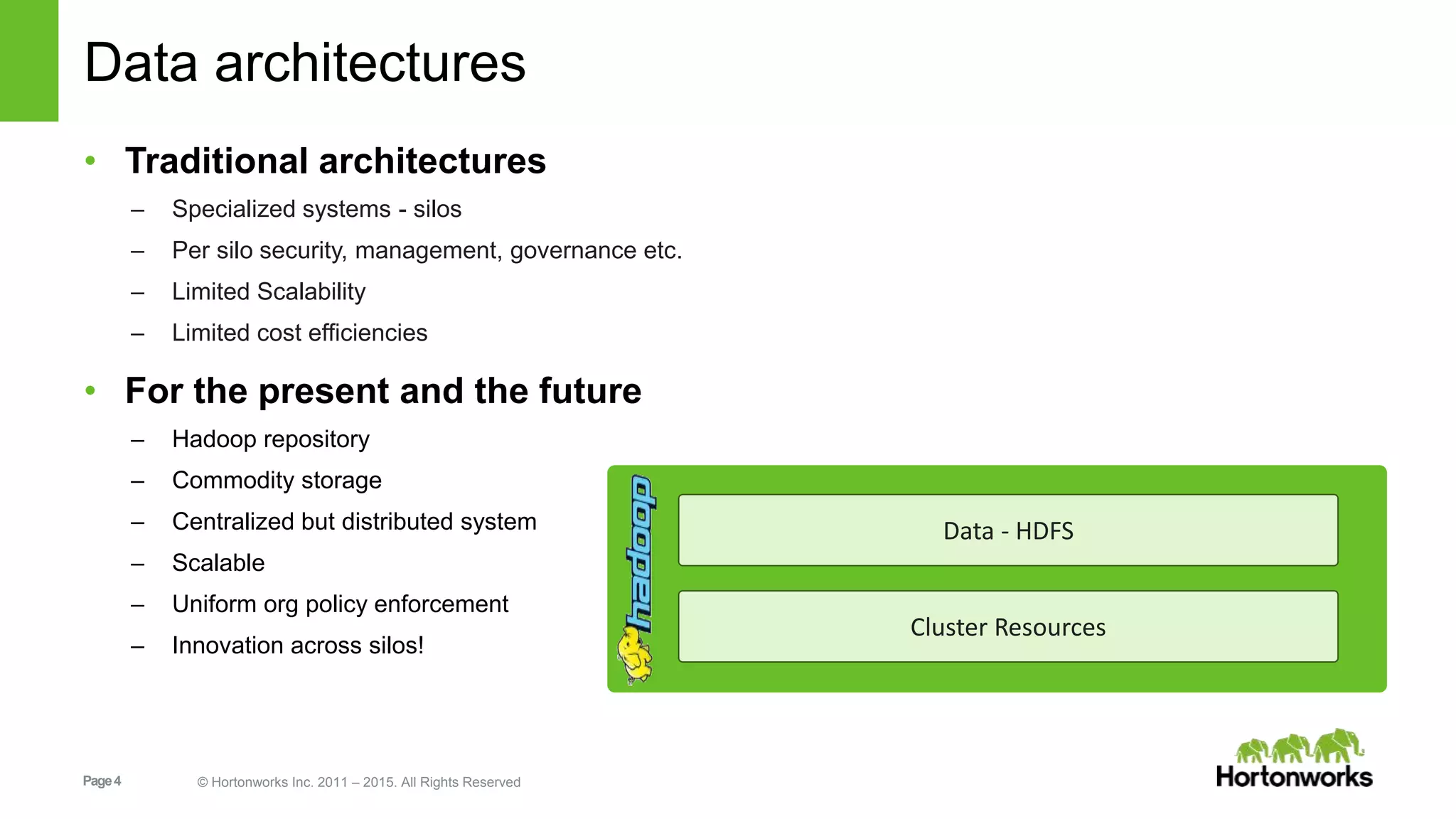
