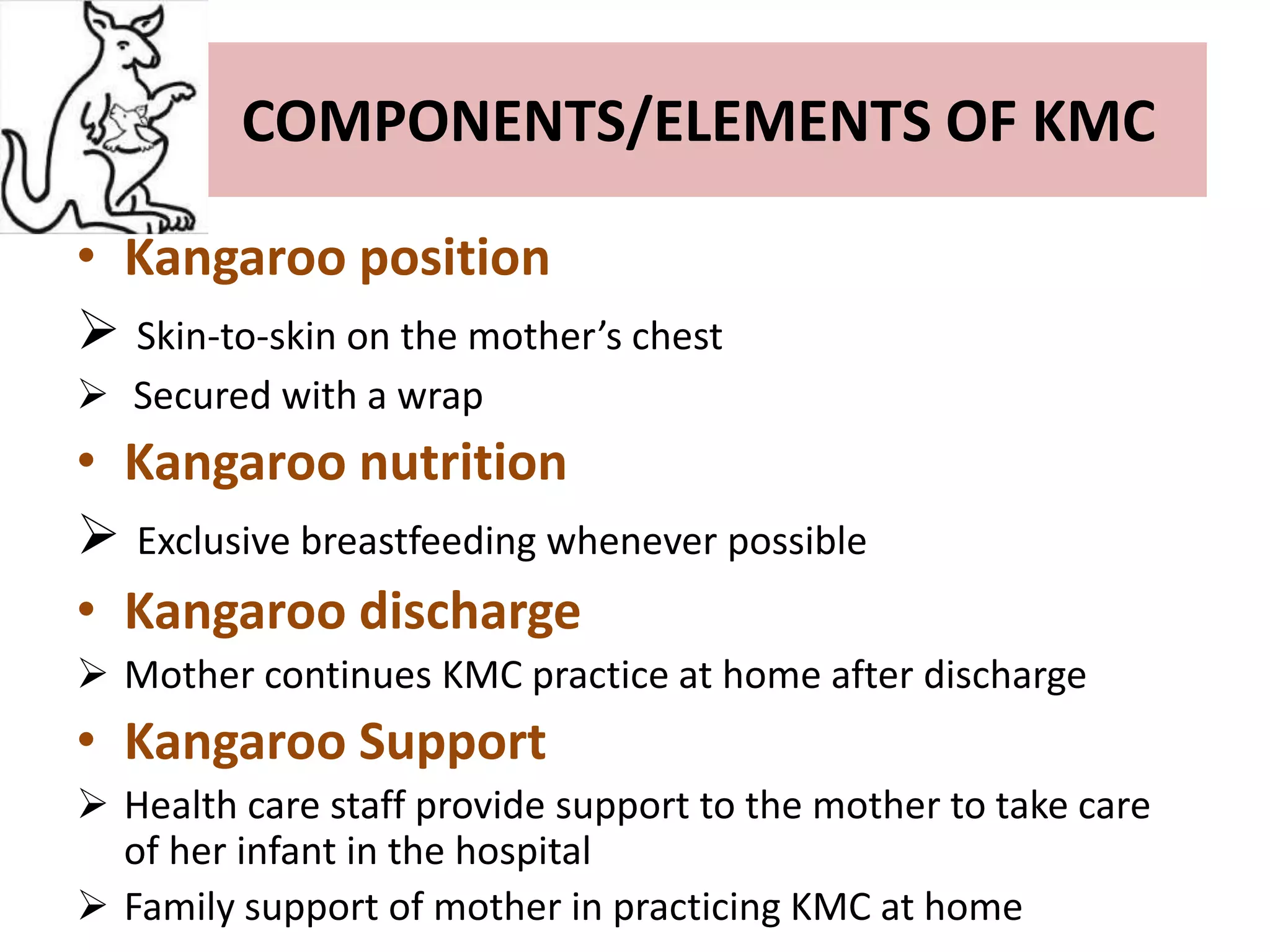
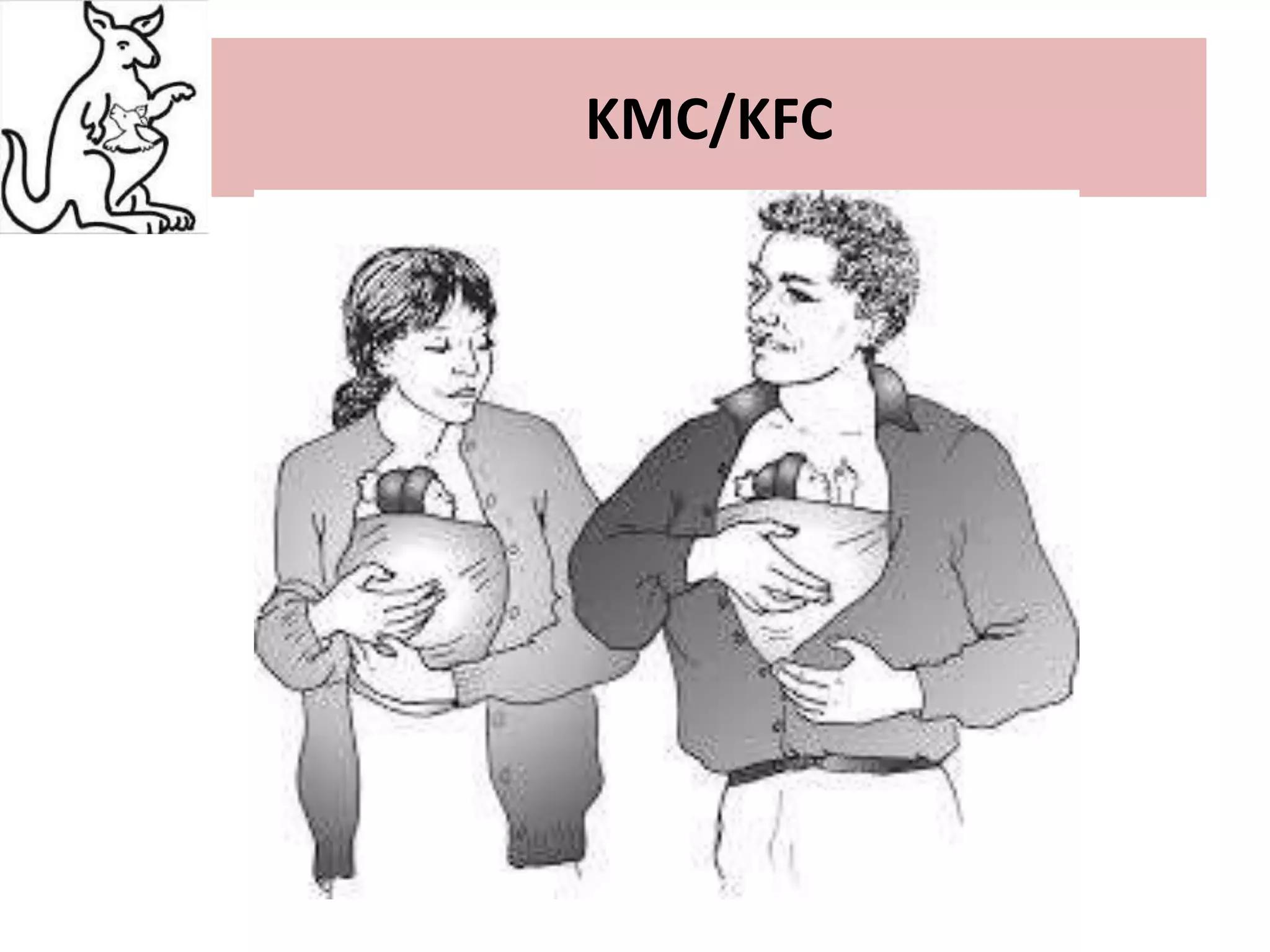
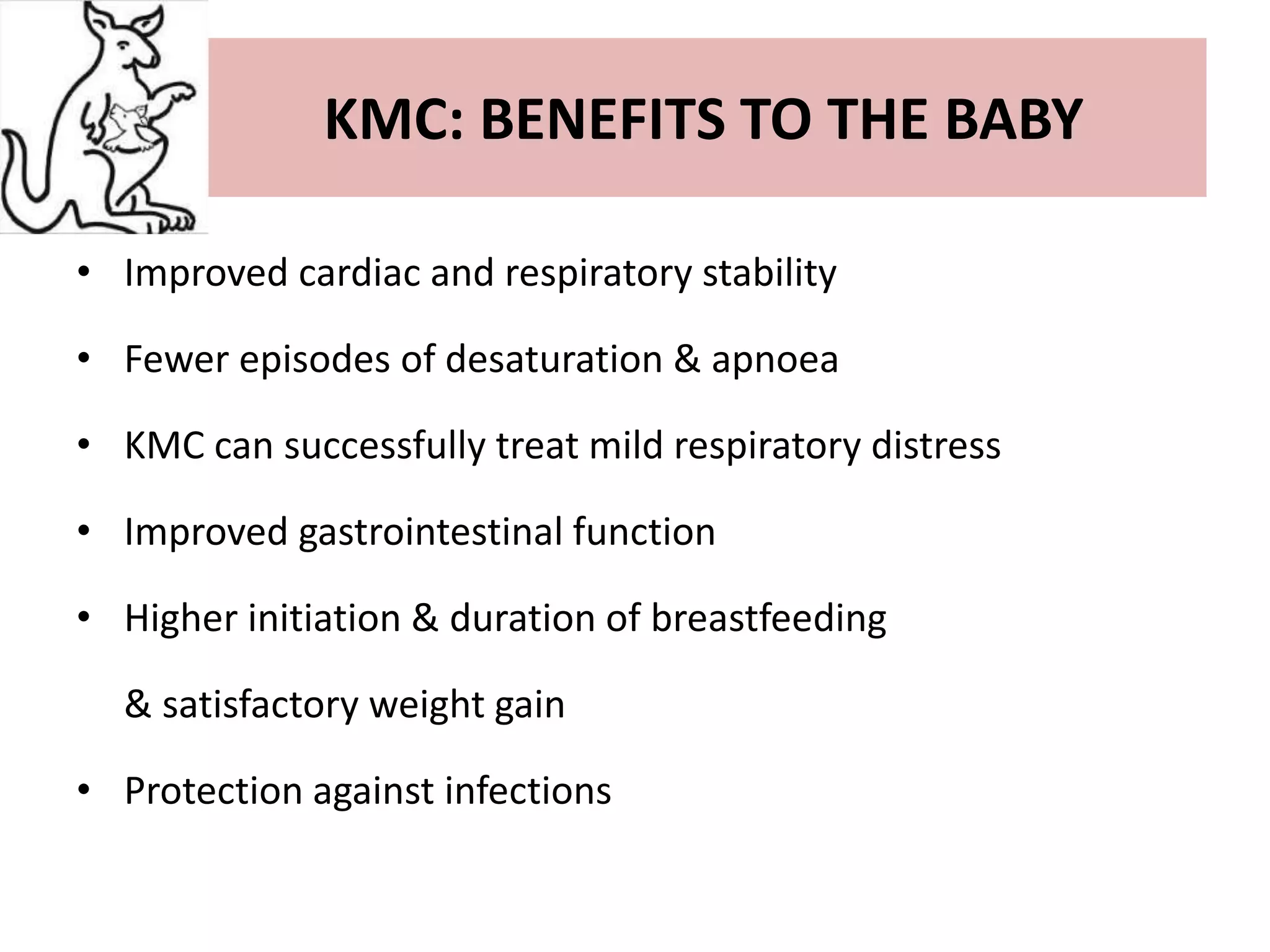
This document discusses Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC), an approach where preterm or low birth weight infants are held skin-to-skin against the mother's chest. KMC aims to provide warmth, safety, nutrition and support to immature newborns, similar to how a kangaroo carries its joey. The document outlines the origins of KMC, components like positioning and breastfeeding, benefits like improved health outcomes and bonding, and calls for KMC to be integrated globally based on its effectiveness.