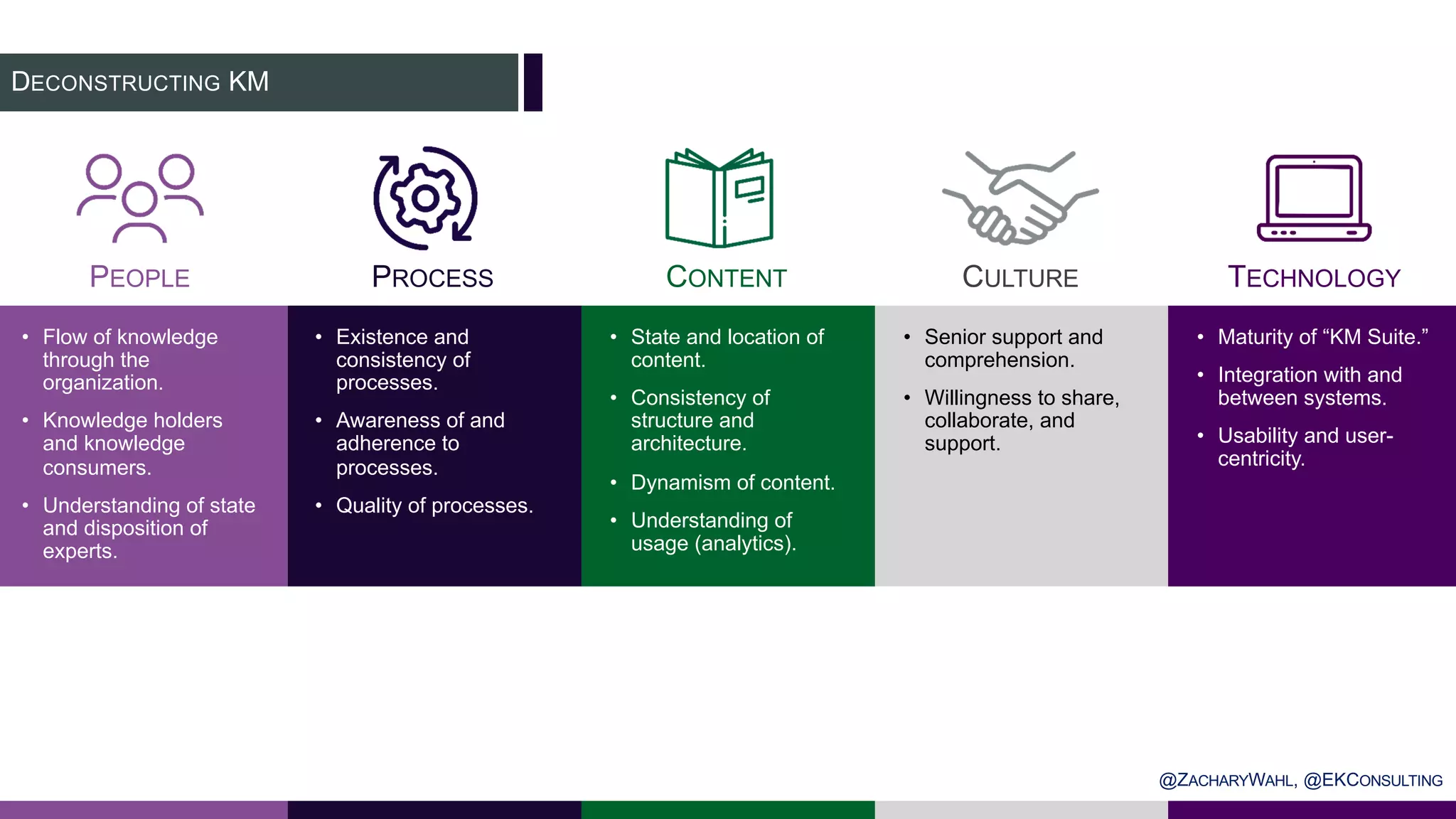
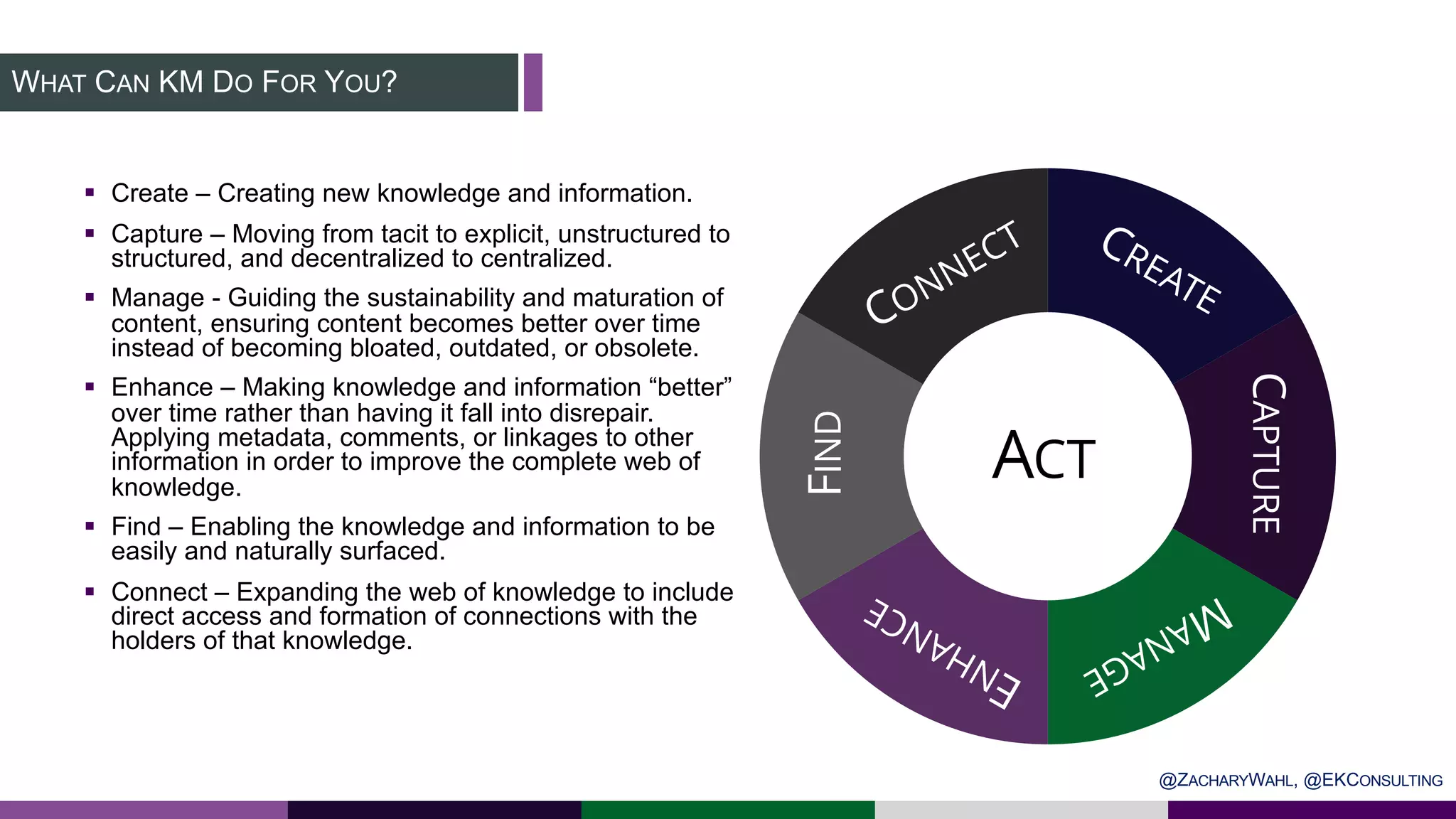
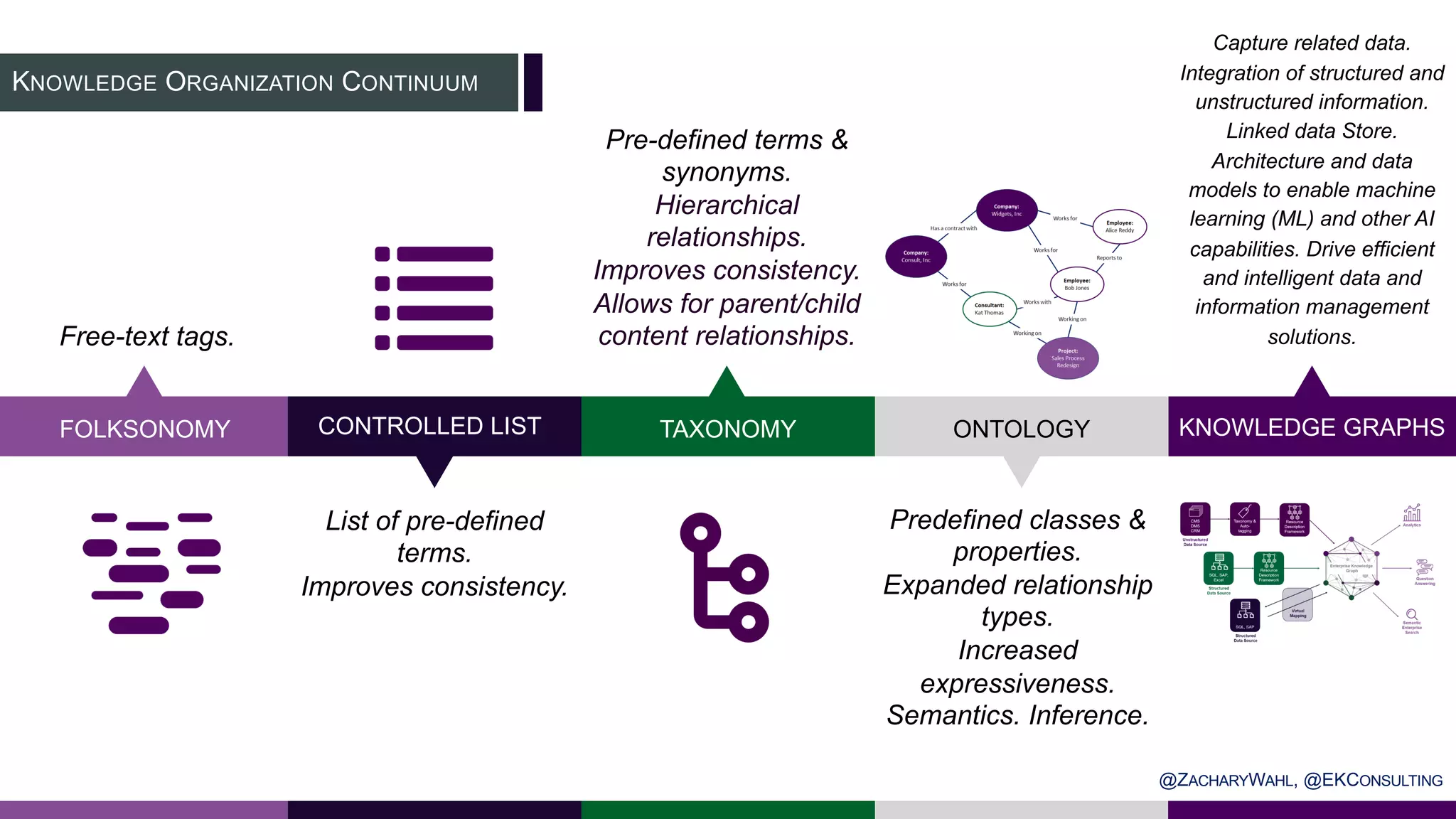