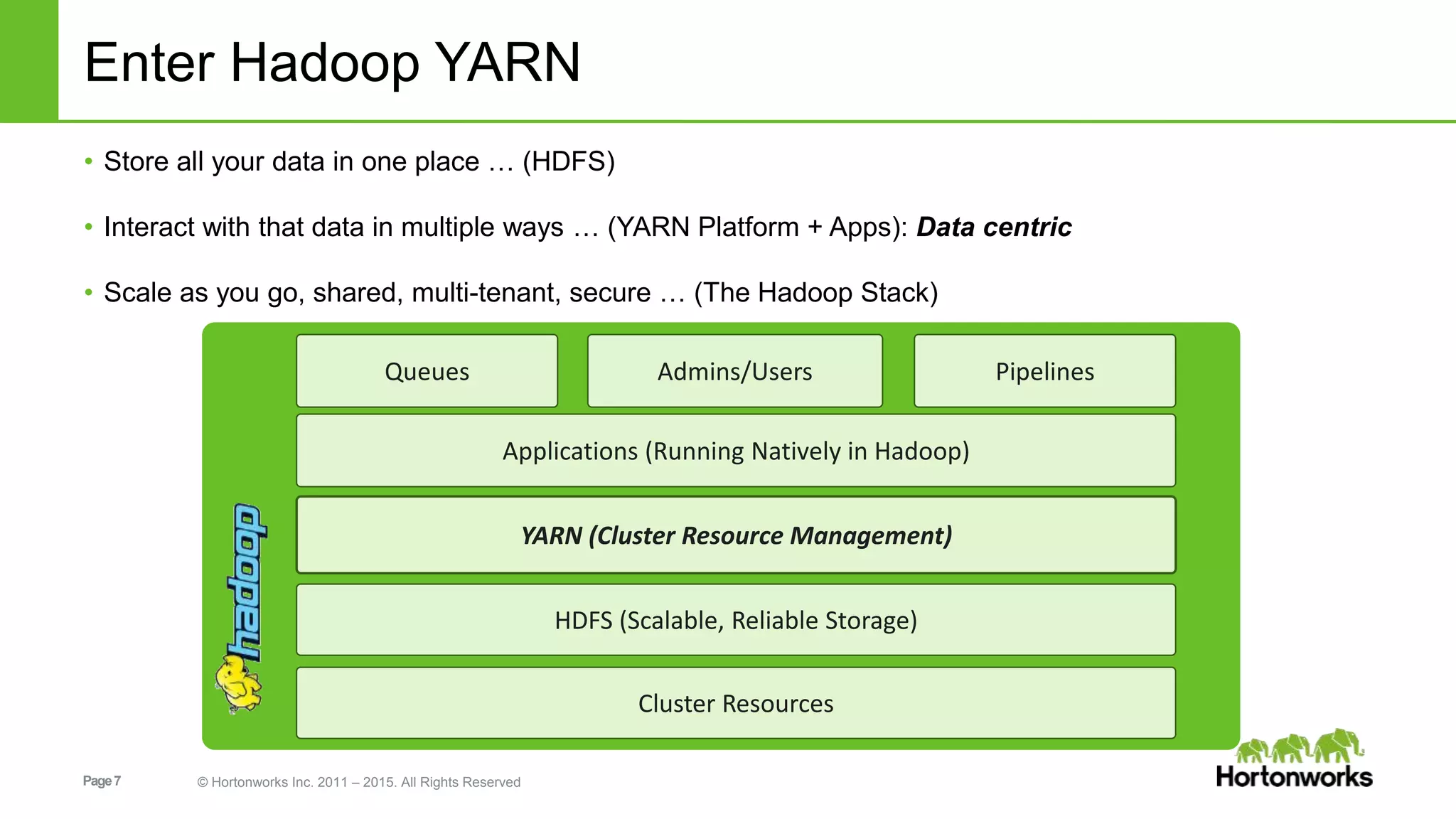
