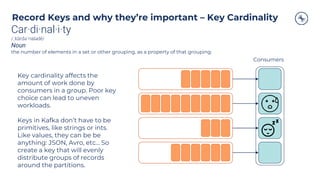
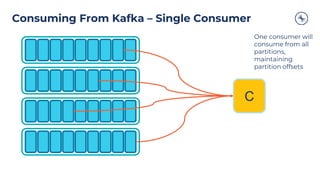
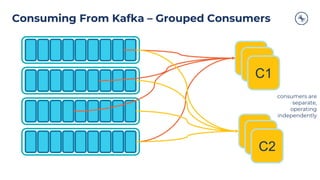
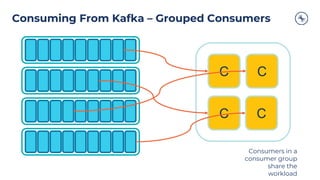
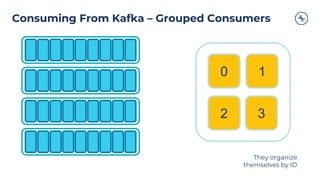
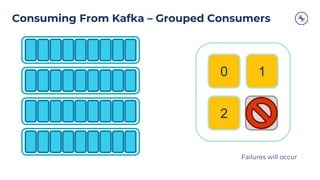
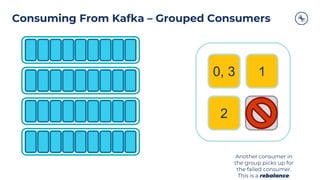
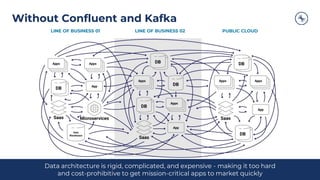
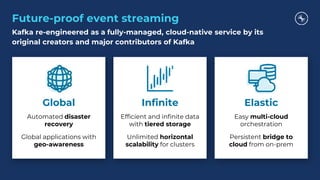
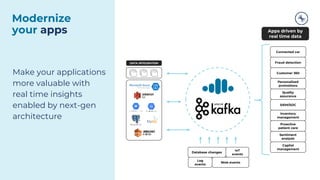
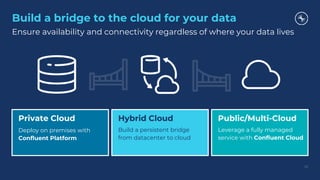
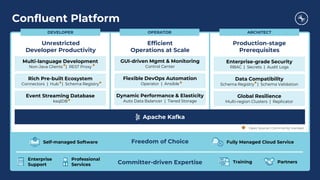
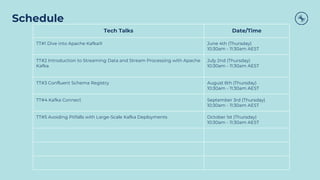
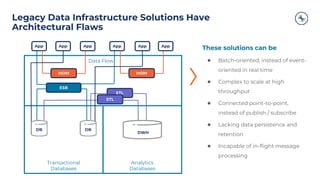
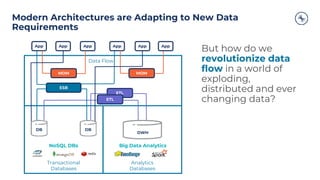
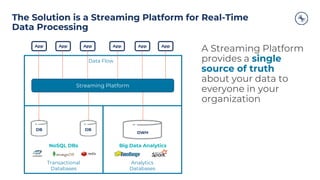
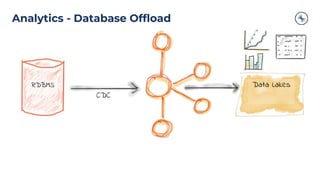
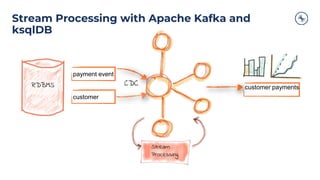
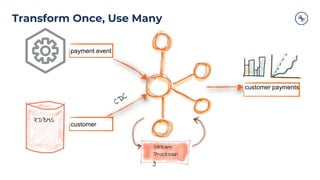
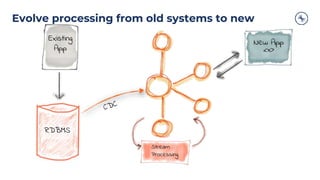
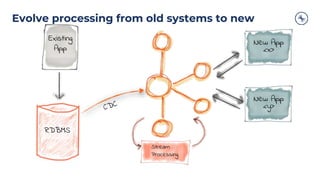
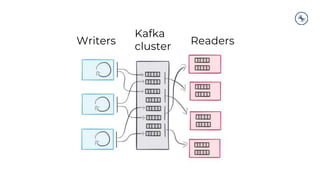
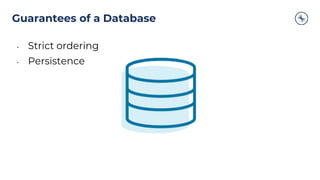
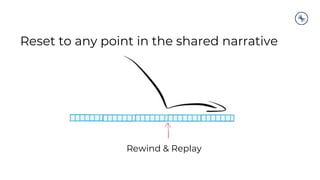
The document outlines a series of tech talks about Apache Kafka, detailing their schedule and topics such as streaming data, schema management, and large-scale deployments. It emphasizes the importance of Kafka as a real-time data processing platform capable of handling massive data flows with strong performance and architectural patterns. Additionally, it highlights Confluent's role as the creator and main contributor to Kafka, promoting its solutions for modern data architectures and cloud integration.









