Embed presentation
Download to read offline

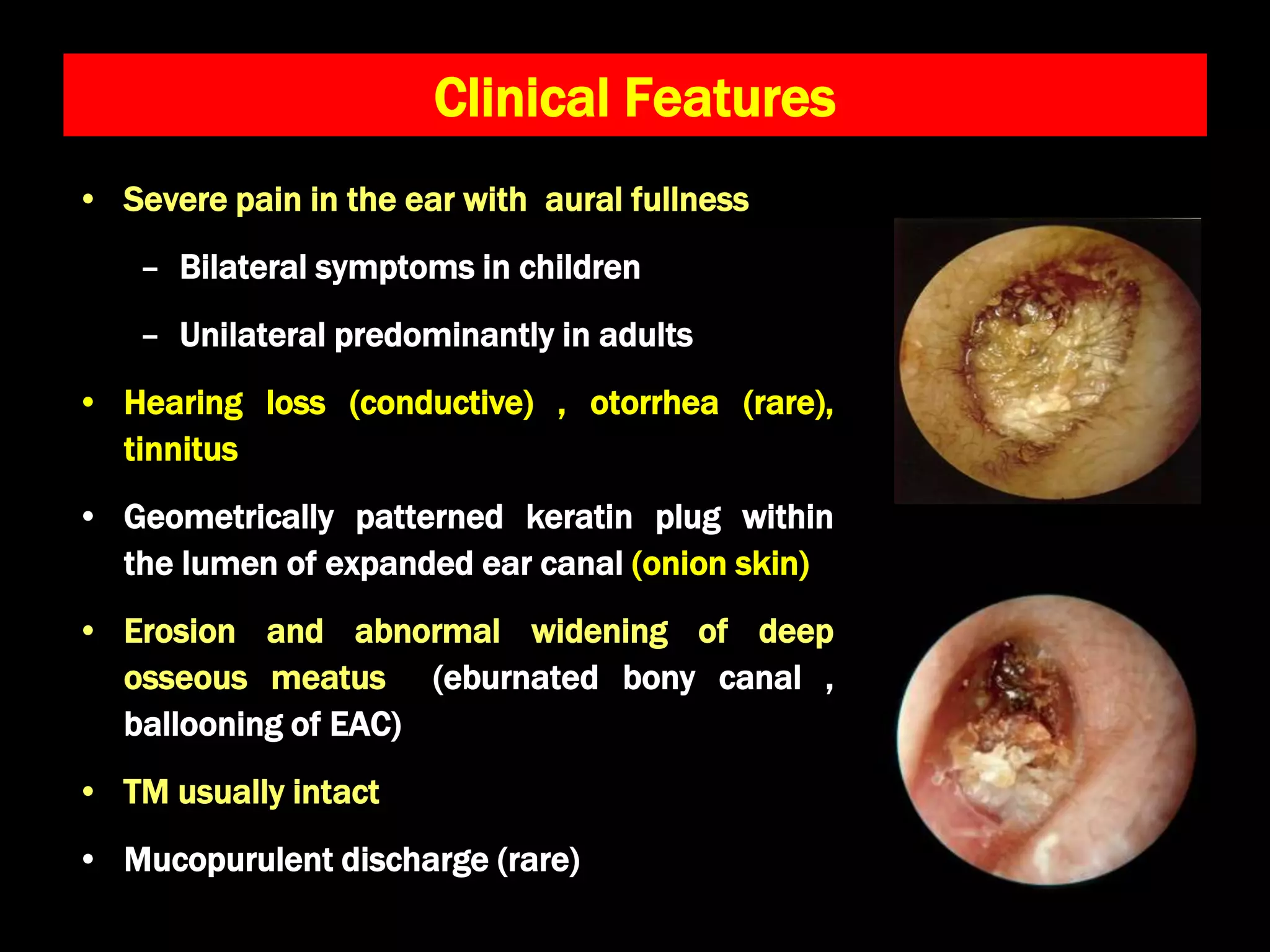

Keratosis obturans is a condition characterized by a keratotic mass of dead skin in the ear canal, often affecting individuals aged 5 to 20. Symptoms include severe ear pain, hearing loss, and a distinctive keratin plug, with potential associations to bronchiectasis and sinusitis. Treatment involves removing the keratin debris and managing inflammation, though recurrence is common.


