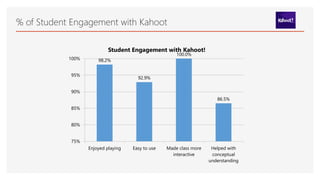
Kahoot! is a game-based learning platform that allows teachers to create and share quizzes, enhancing student engagement through gamification. It promotes active learning by using students' devices to respond to questions in real-time, accommodating various learning theories and appealing to diverse student needs. While it offers numerous benefits like increased motivation and engagement, concerns about its effectiveness and potential drawbacks also exist, highlighting the importance of balanced use in educational settings.