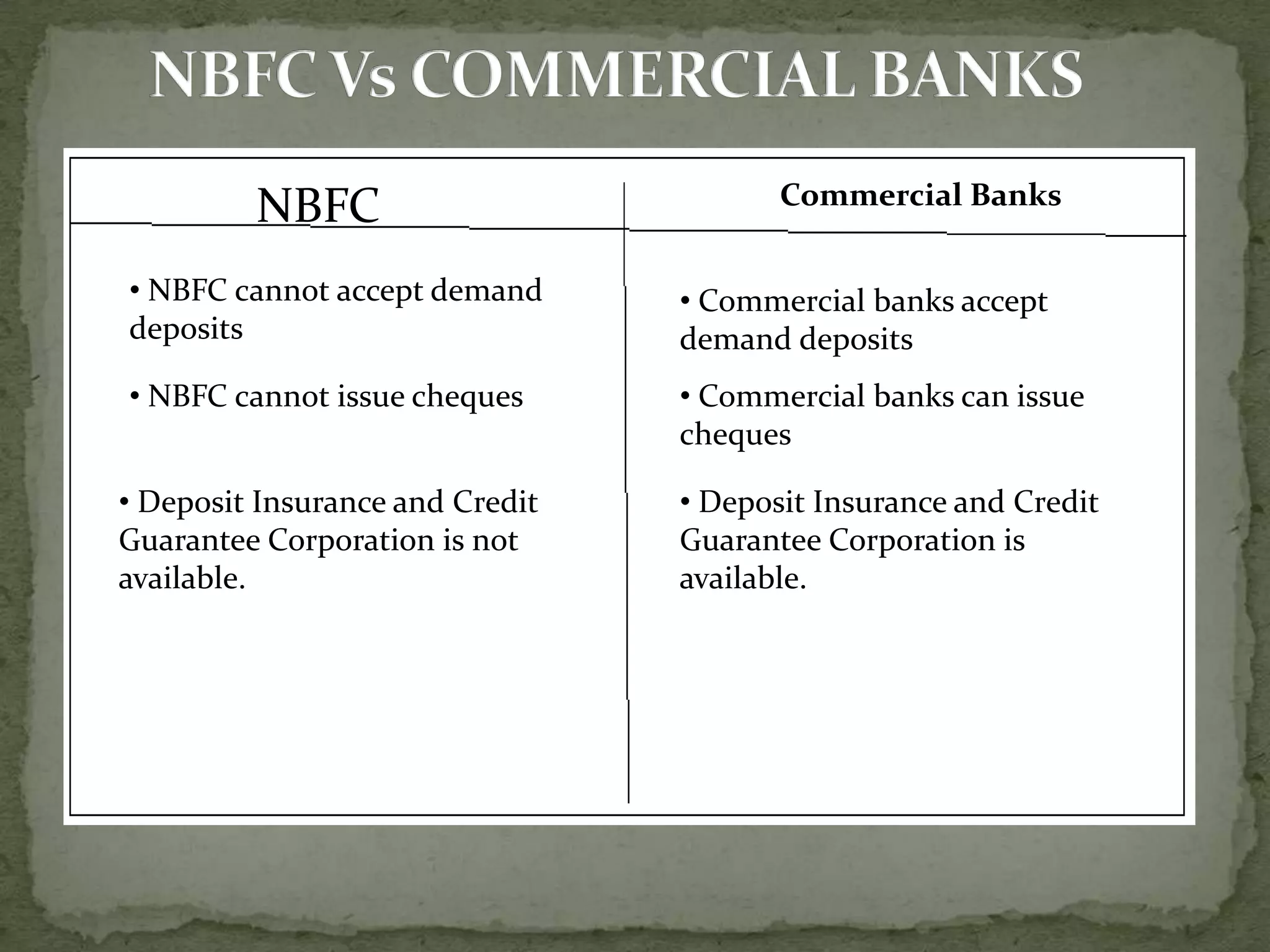
Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) are non-banking institutions that provide banking services such as loans and advances. NBFCs are registered under the Companies Act and regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. Major NBFCs include HDFC and HUDCO. Unlike commercial banks, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits or issue checks, and deposit insurance is not available for NBFC depositors. The RBI is considering providing banking licenses to select NBFCs and private sector companies if they meet eligibility criteria, which could strengthen competition in the banking sector and promote financial inclusion.