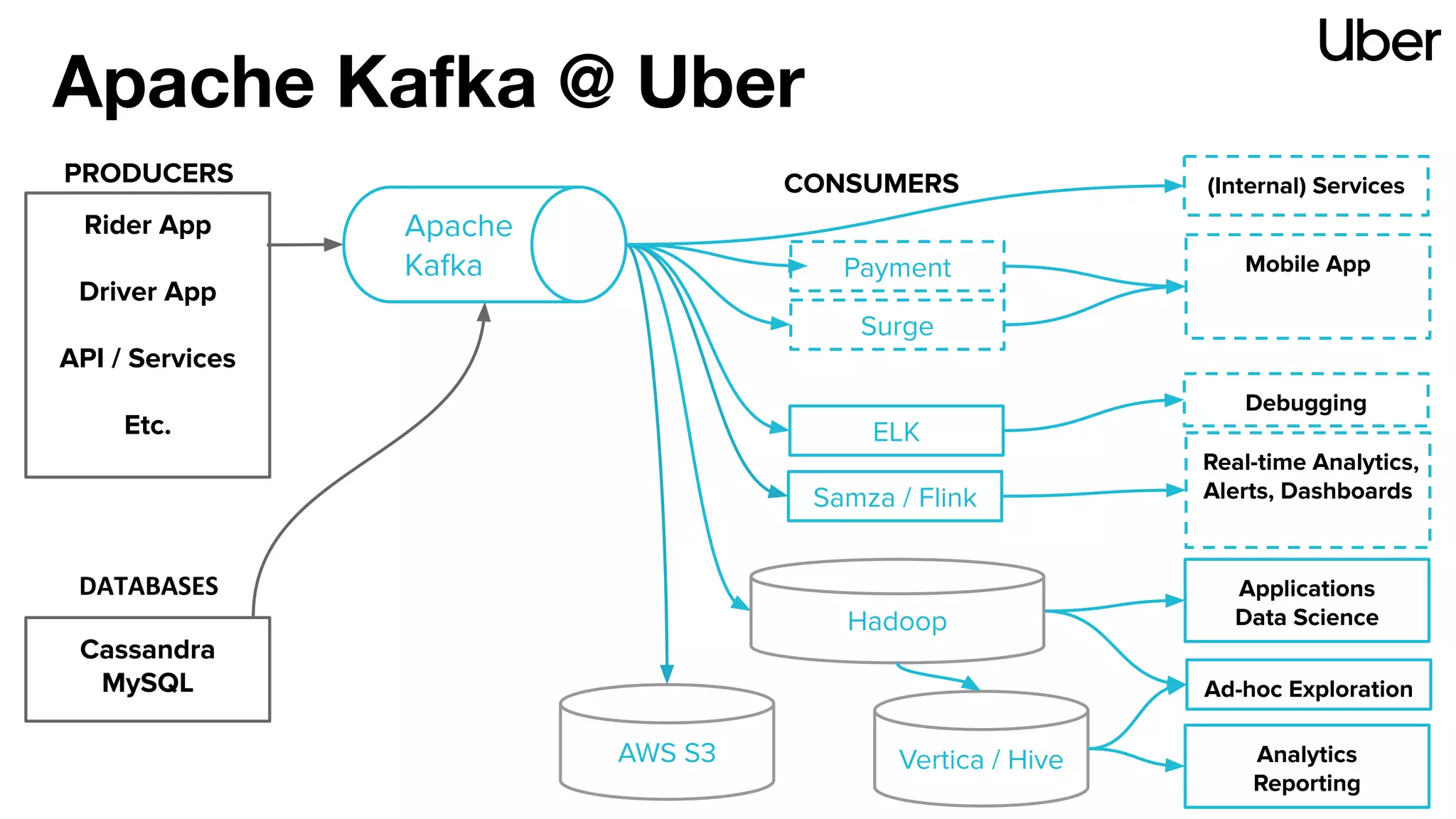
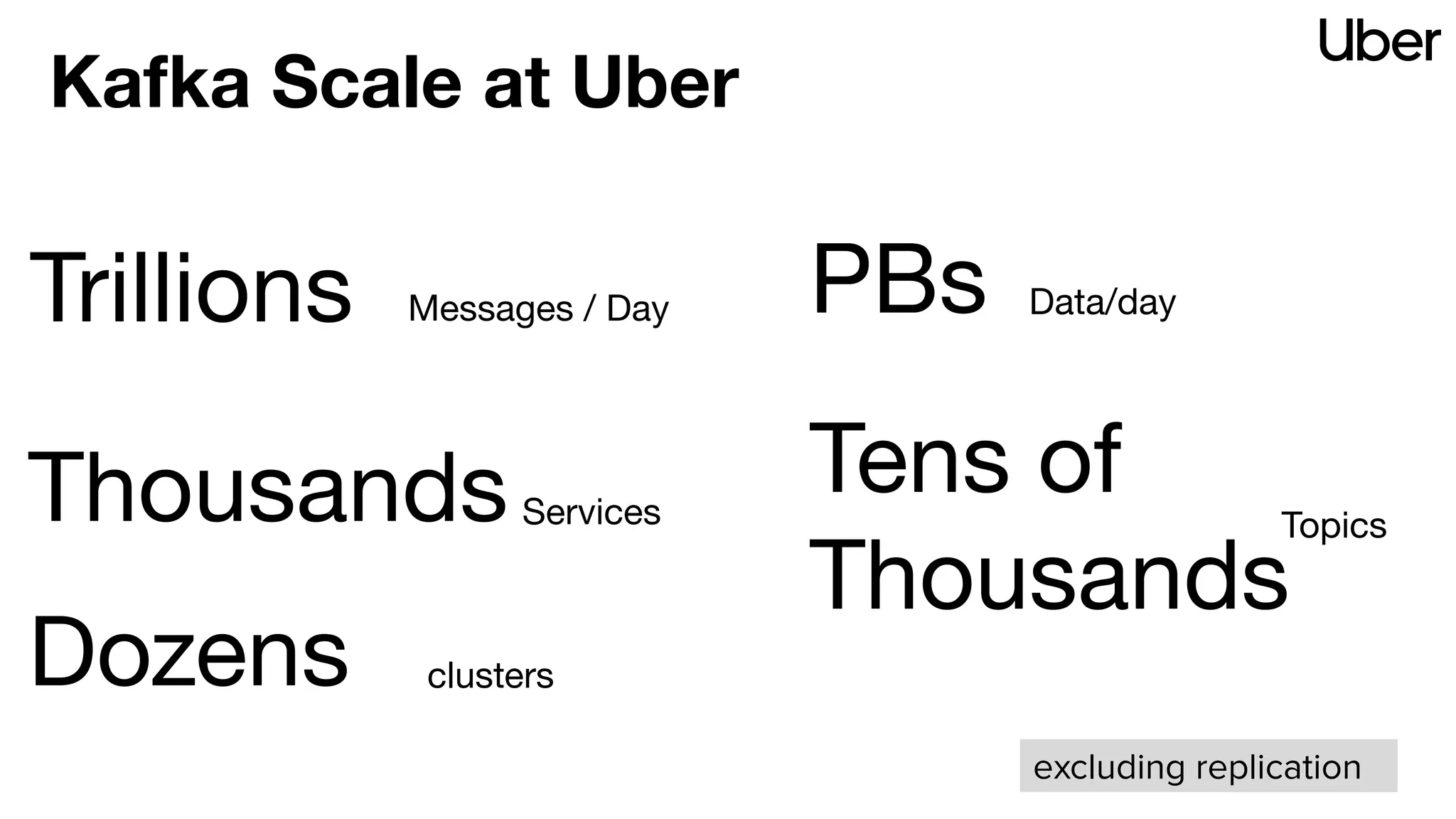
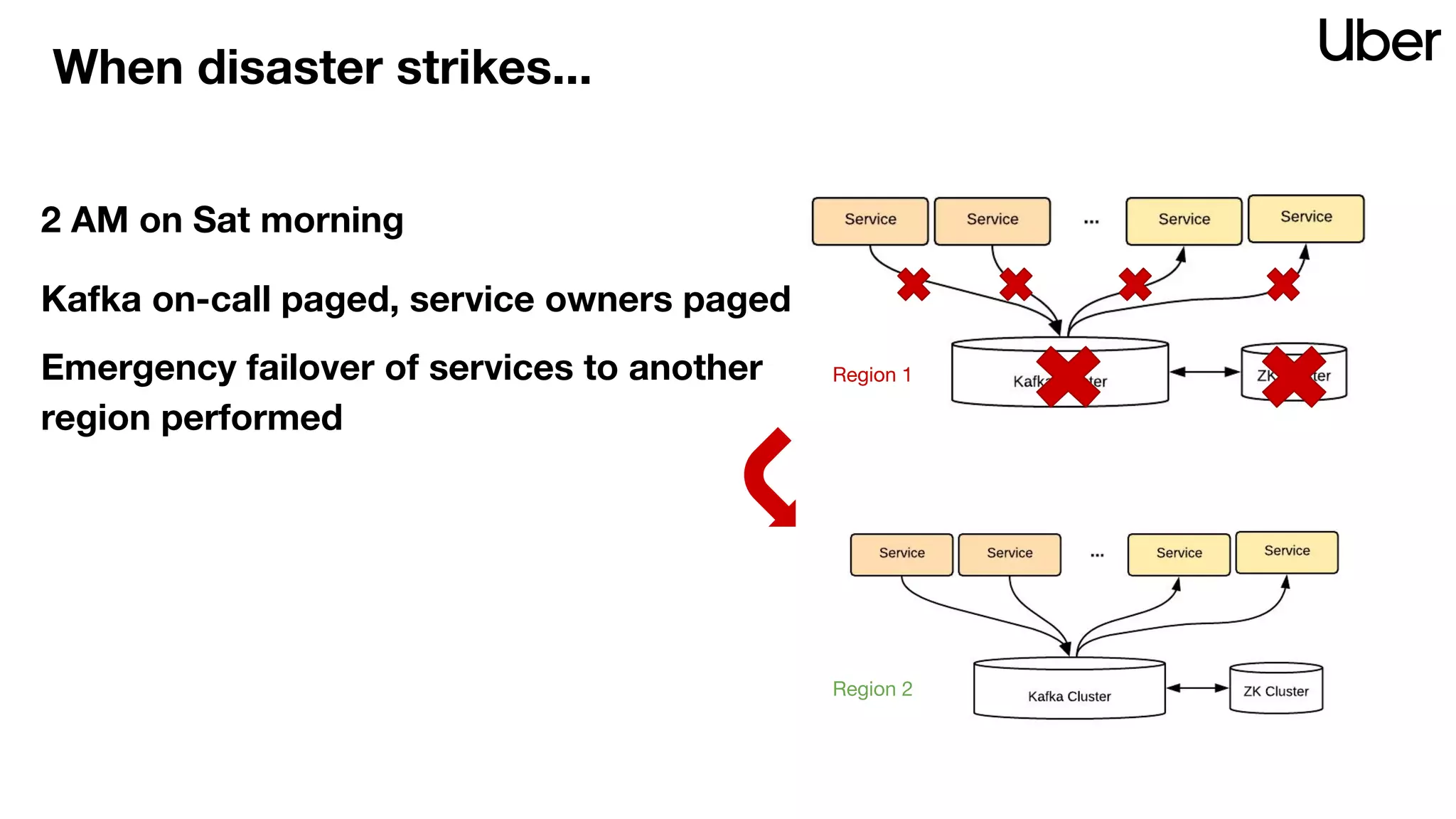
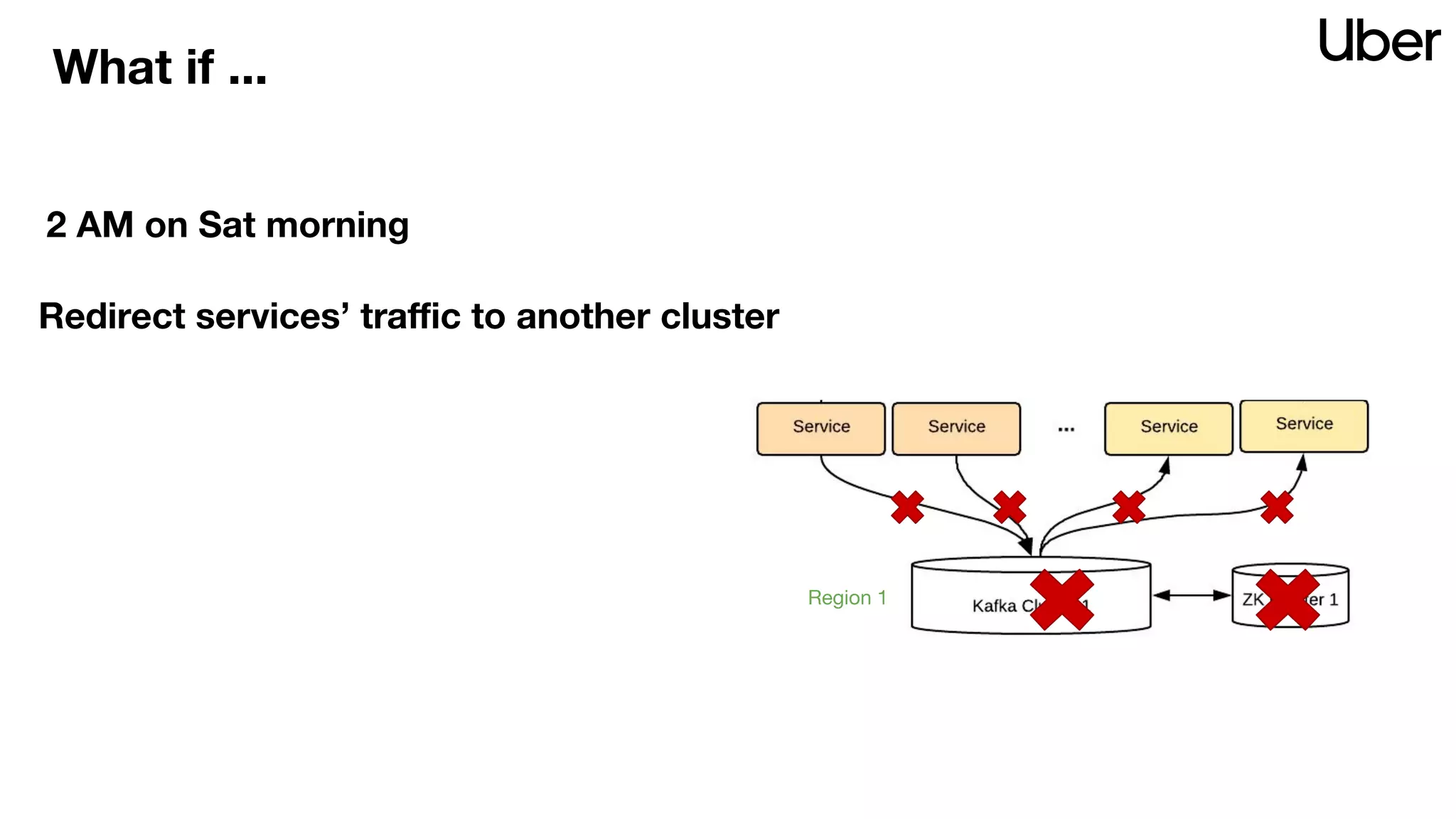
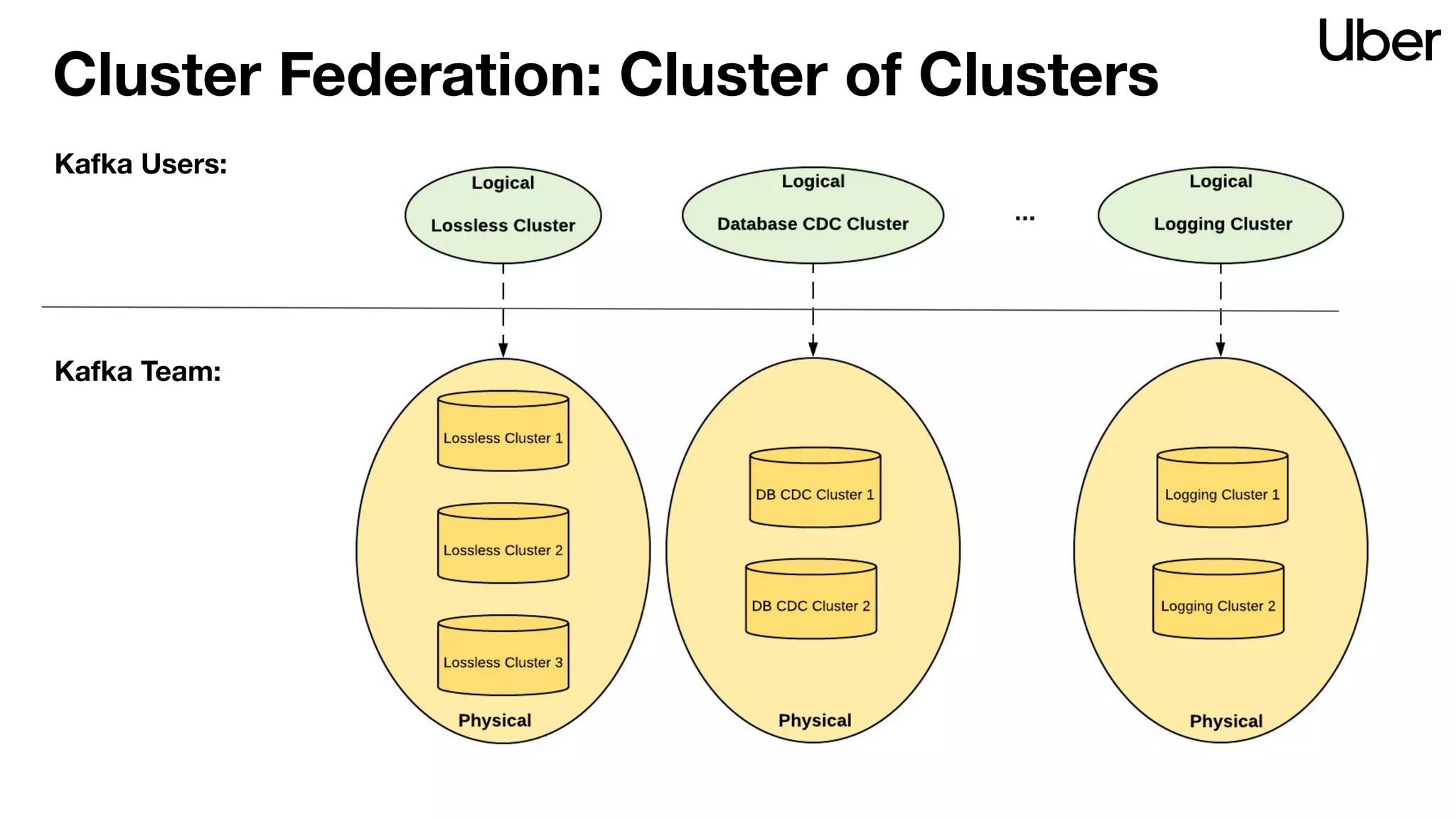
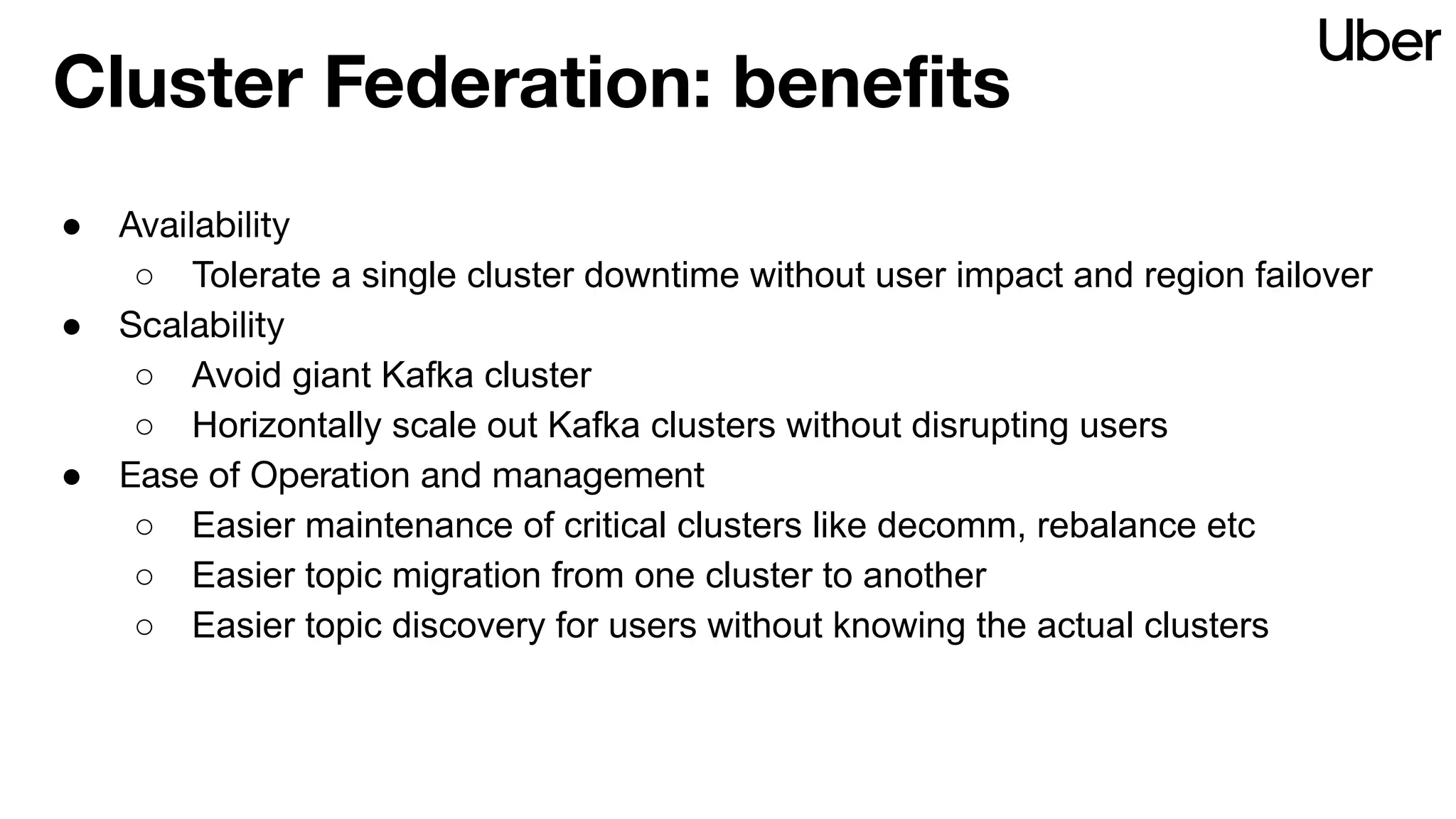