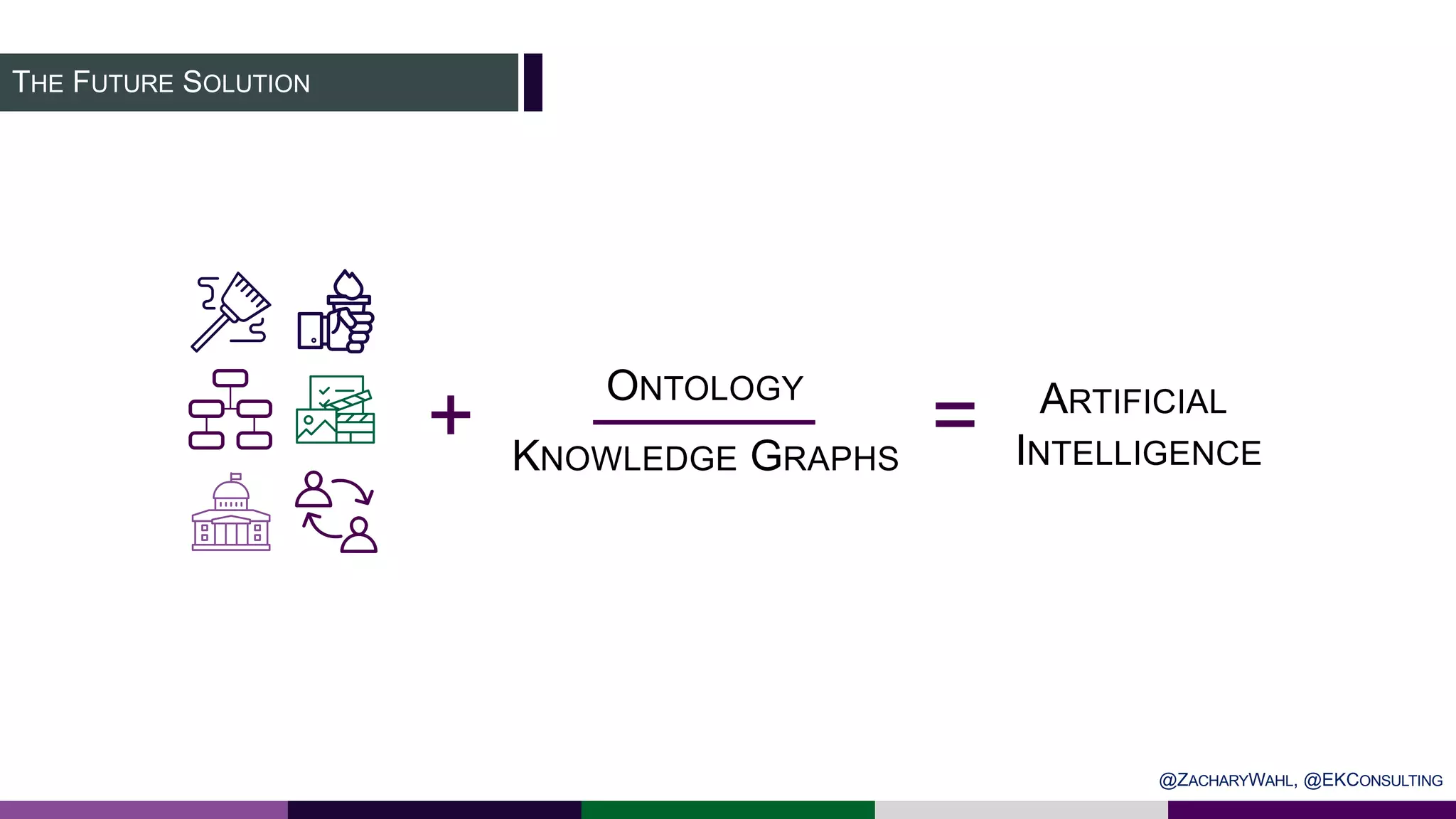
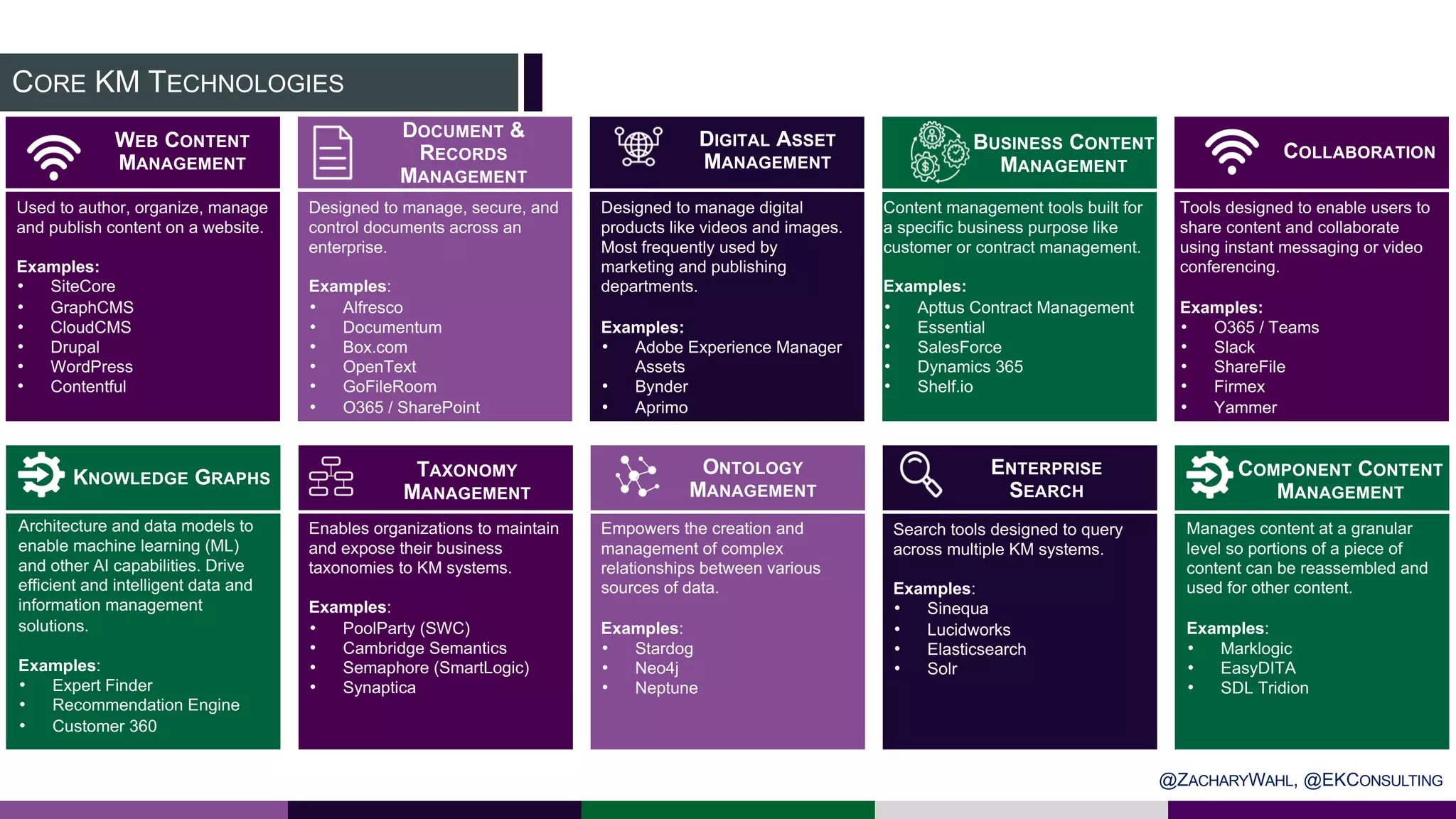