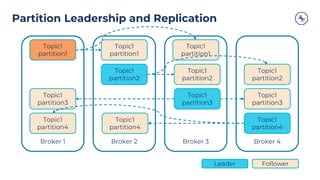
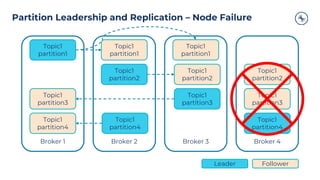

![Clients – Producer Design
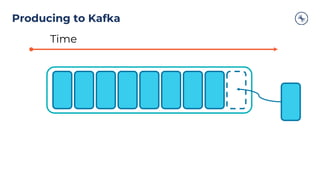
ProducerProducer Record
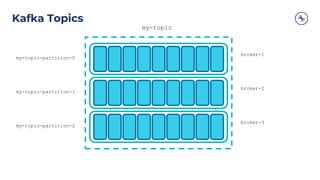
Topic
[Partition]
[Timestamp]
Value
Serializer Partitioner
Topic A
Partition 0
Batch 0
Batch 1
Batch 2
Topic B
Partition 1
Batch 0
Batch 1
Batch 2
Kafka
Broker
Send()
Retry
?
Fail
?
Yes
No
Can’t retry,
throw exception
Success: return
metadata
Yes
[Headers]
[Key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-29-320.jpg)

![Record Keys and why they’re important - Ordering
Producer Record
Topic
[Partition]
[Key]
Value
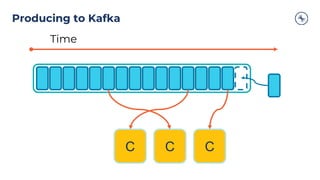
Record keys determine the partition with the
default kafka partitioner
If a key isn’t provided, messages will be
produced in a round robin fashion
partitioner](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-32-320.jpg)
![Record Keys and why they’re important - Ordering
Producer Record
Topic
[Partition]
AAAA
Value
Record keys determine the partition with the default kafka
partitioner, and therefore guarantee order for a key
Keys are used in the default partitioning algorithm:
partition = hash(key) % numPartitions
partitioner](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-33-320.jpg)
![Record Keys and why they’re important - Ordering
Producer Record
Topic
[Partition]
BBBB
Value
Keys are used in the default partitioning algorithm:
partition = hash(key) % numPartitions
partitioner
Record keys determine the partition with the default kafka
partitioner, and therefore guarantee order for a key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-34-320.jpg)
![Record Keys and why they’re important - Ordering
Producer Record
Topic
[Partition]
CCCC
Value
Keys are used in the default partitioning algorithm:
partition = hash(key) % numPartitions
partitioner
Record keys determine the partition with the default kafka
partitioner, and therefore guarantee order for a key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-35-320.jpg)
![Record Keys and why they’re important - Ordering
Producer Record
Topic
[Partition]
DDDD
Value
Keys are used in the default partitioning algorithm:
partition = hash(key) % numPartitions
partitioner
Record keys determine the partition with the default kafka
partitioner, and therefore guarantee order for a key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westpacbanktechtalk1diveintoapachekafka-200716011434/85/Westpac-Bank-Tech-Talk-1-Dive-into-Apache-Kafka-36-320.jpg)