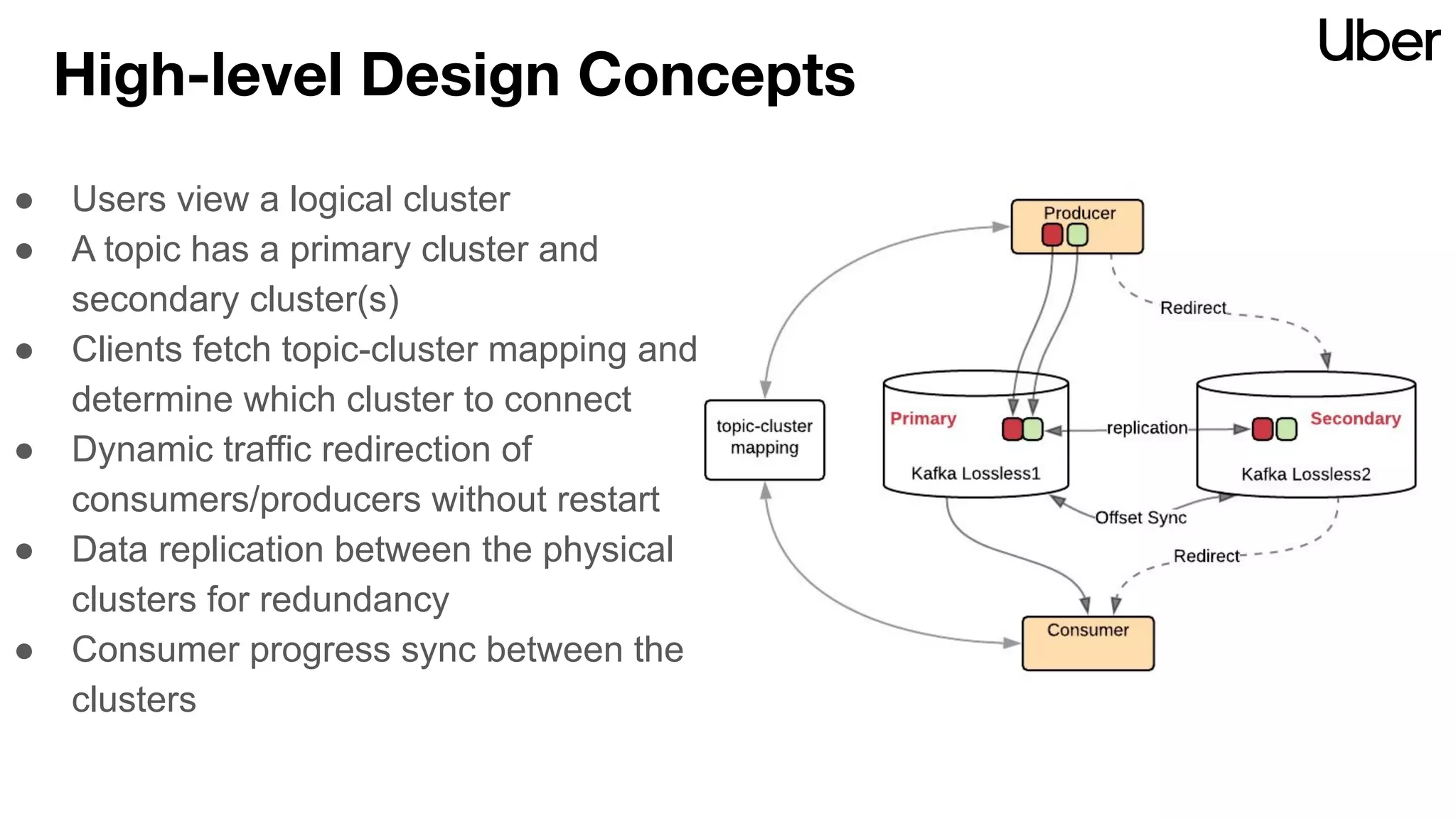
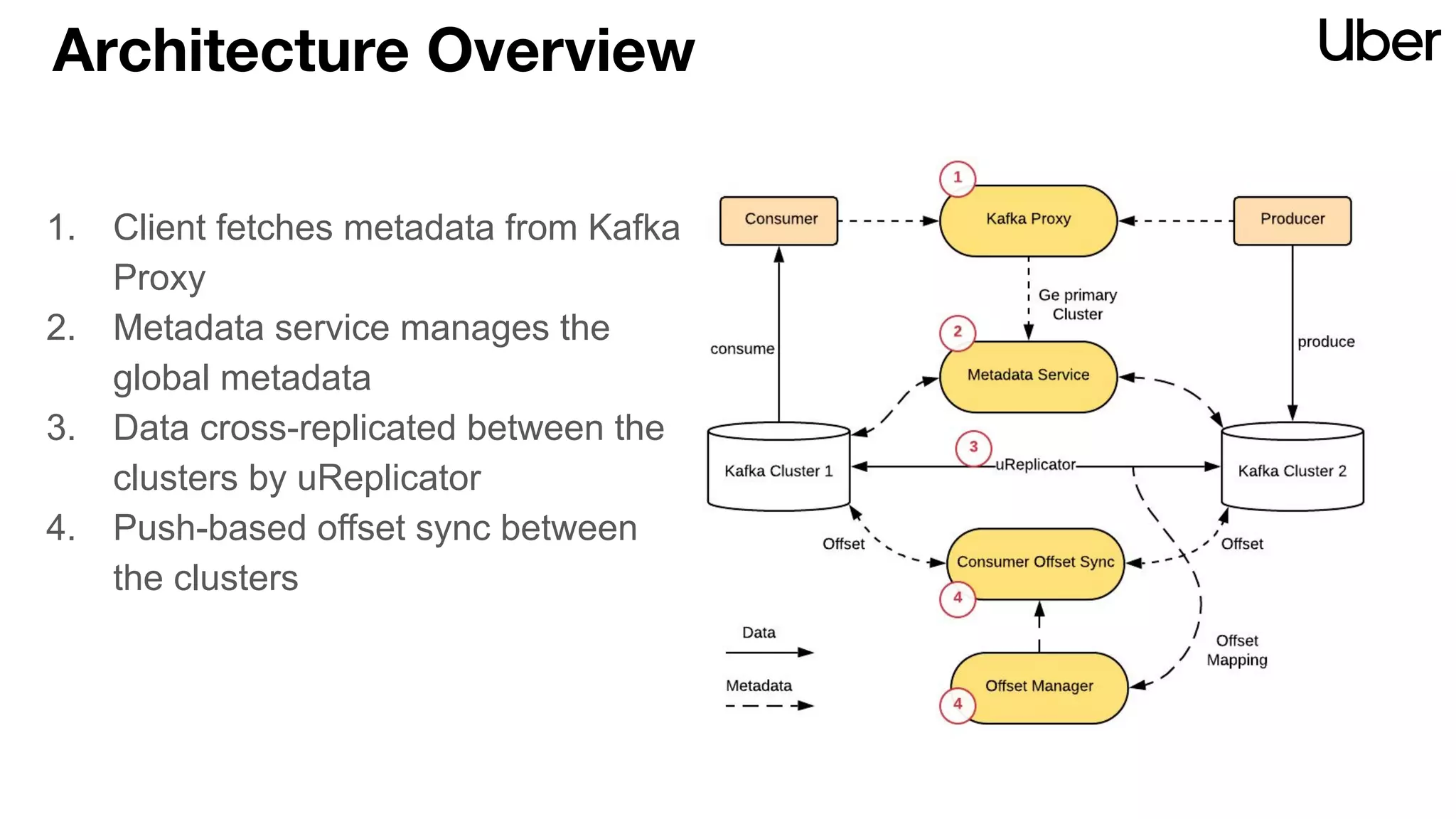
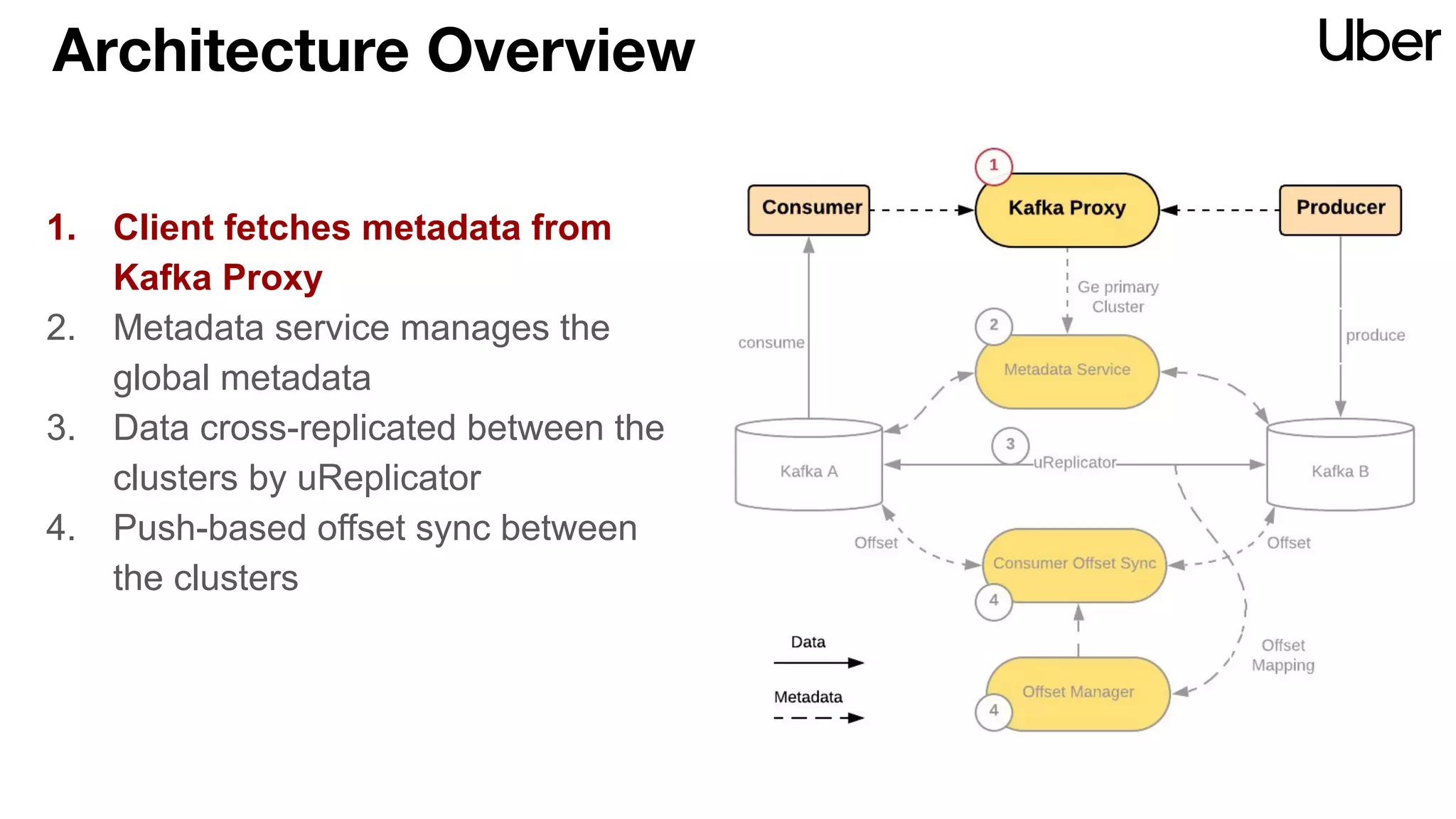
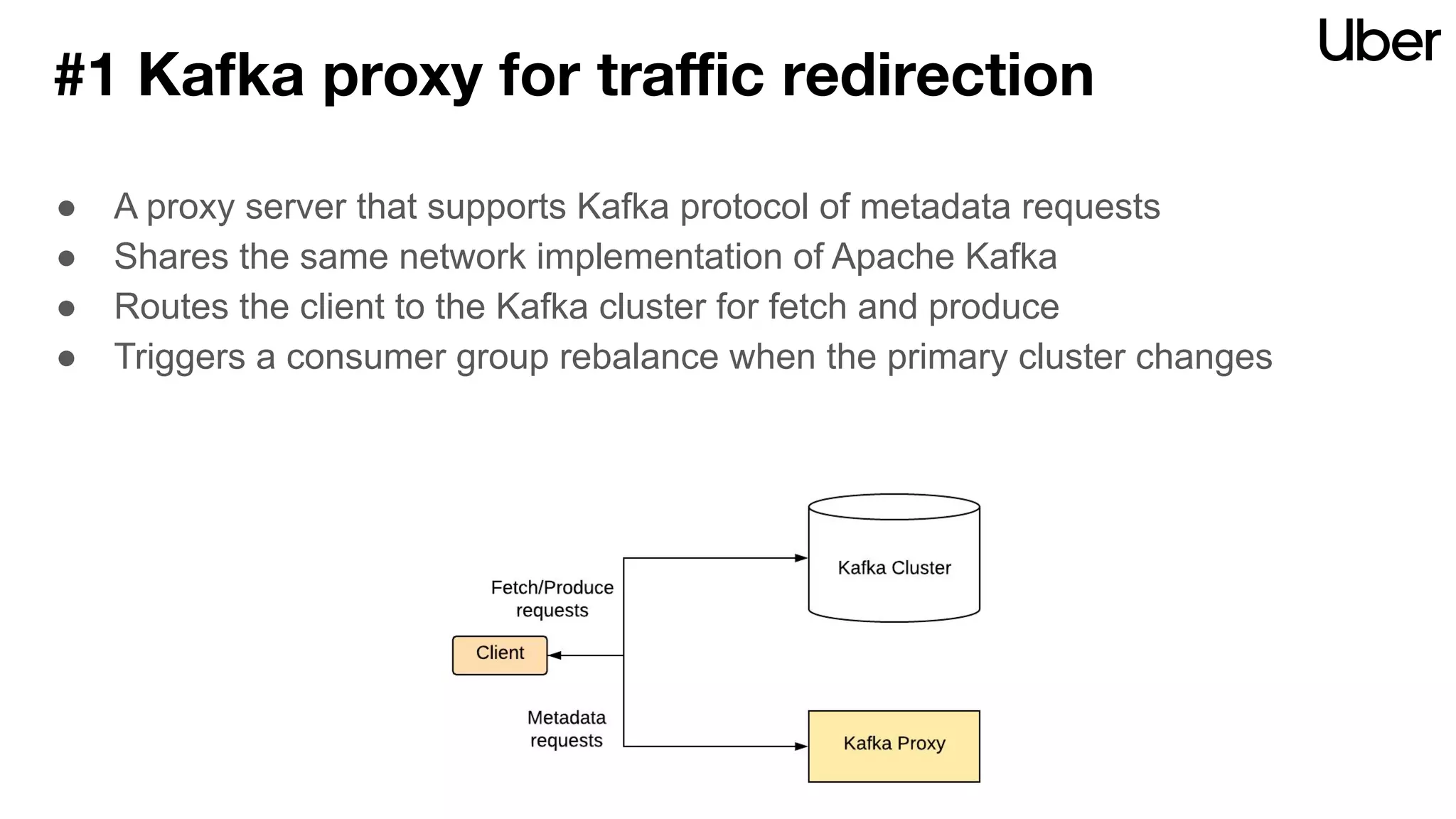
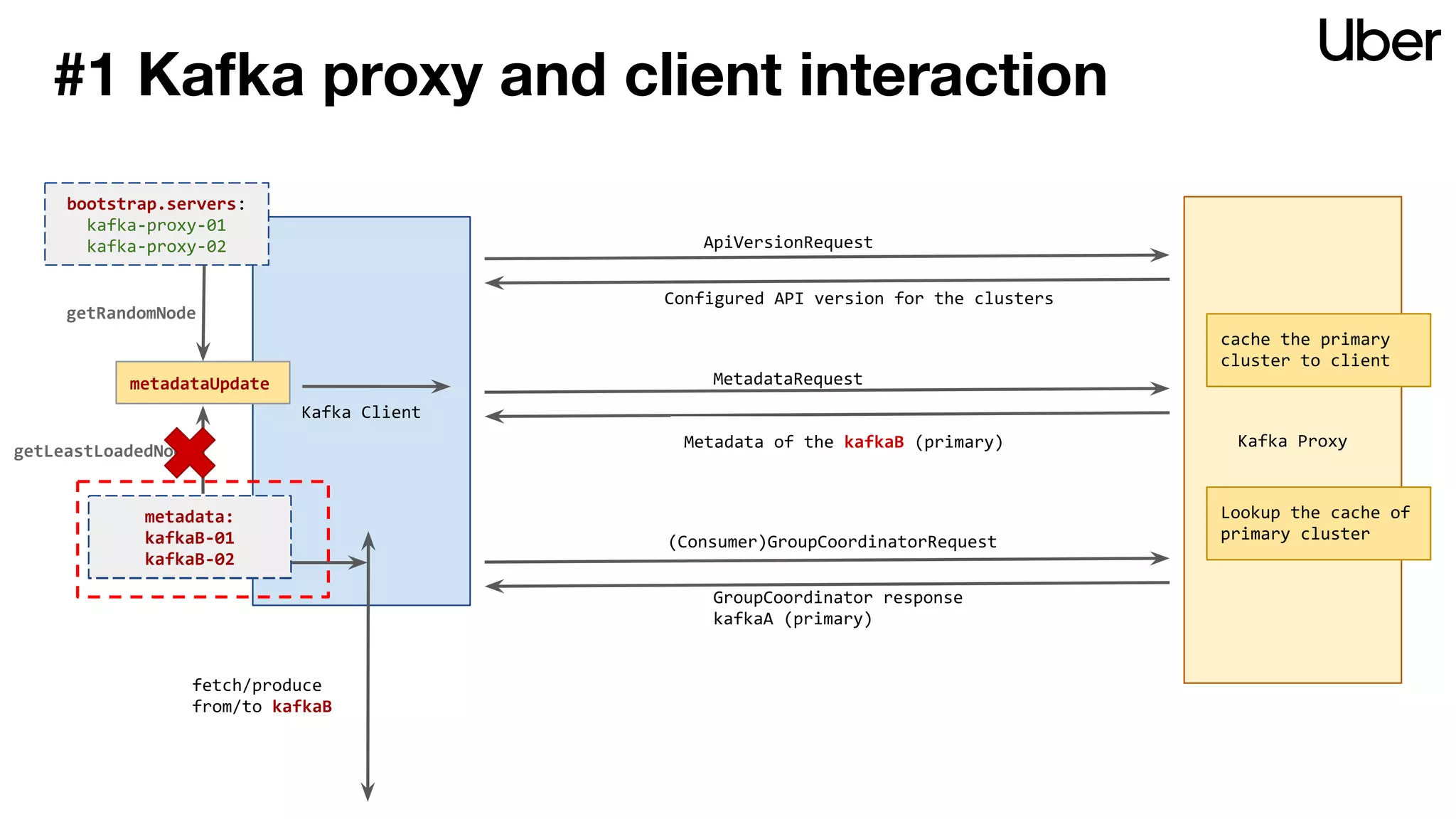
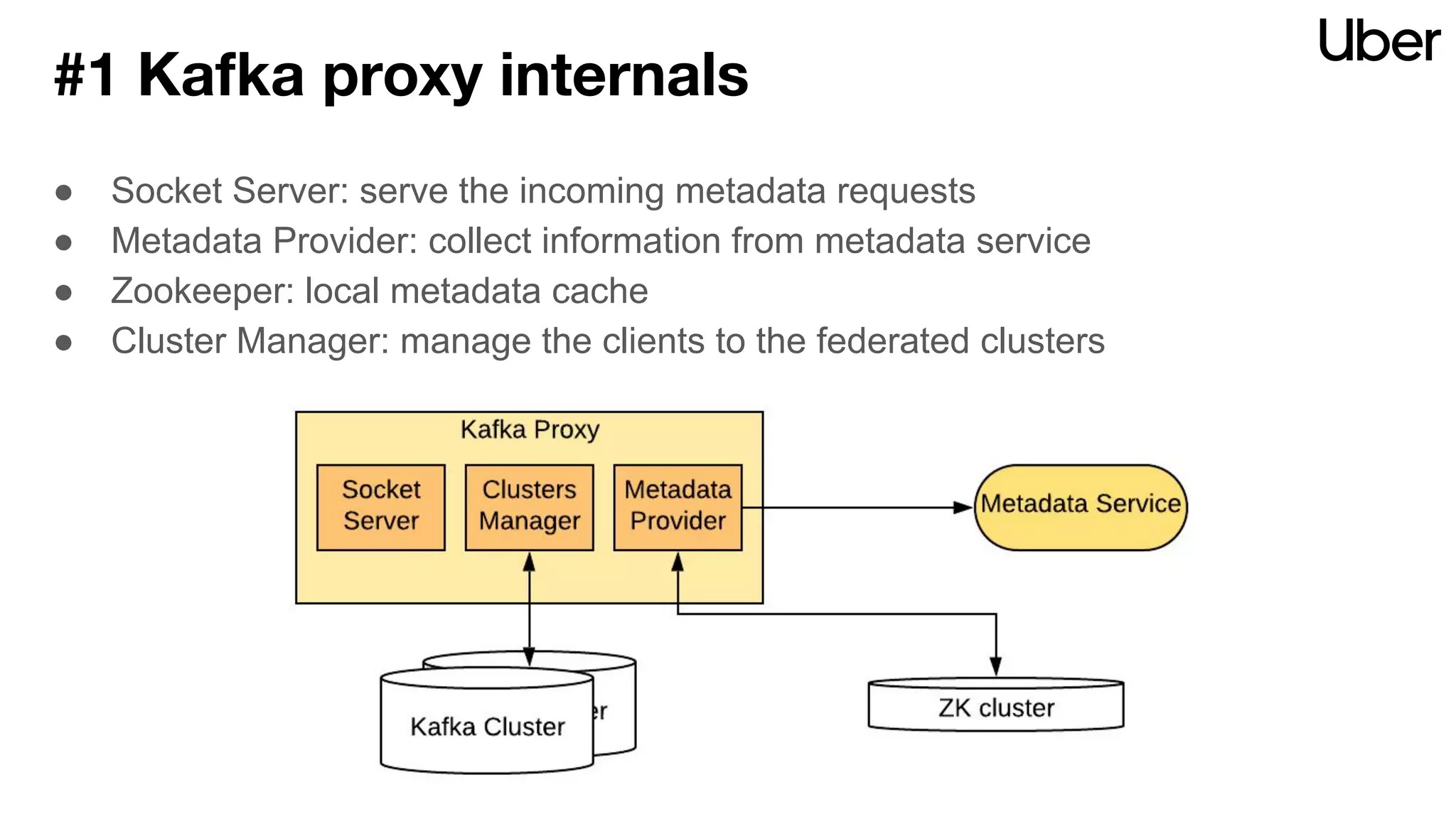