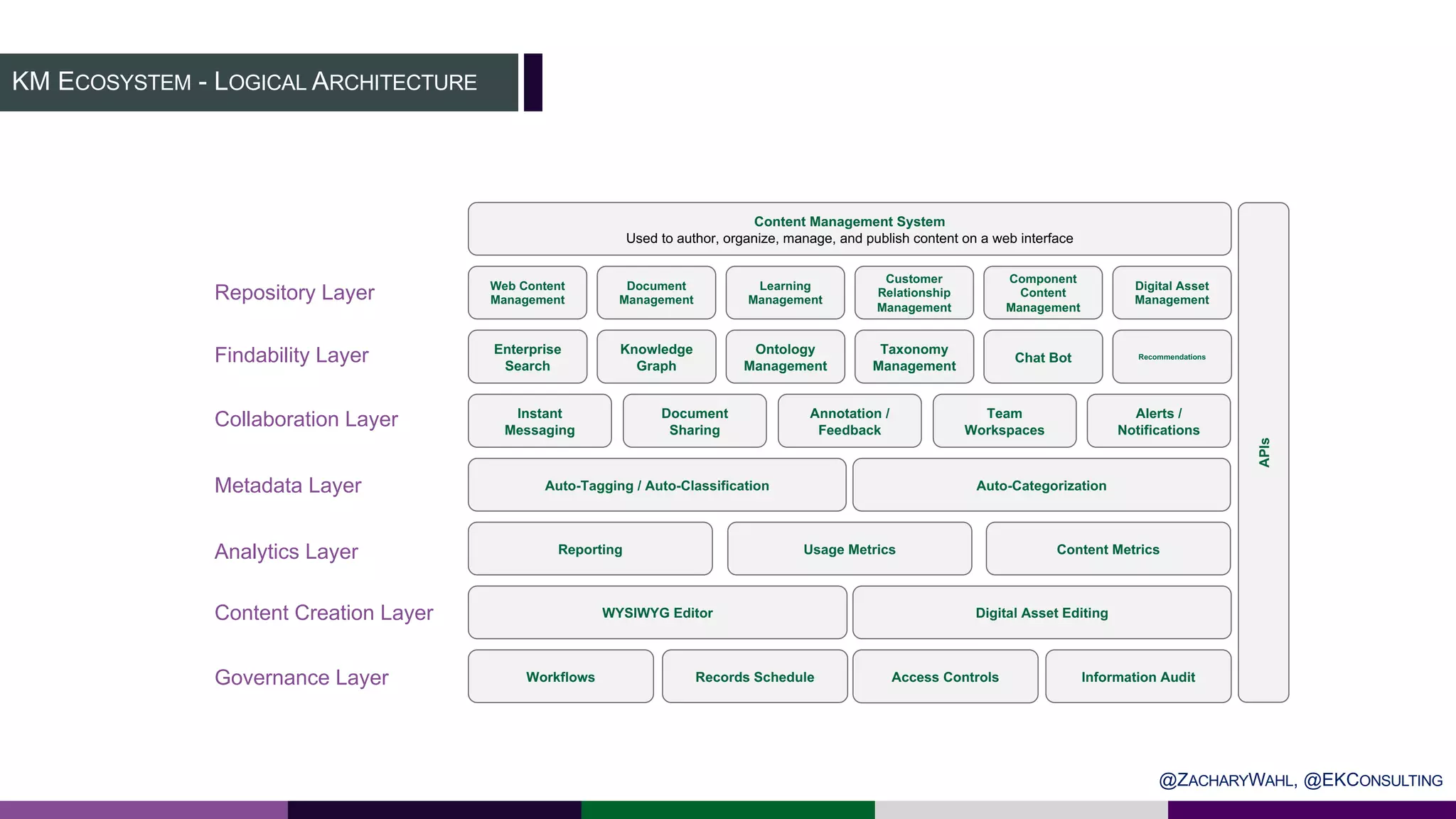
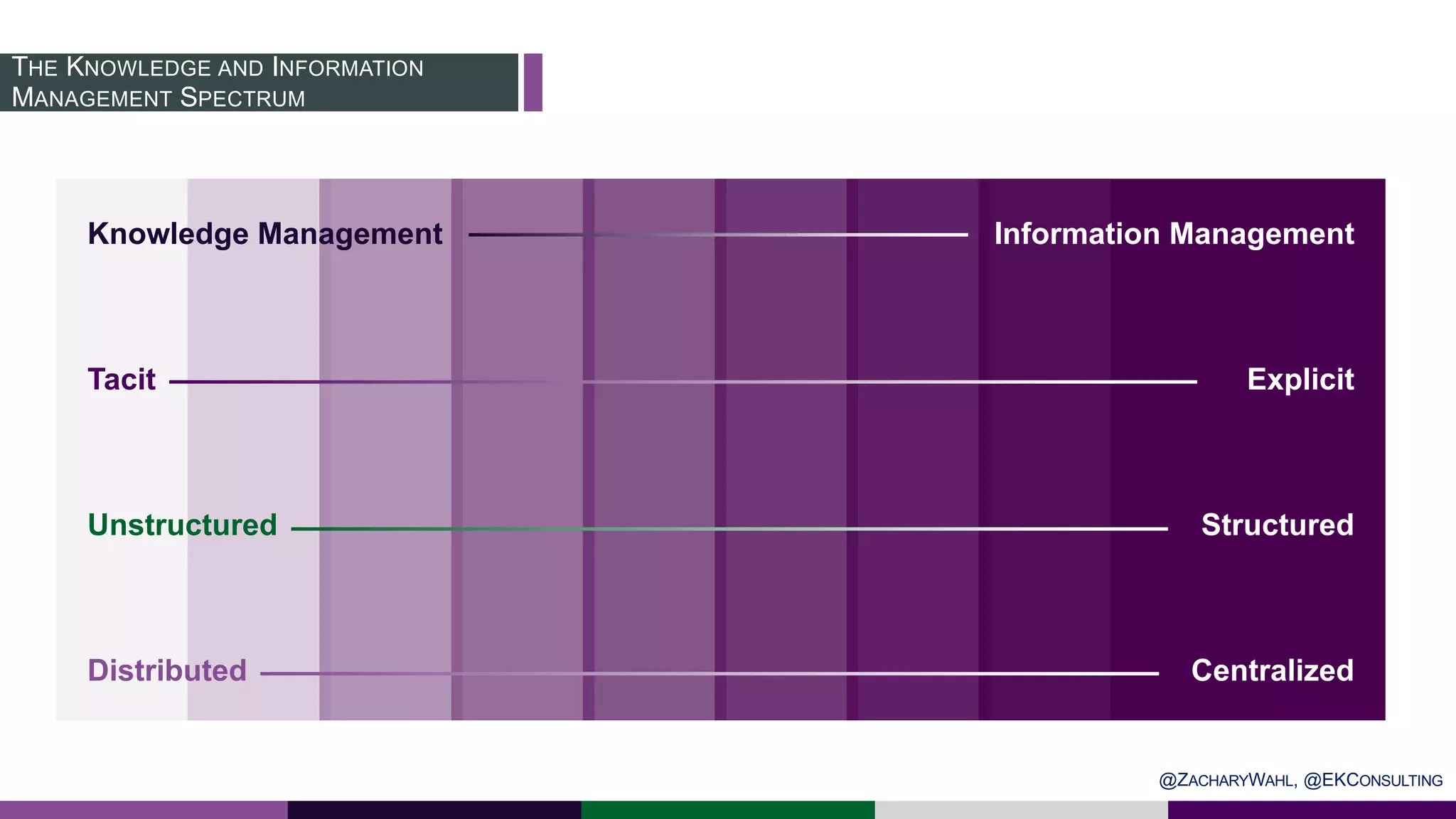
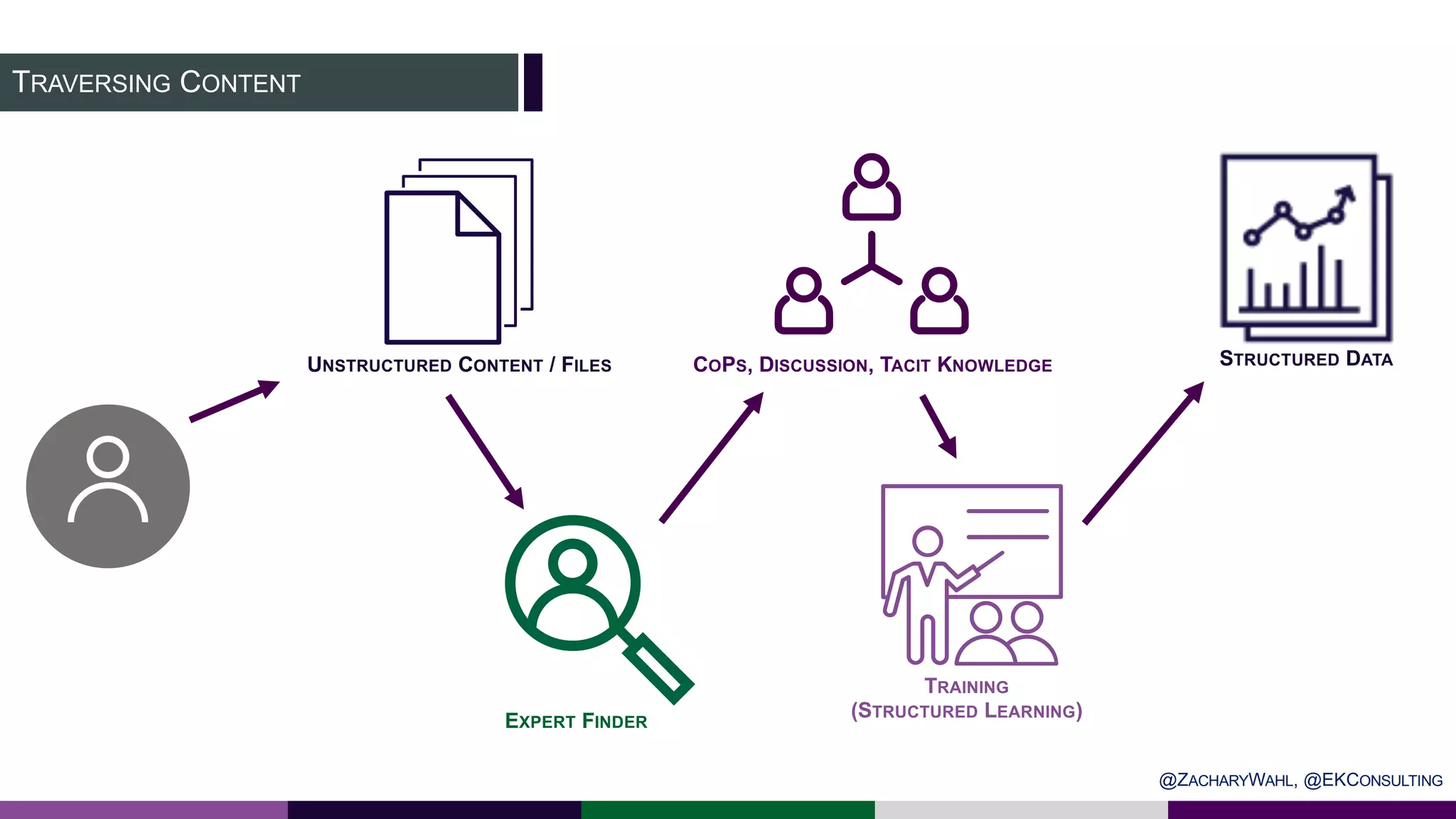