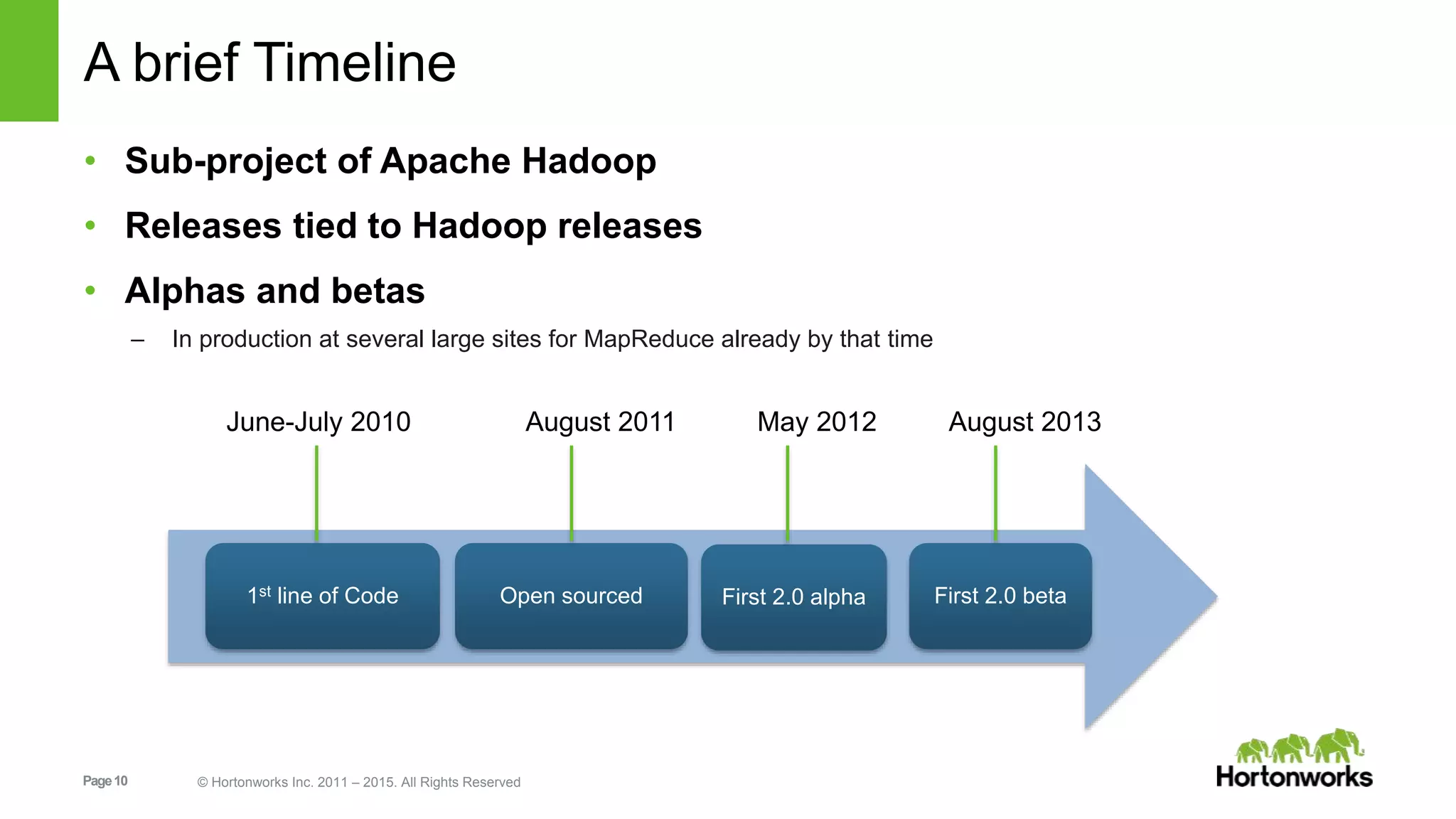