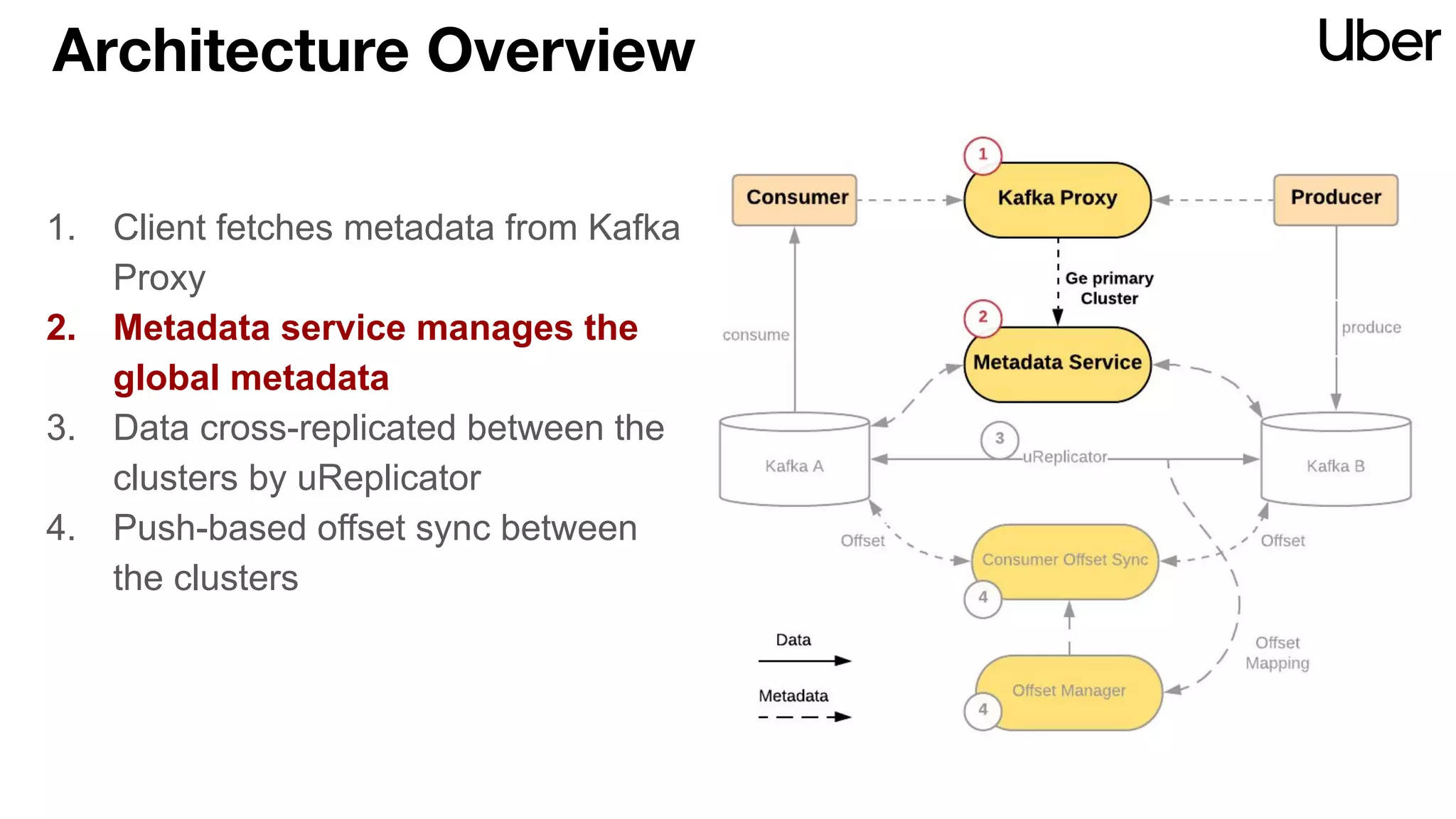
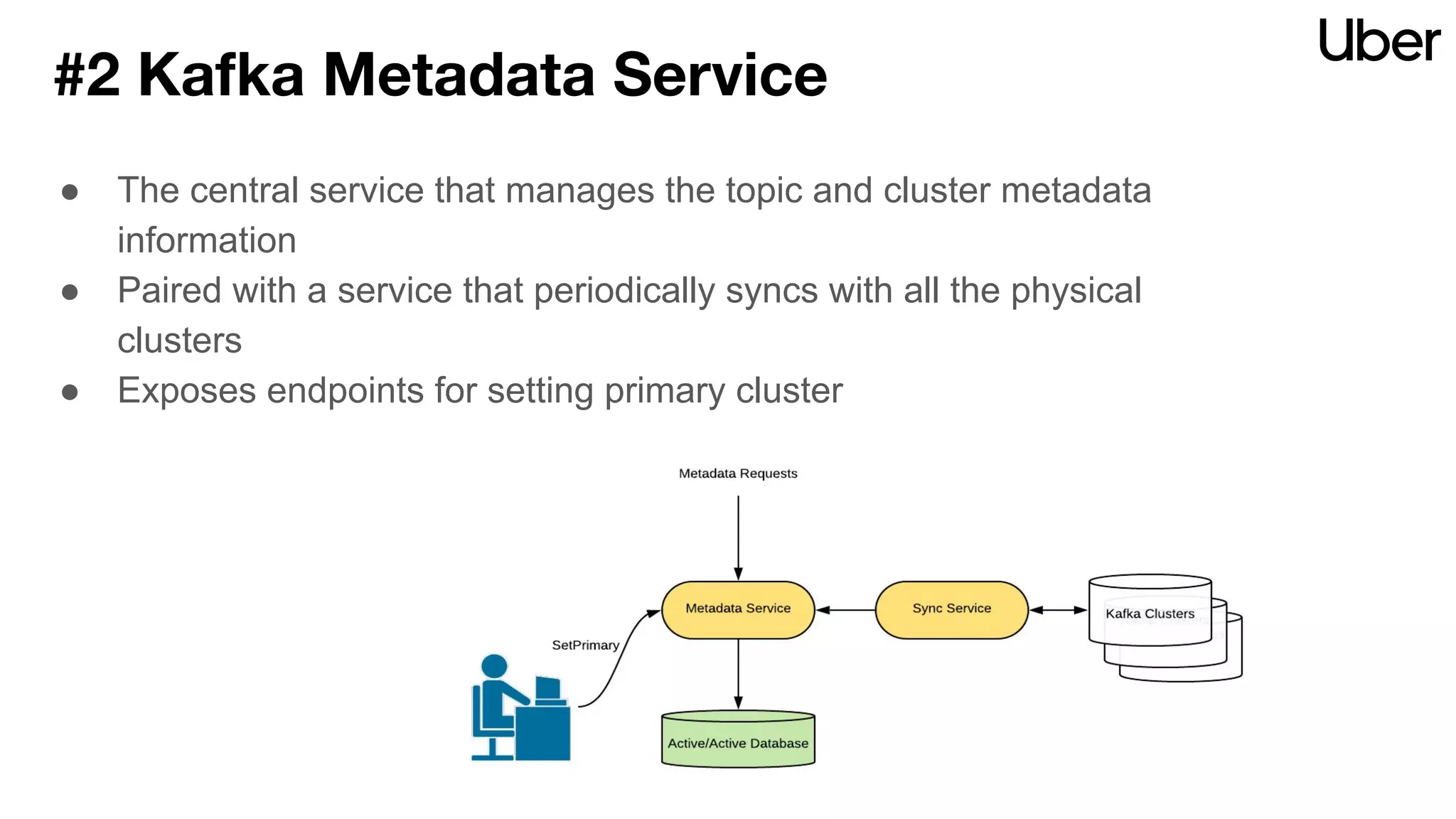
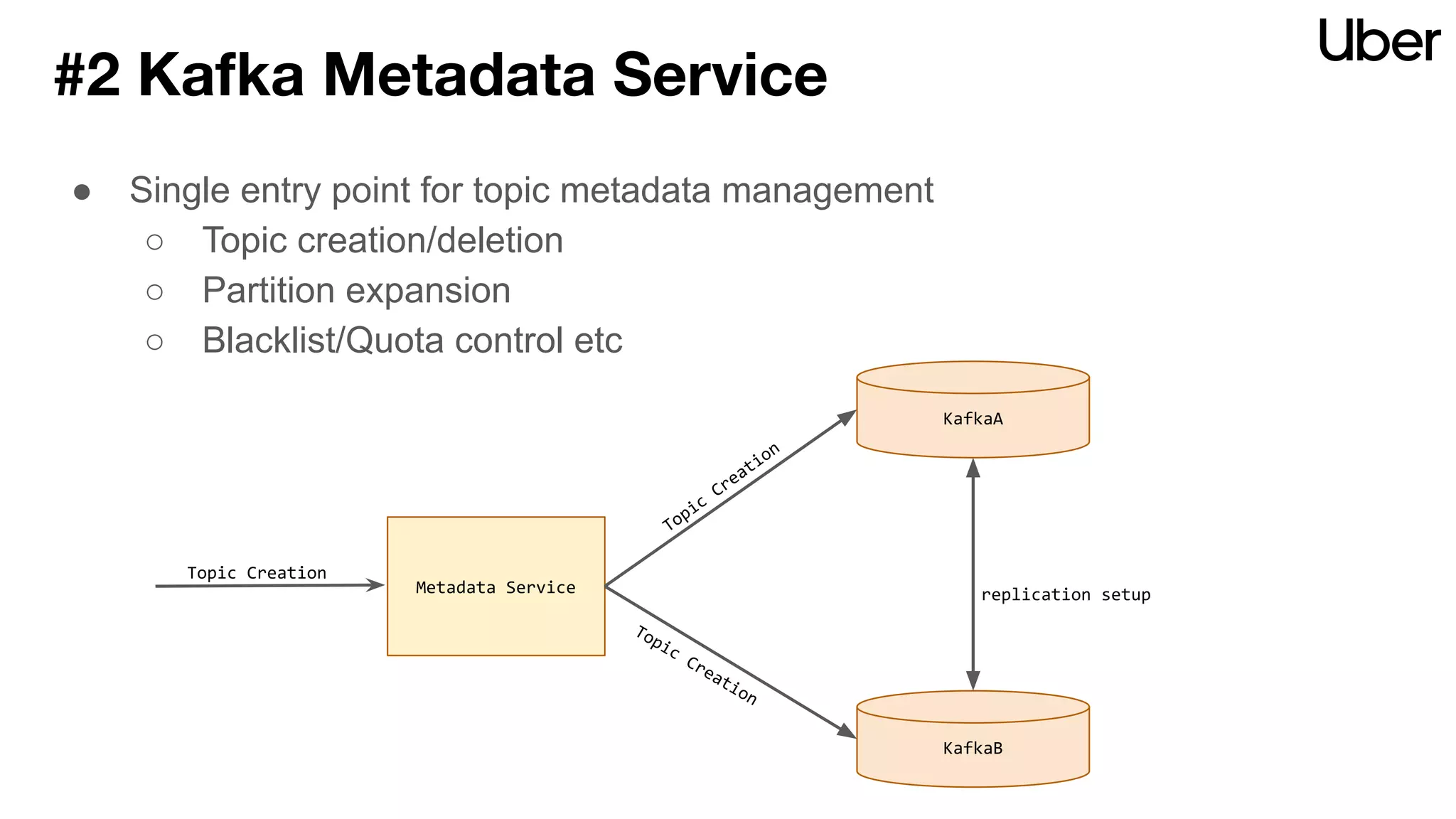
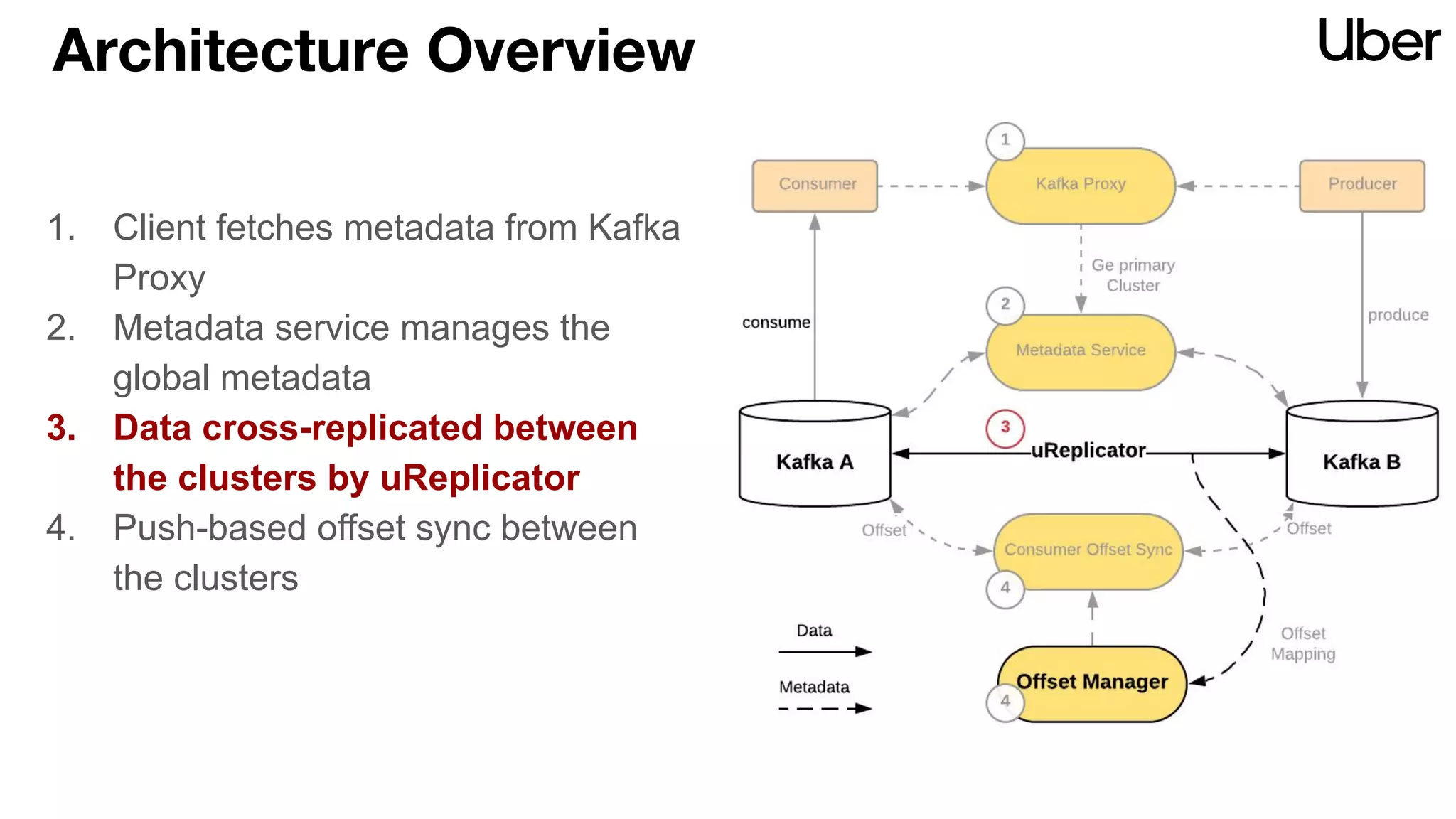
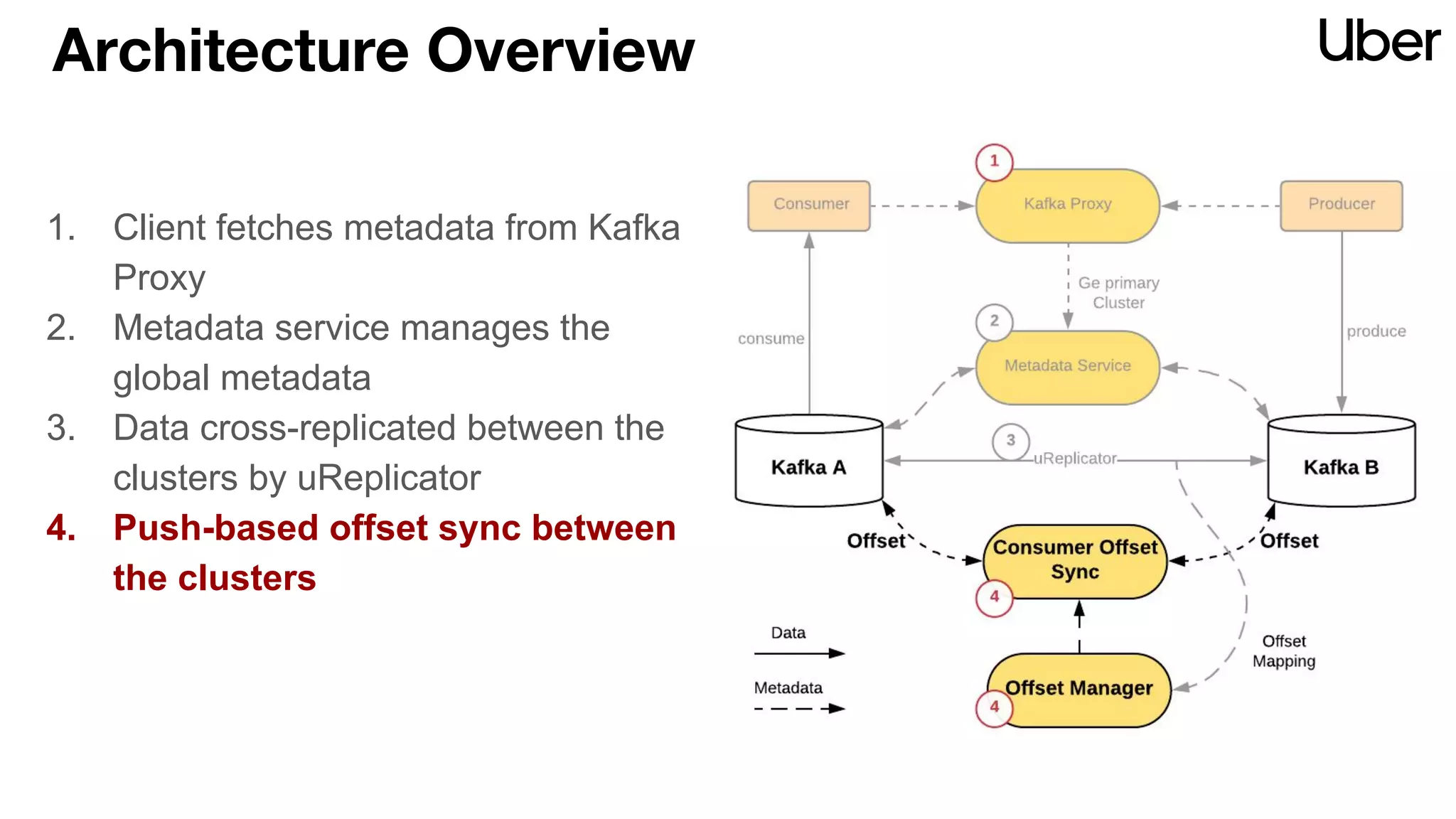
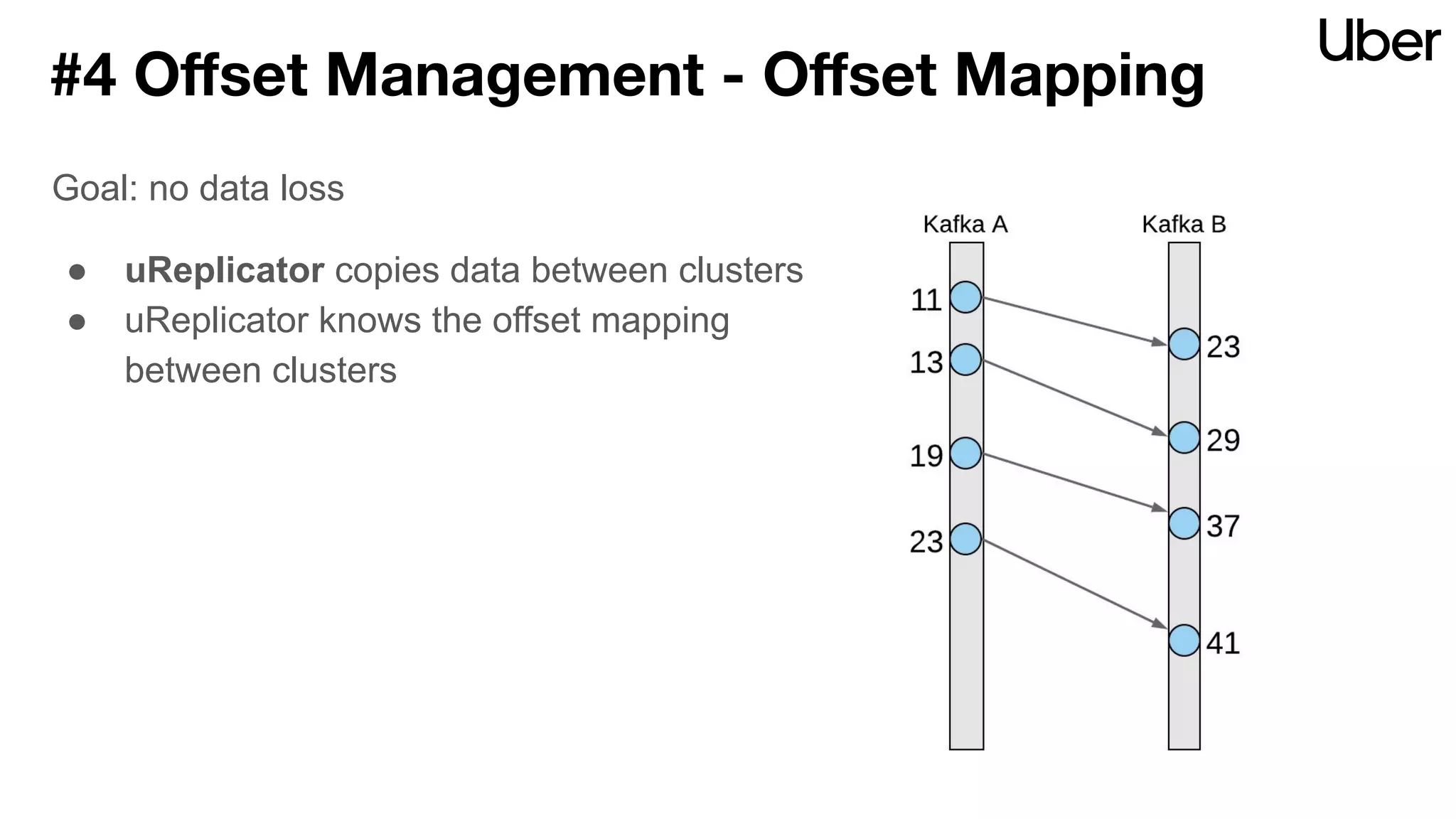
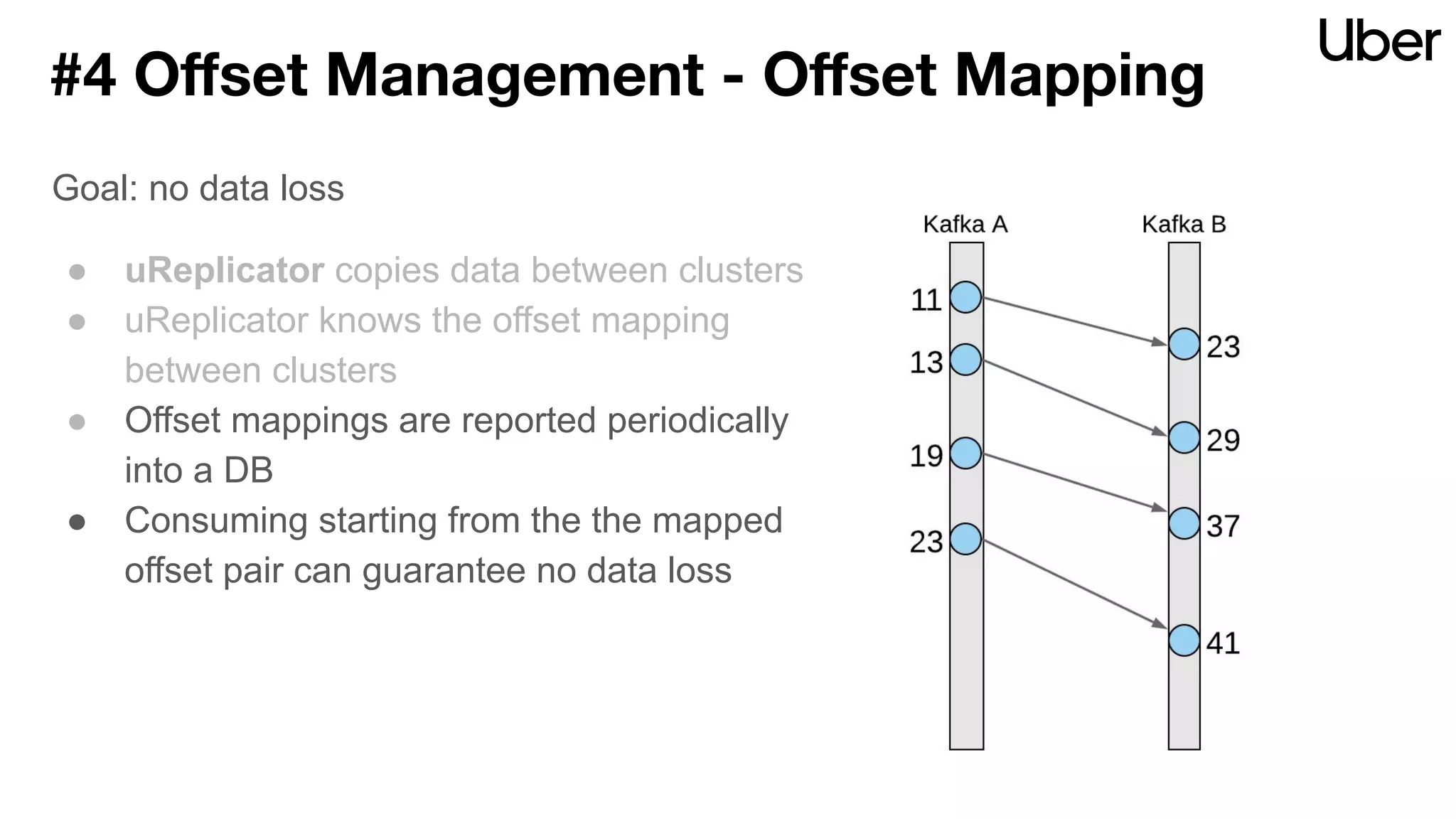
