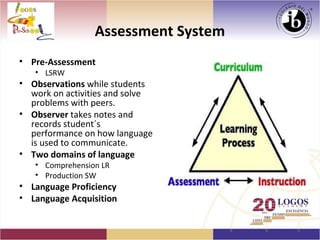
The document analyzes a pre-school English language program through assessments, observations, and adjustments based on student needs. It discusses domains of language comprehension and production, as well as language proficiency and acquisition versus learning. Standards from TESOL are presented along with strategies for language instruction and acquisition based on cognitive science and how students learn.