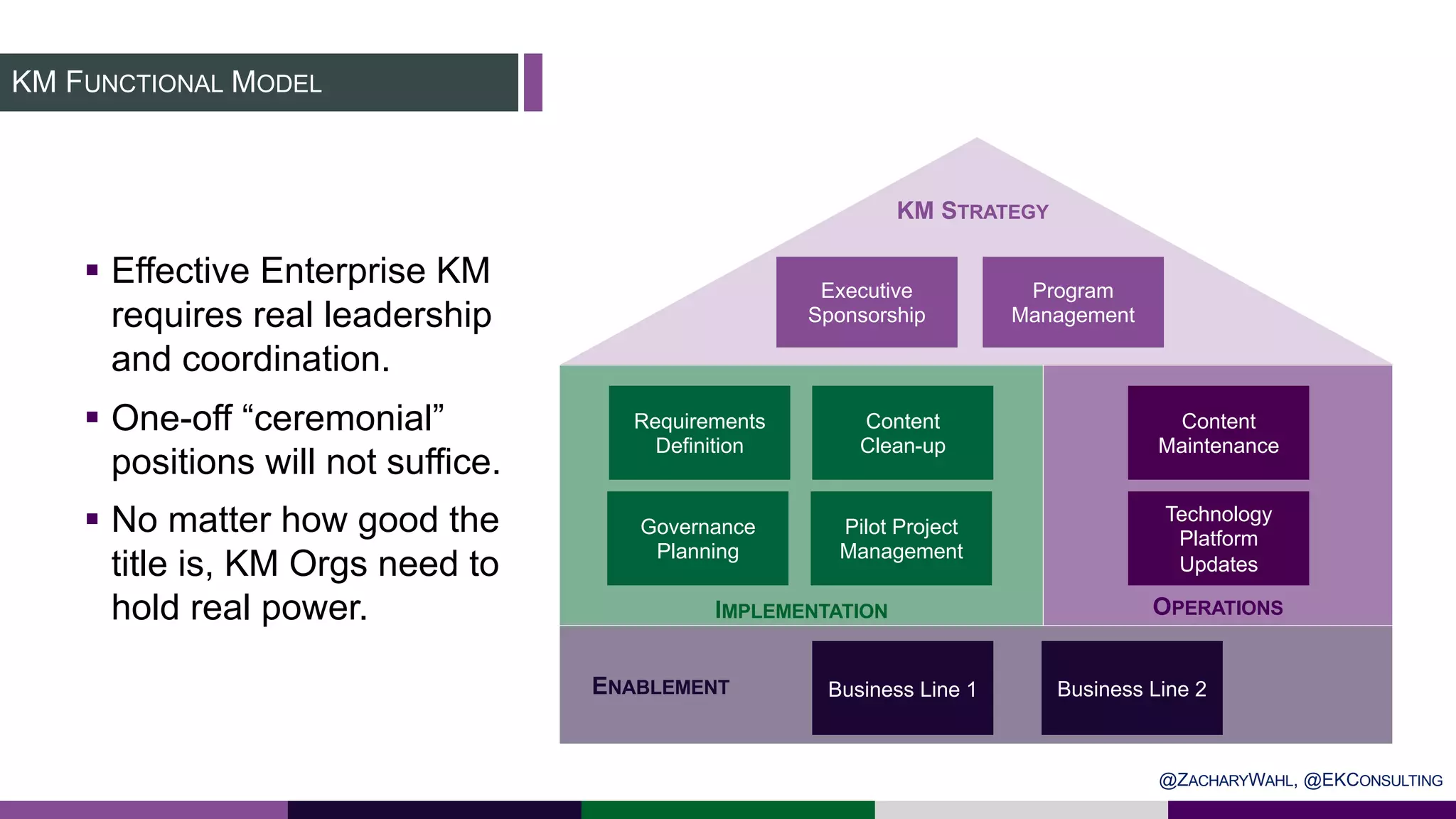
The document outlines key insights and trends in knowledge management (KM) presented at a conference held on March 4, 2020. It emphasizes the foundational aspects of KM—including people, processes, culture, and technology—and discusses emerging trends such as the integration of AI and ontologies in KM practices. Additionally, it highlights the importance of improving content discoverability and organizational alignment for better business outcomes.