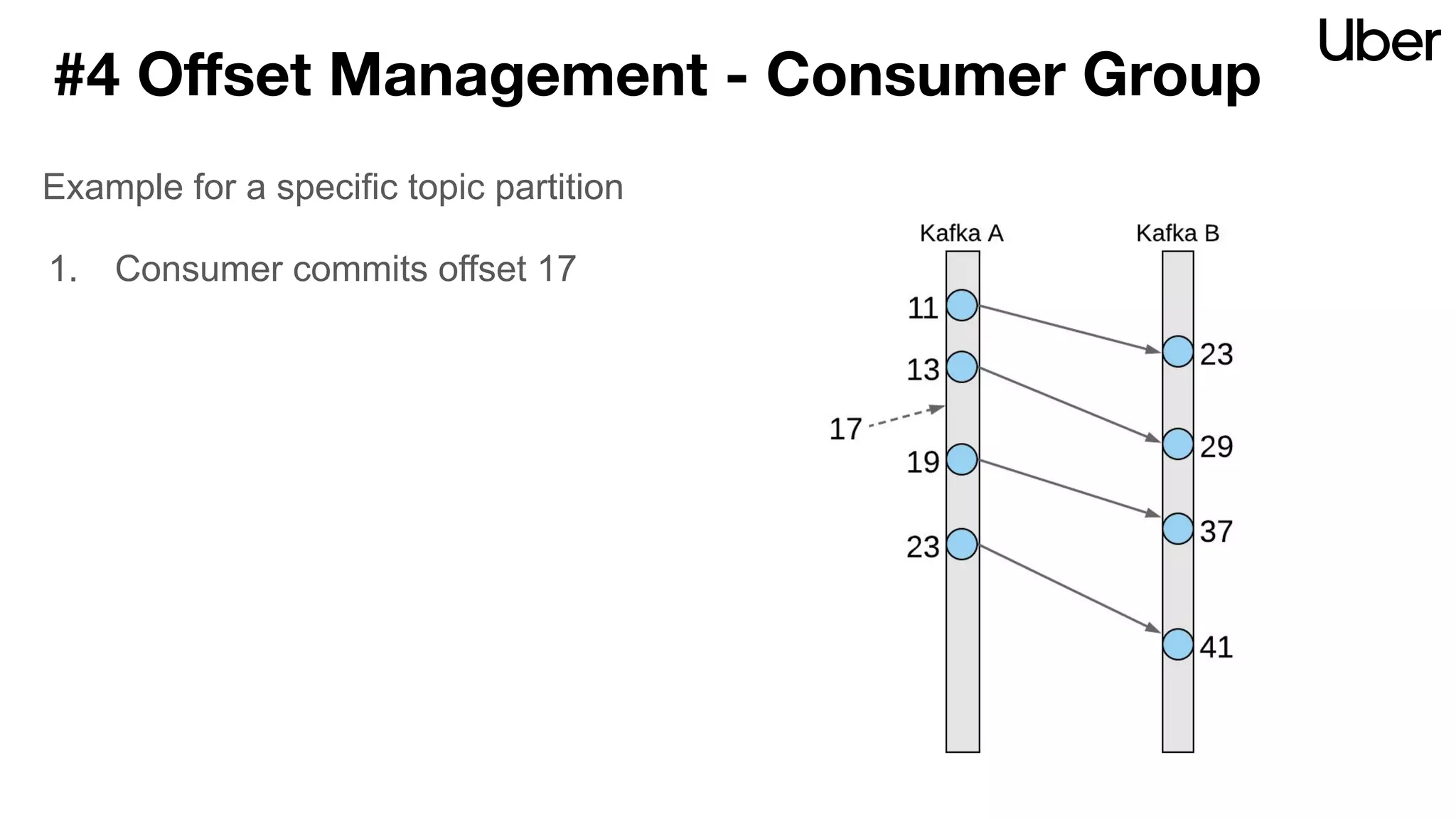
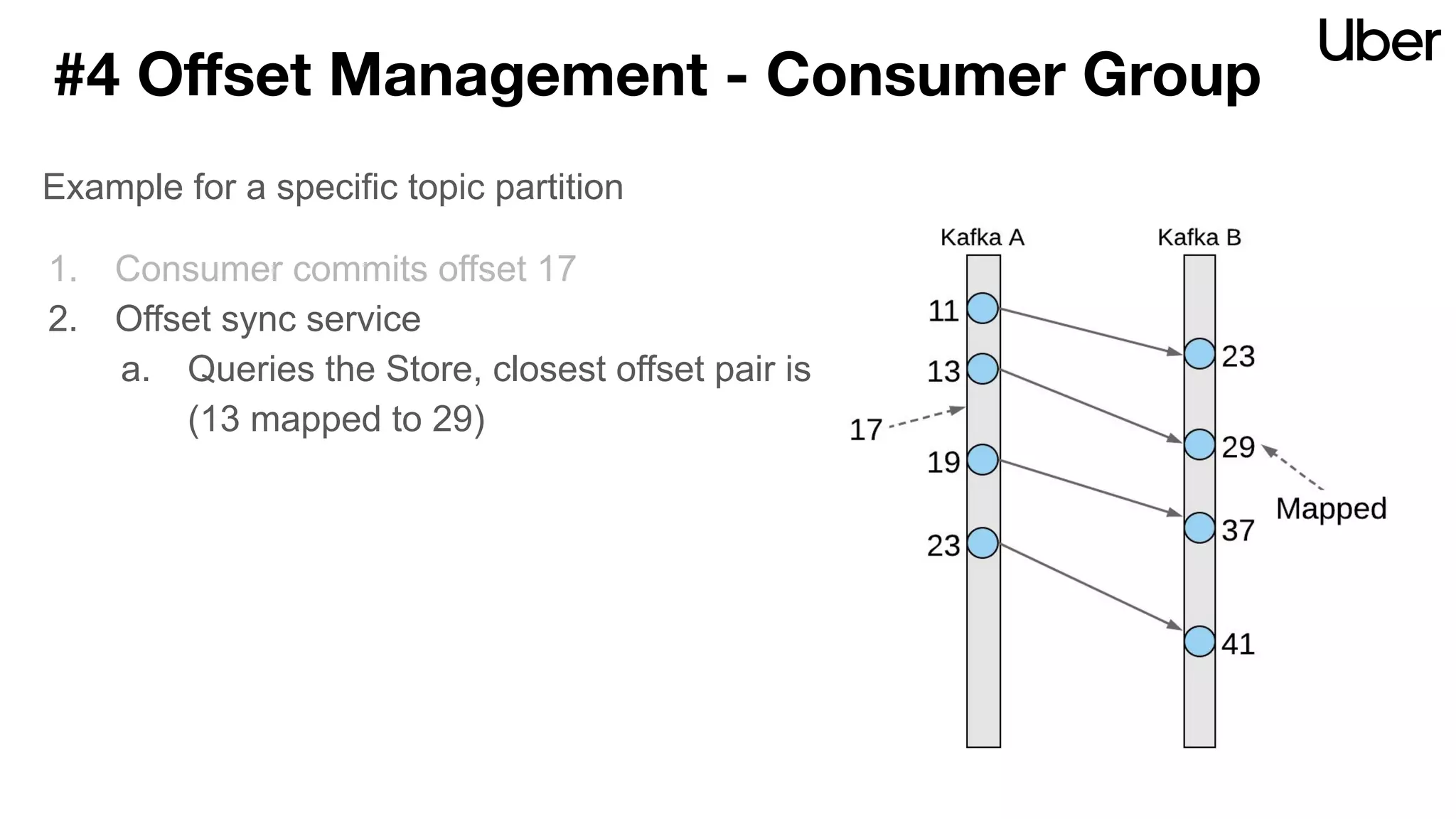
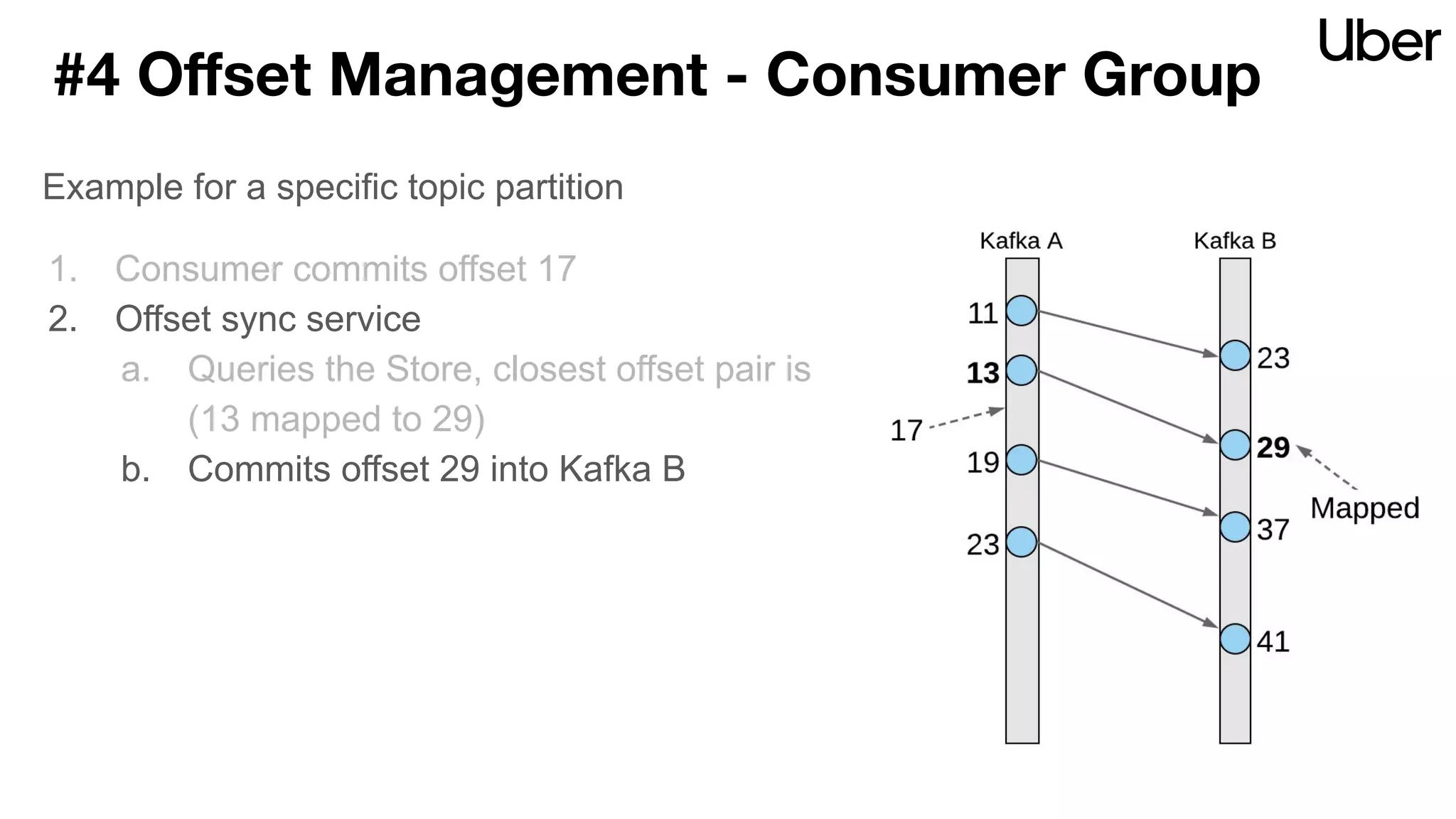
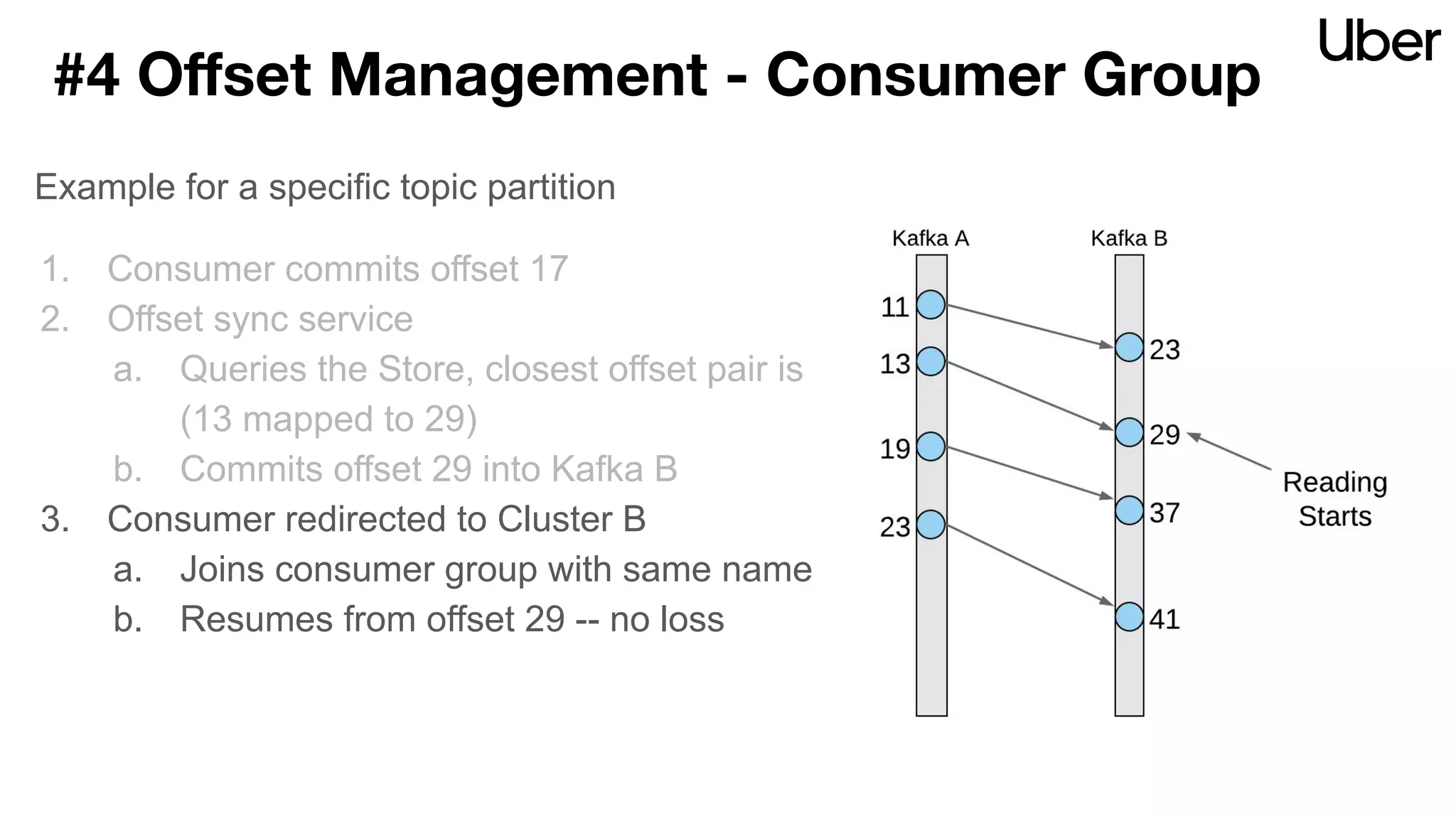
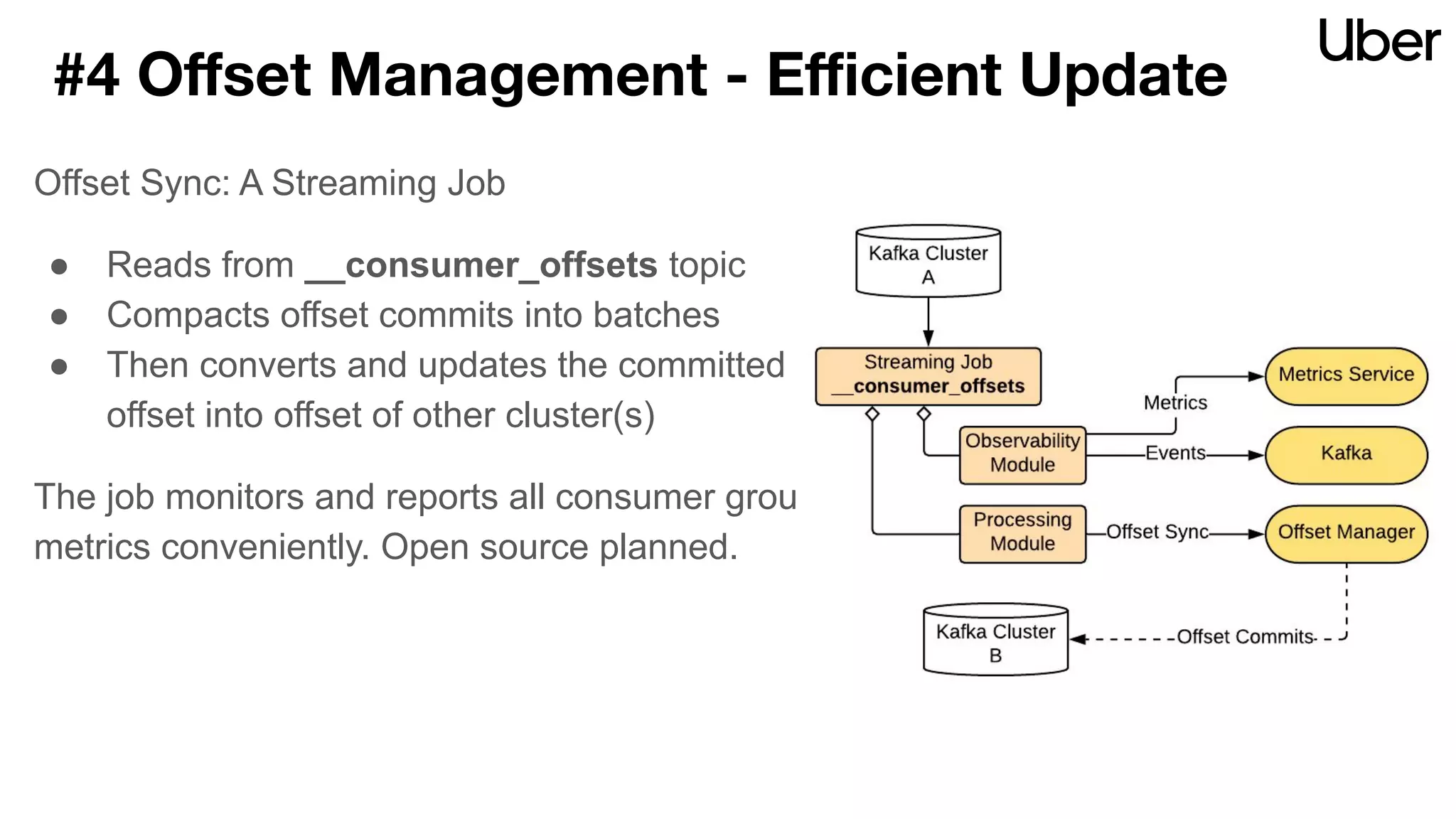
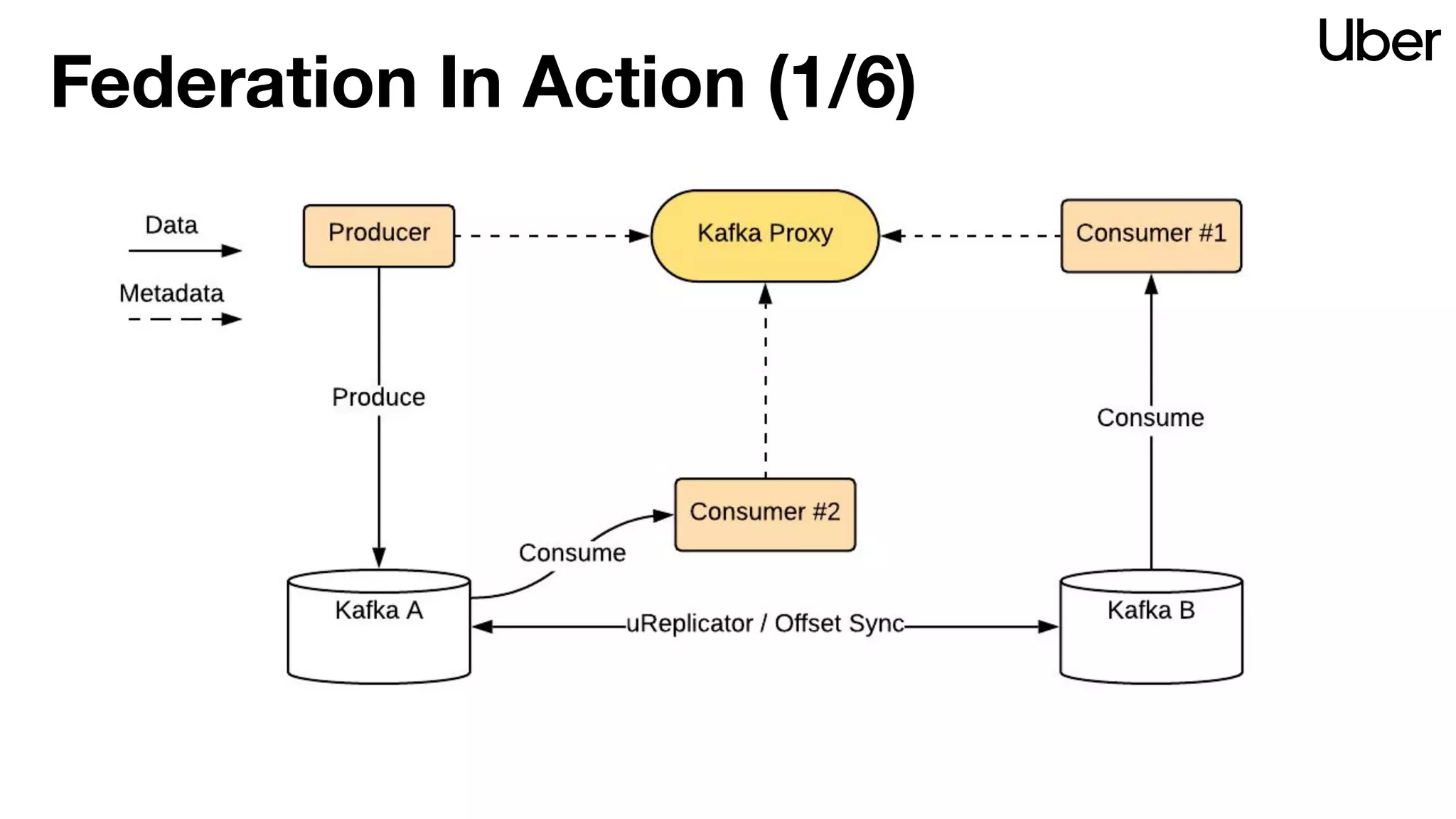
