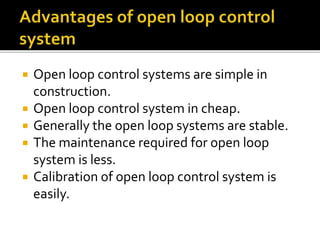
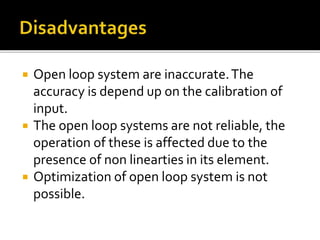
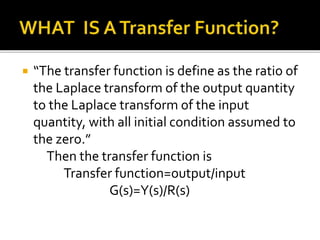
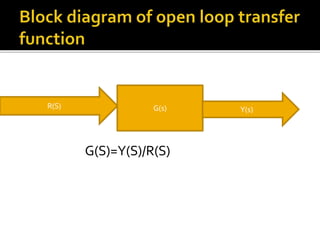
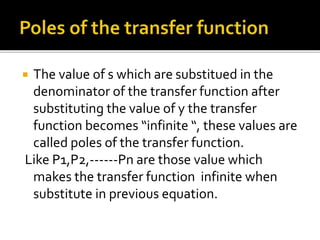
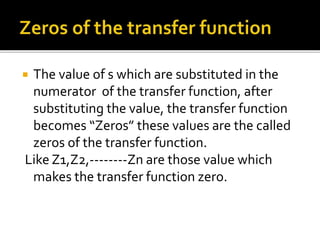
This document discusses open loop control systems and their transfer functions. It defines open loop systems as those without feedback, and describes their basic elements and properties. The document then defines the transfer function as the ratio of the Laplace transforms of the output and input quantities. It explains that the transfer function provides information about the system's gain and converts differential equations to algebraic equations. The transfer function depends on system parameters but not inputs. Zeros and poles are also defined as the roots of the numerator and denominator polynomials. System stability depends on the location of poles in the complex plane. Examples of transfer function calculations and analyses are provided.







![ P1=[8 56 96];
Q1=[1 4 9 10];
Sys=tf(P1,Q1)
Roots(P1);
Roots(Q1);
pzMAP(sys);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k10945controlassignmentgajendrameena-160510151005/85/K10945-control-assignment-gajendra-meena-15-320.jpg)
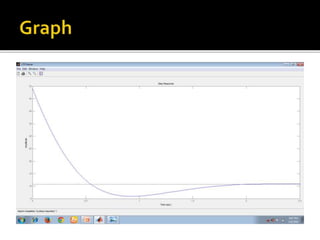
![ Num=[49];
Den=[ 1 4 9 ];
Sys=tf(num,den);
load ltiexamples
ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k10945controlassignmentgajendrameena-160510151005/85/K10945-control-assignment-gajendra-meena-17-320.jpg)
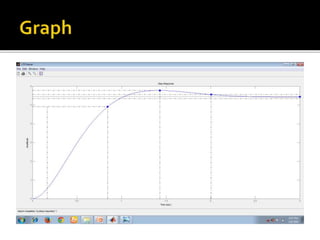
![ Num=[49 89 96];
Den=[1 4 9];
Sys=tf[Num,Den];
Load ltiexamples
ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k10945controlassignmentgajendrameena-160510151005/85/K10945-control-assignment-gajendra-meena-19-320.jpg)