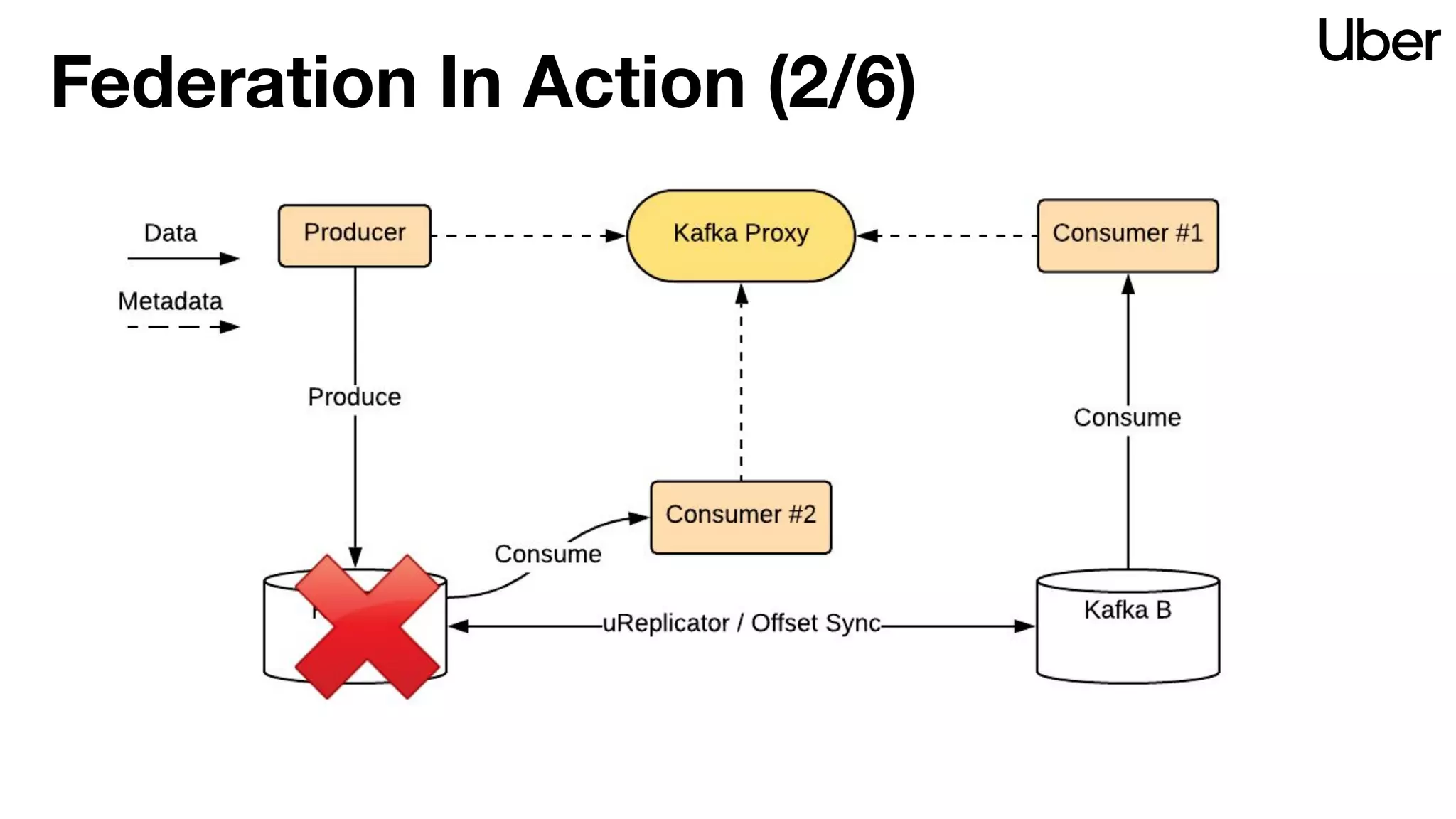
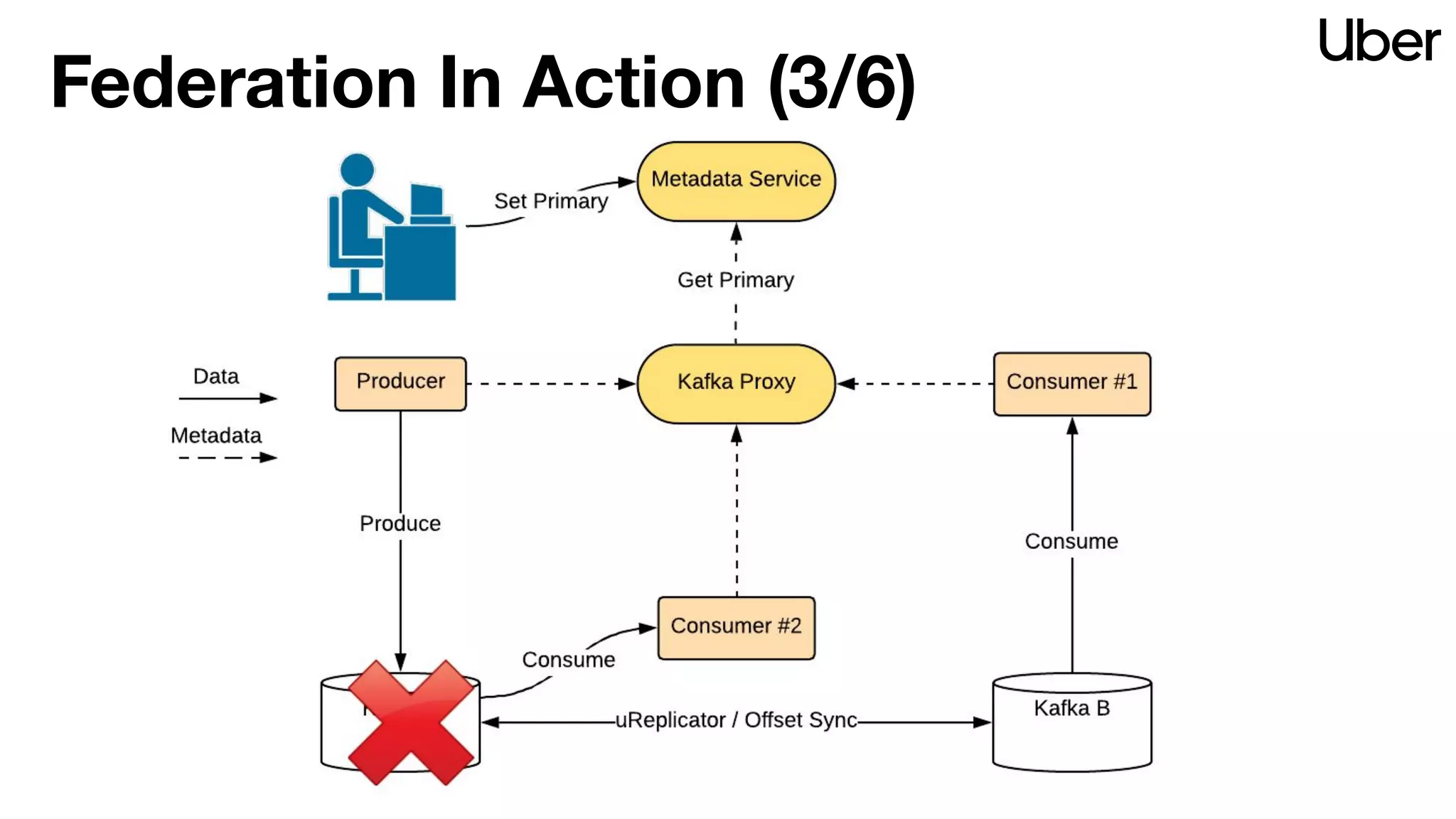
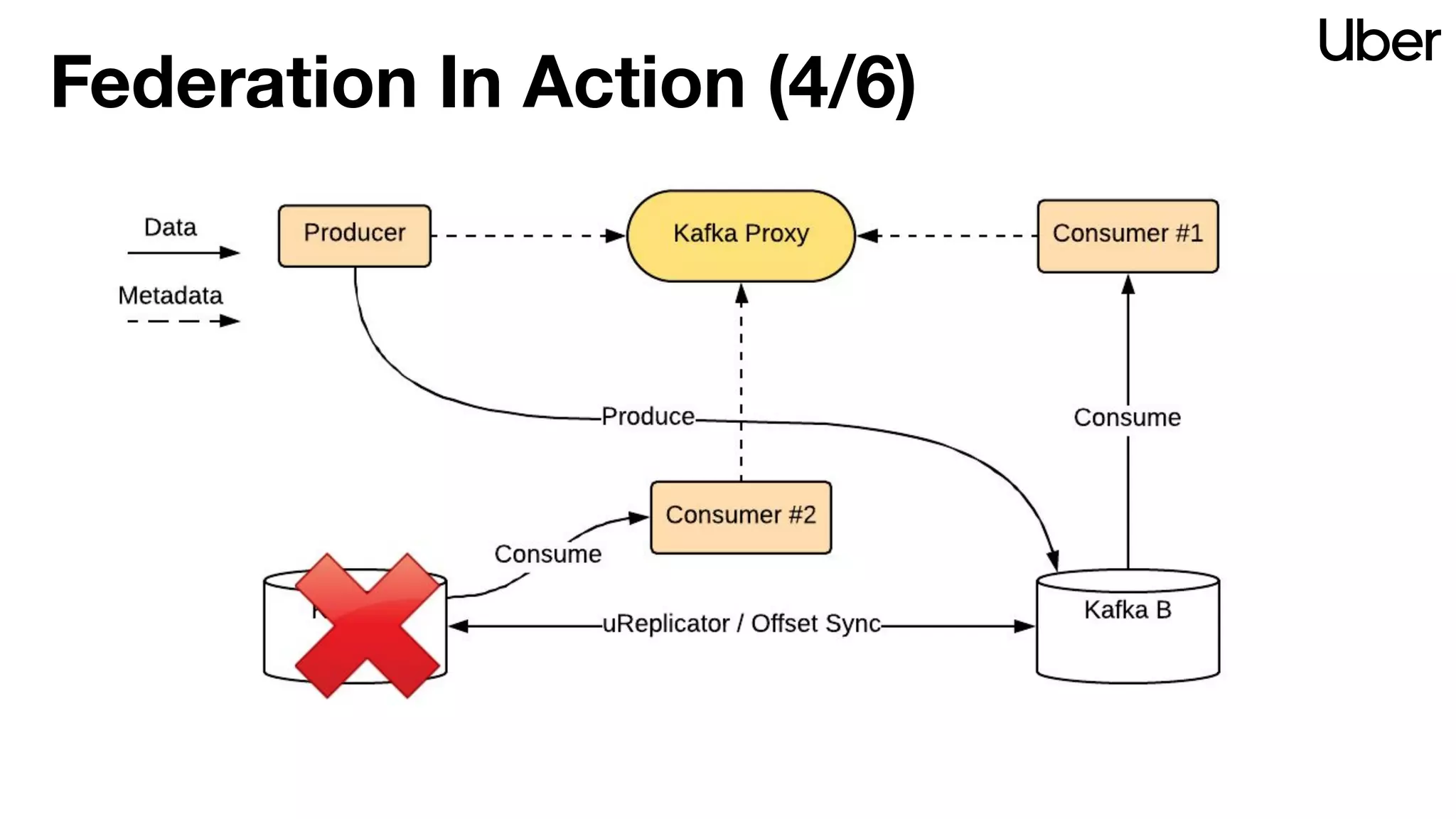
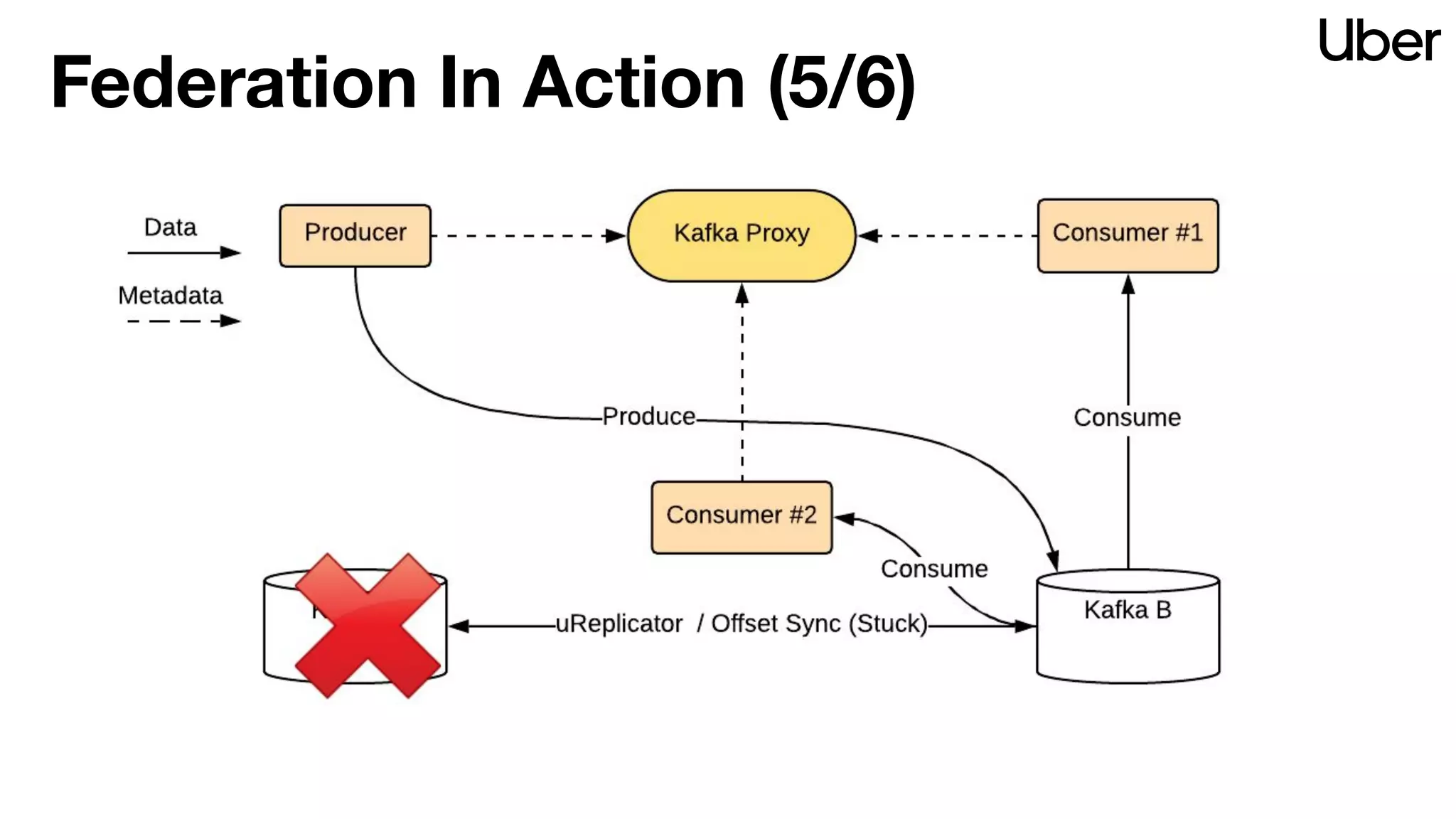
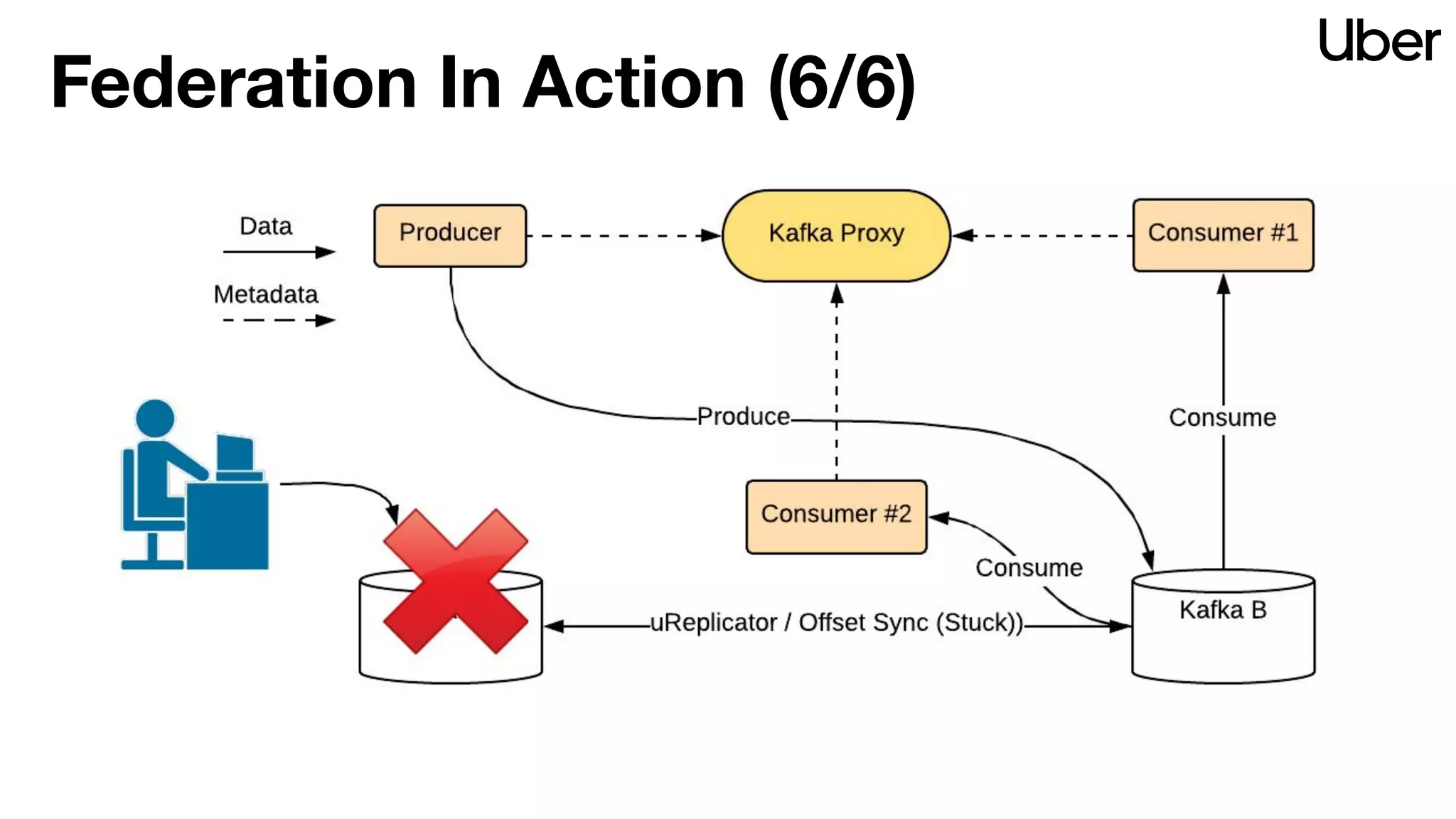
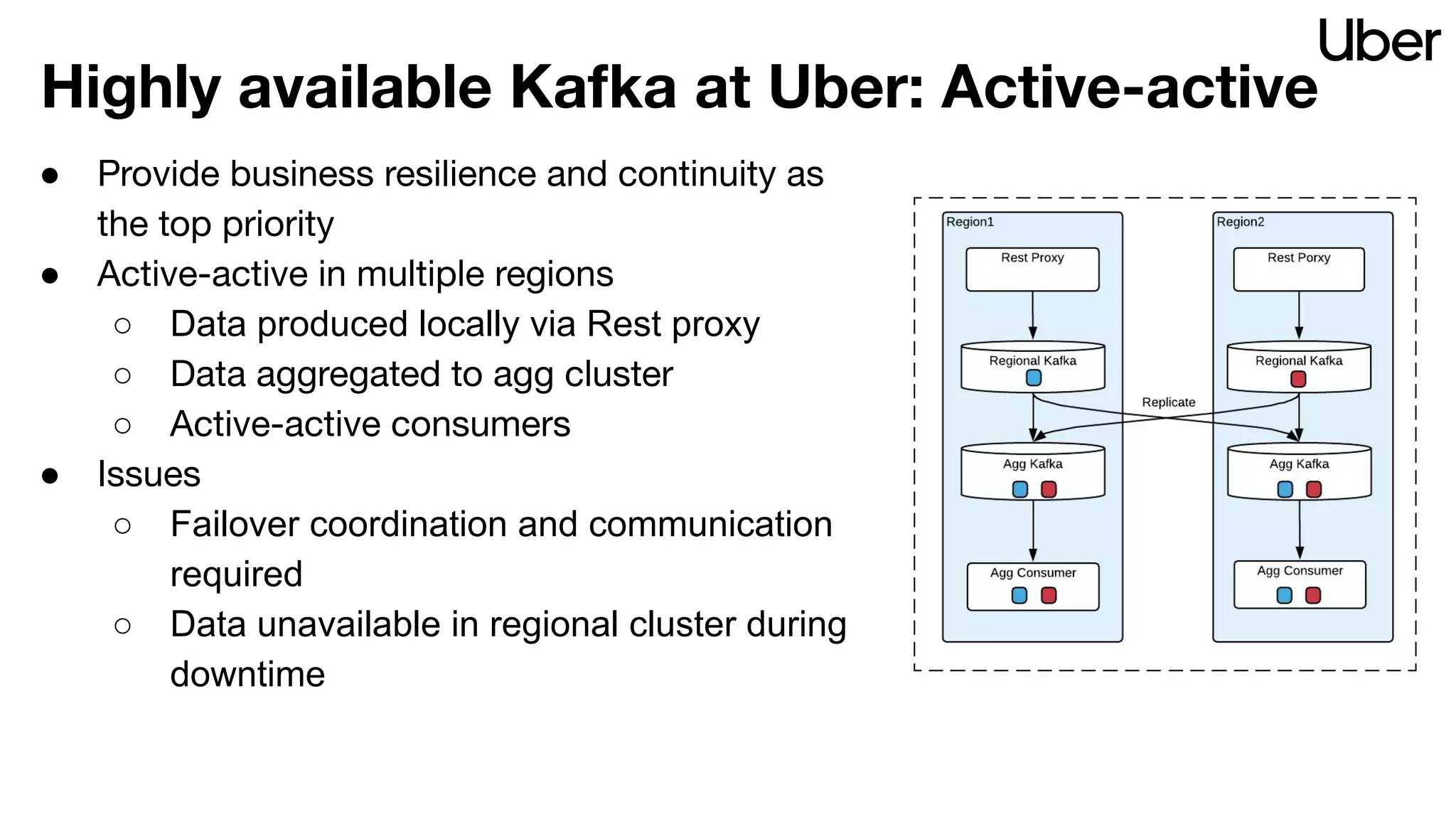
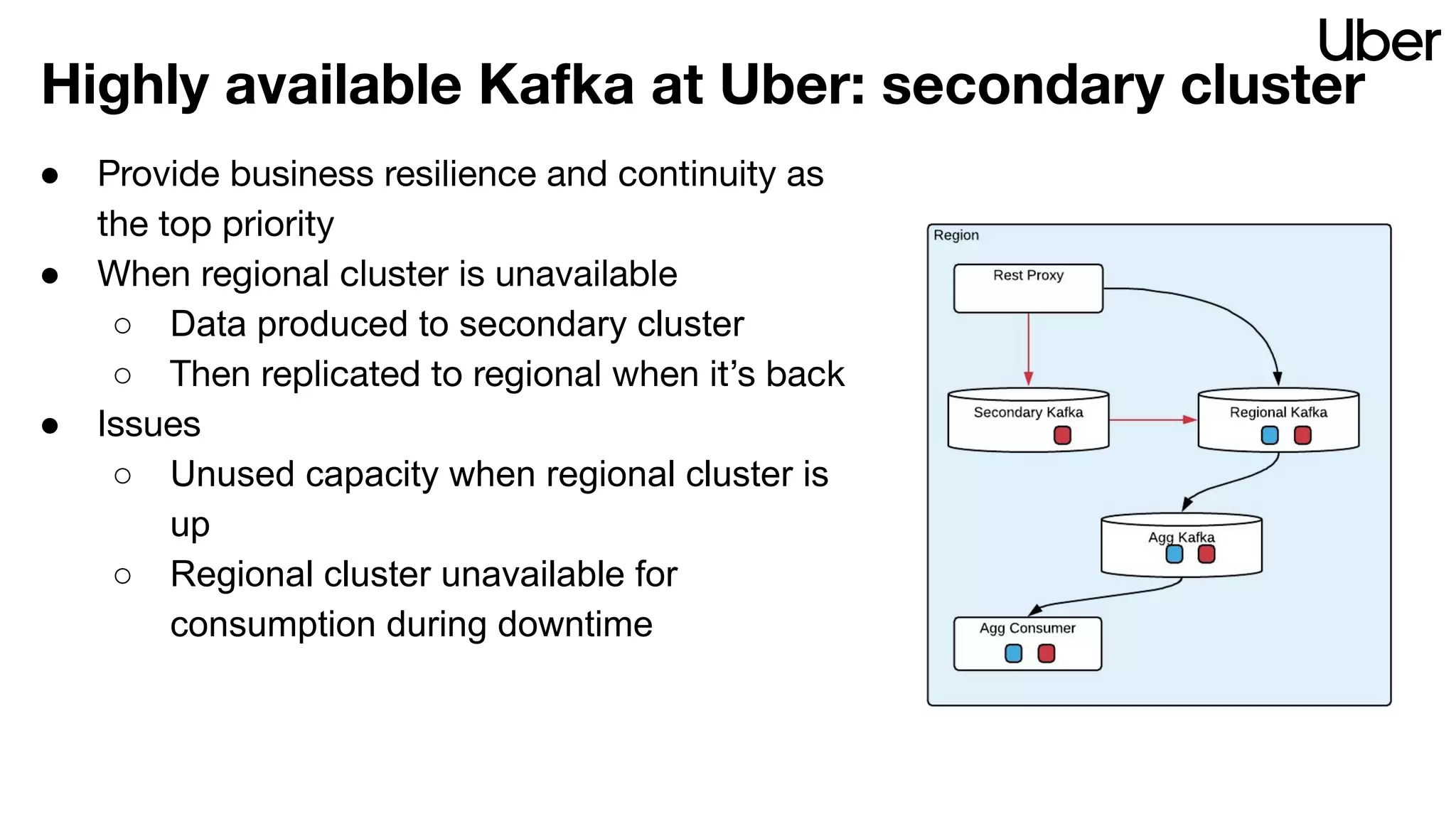
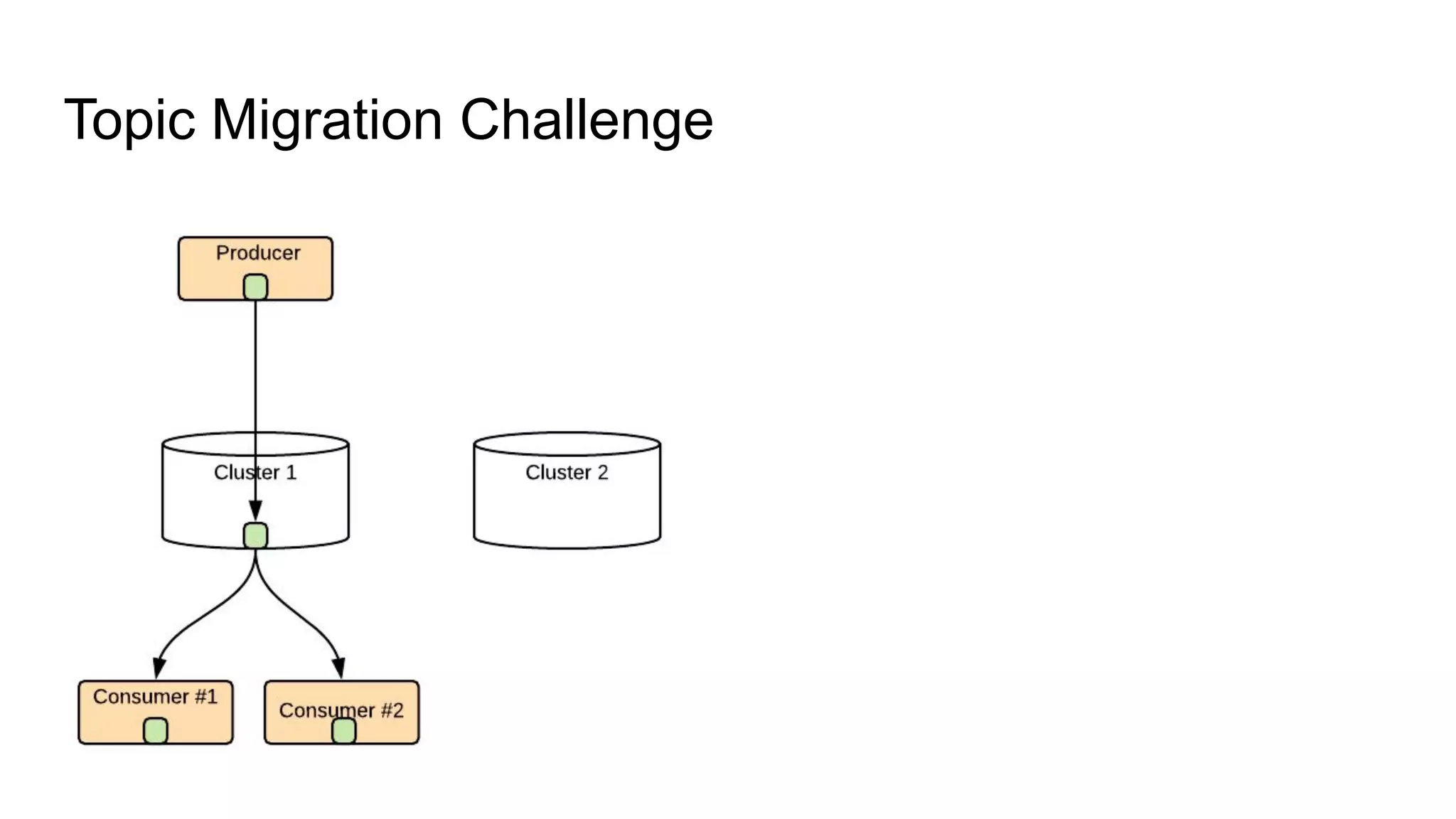
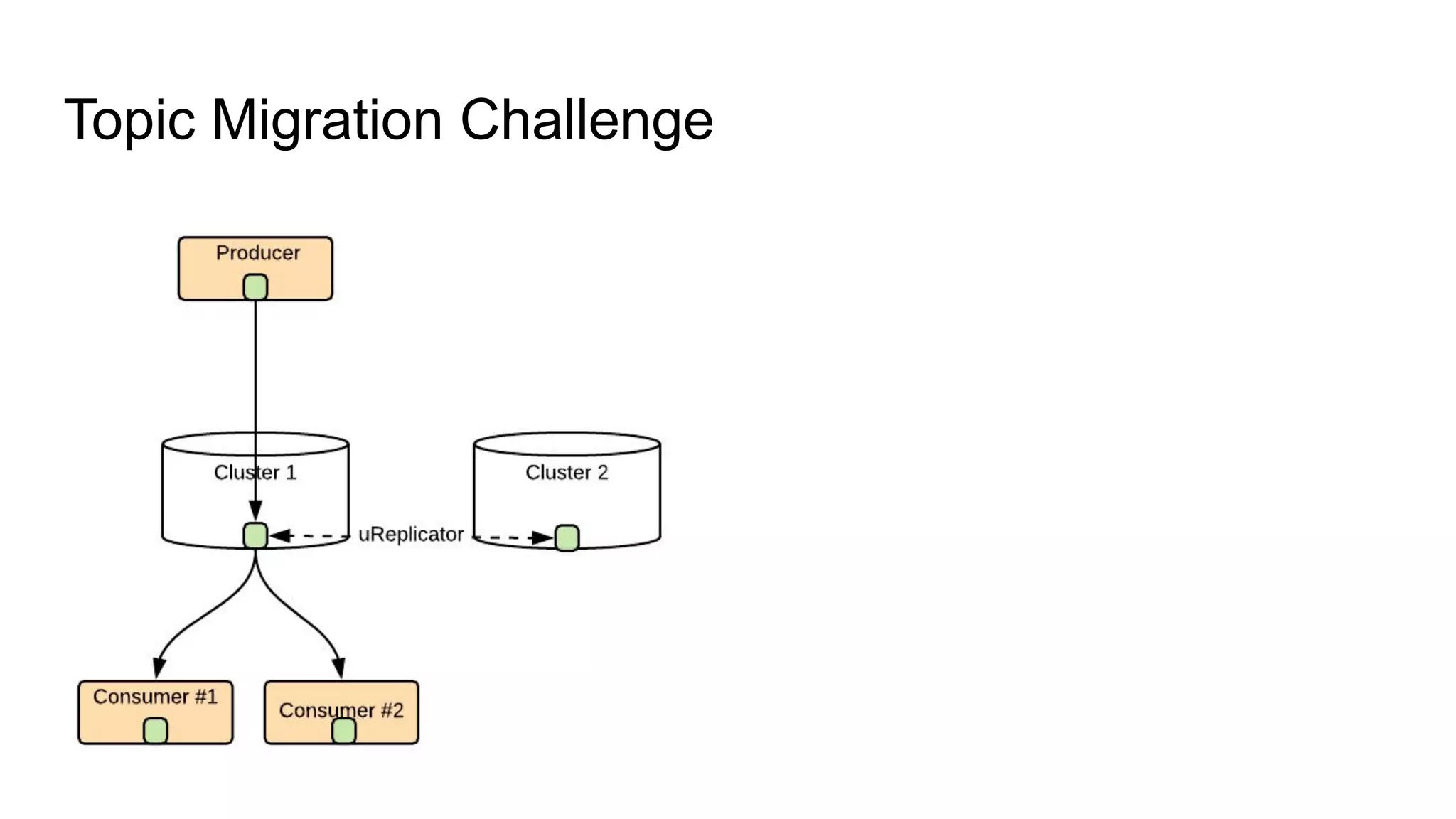
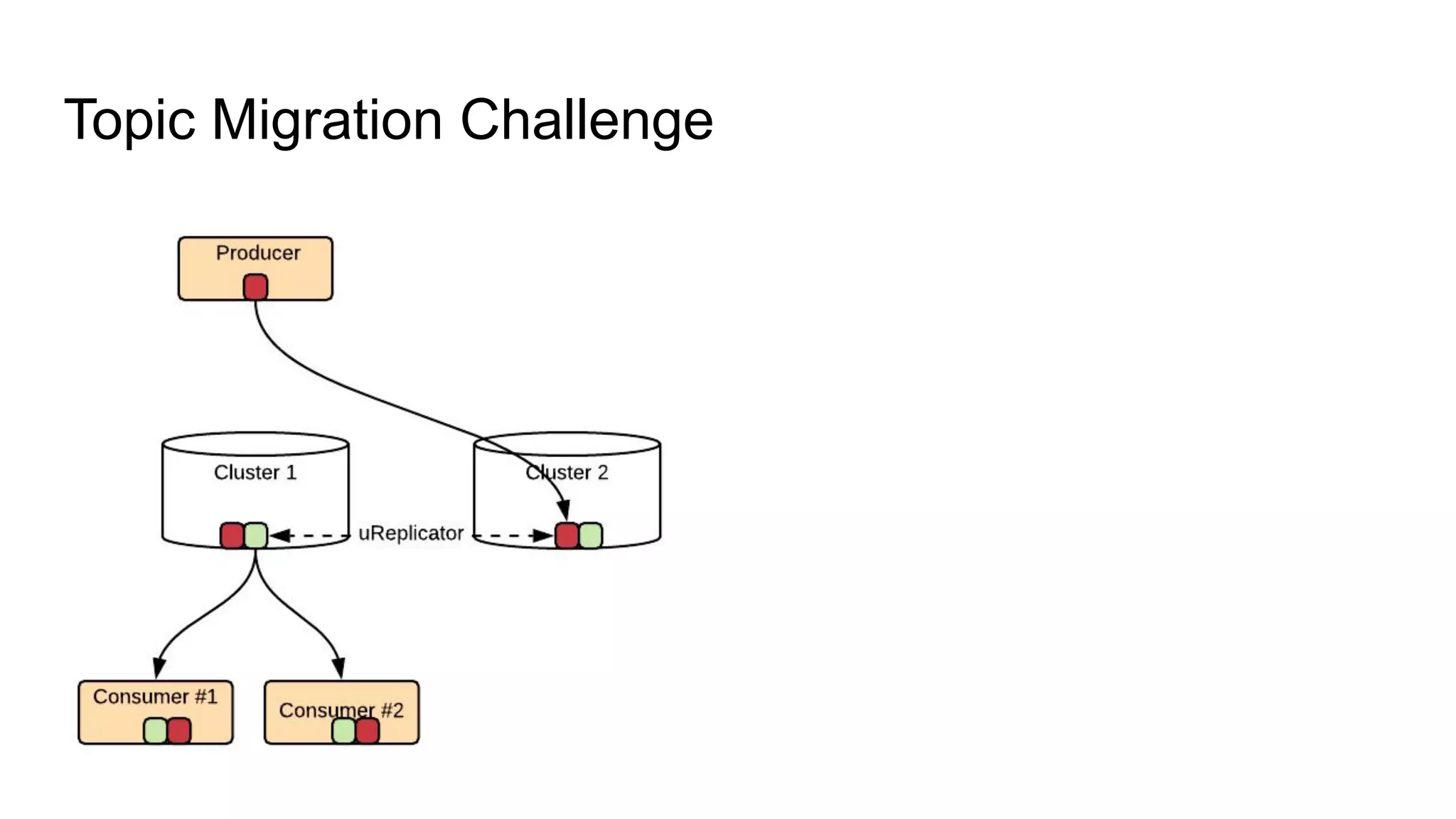
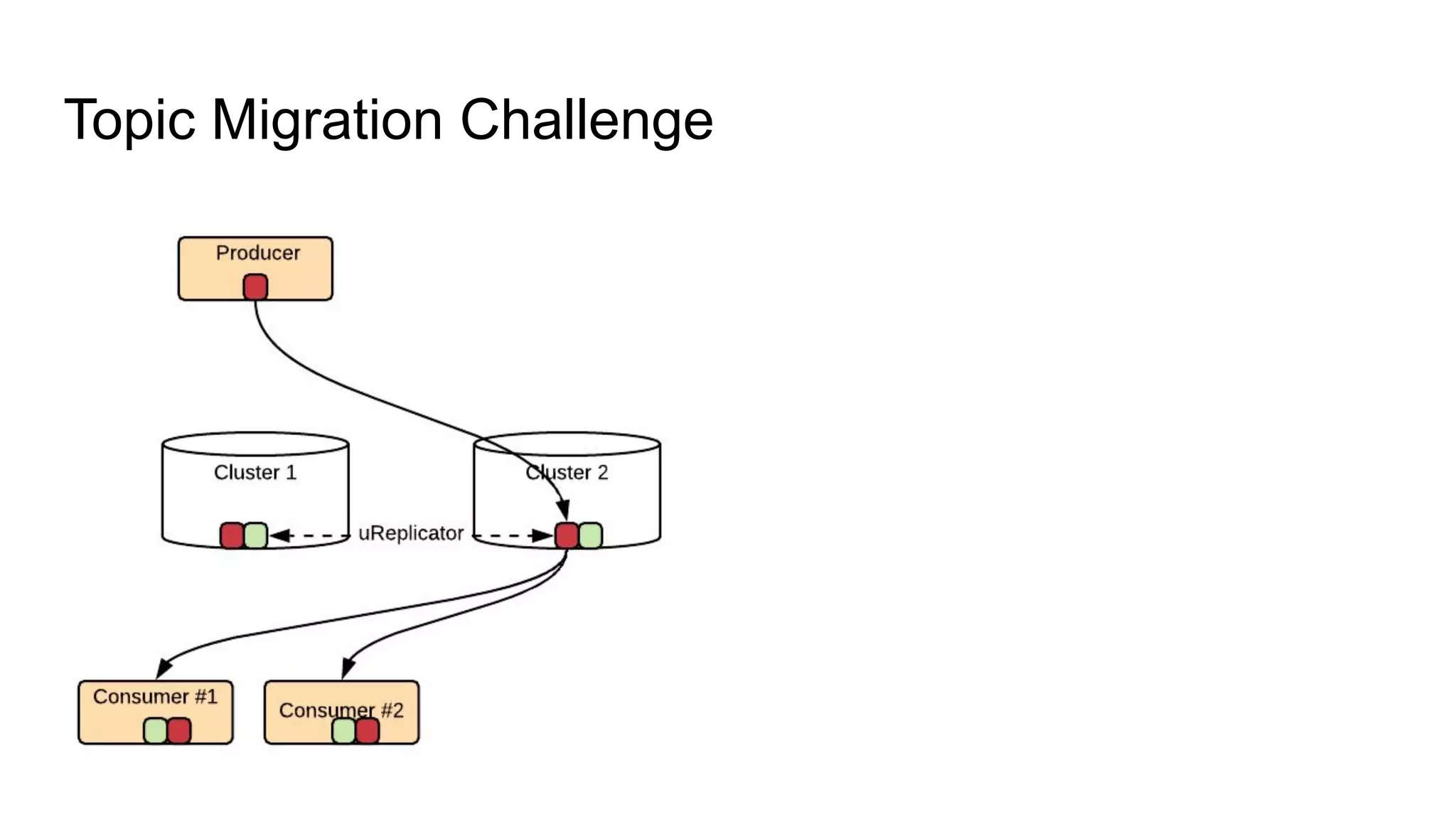
The document discusses Uber's implementation of Kafka cluster federation, focusing on enhancing availability, scalability, and ease of management for their streaming data services. It outlines the architecture, including the use of Kafka proxies, metadata services, and data replication to facilitate seamless traffic redirection and consumer offset management across multiple clusters. Challenges such as data redundancy, message order during failover, and regional cluster management are also highlighted within the context of maintaining business resilience.