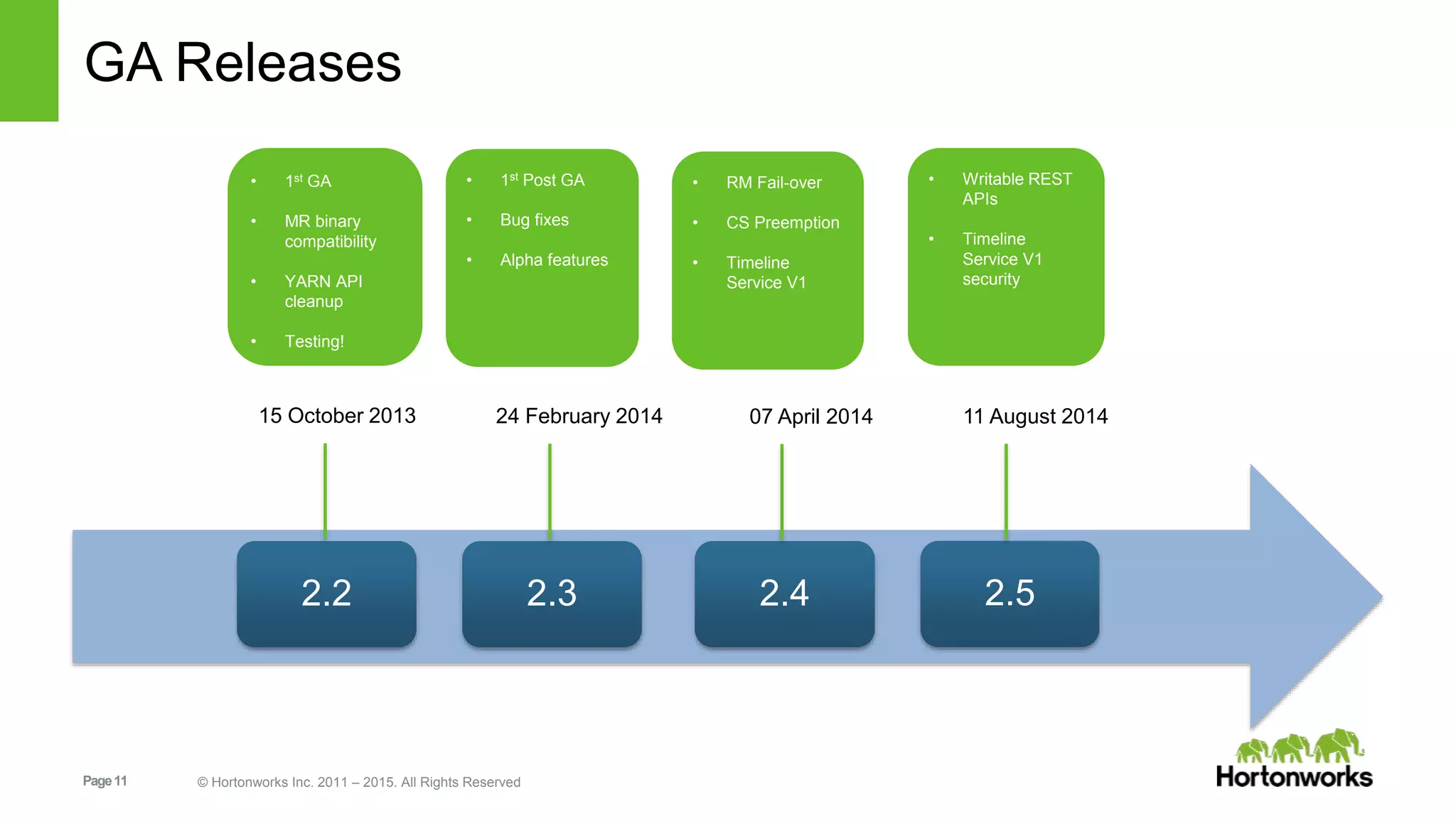
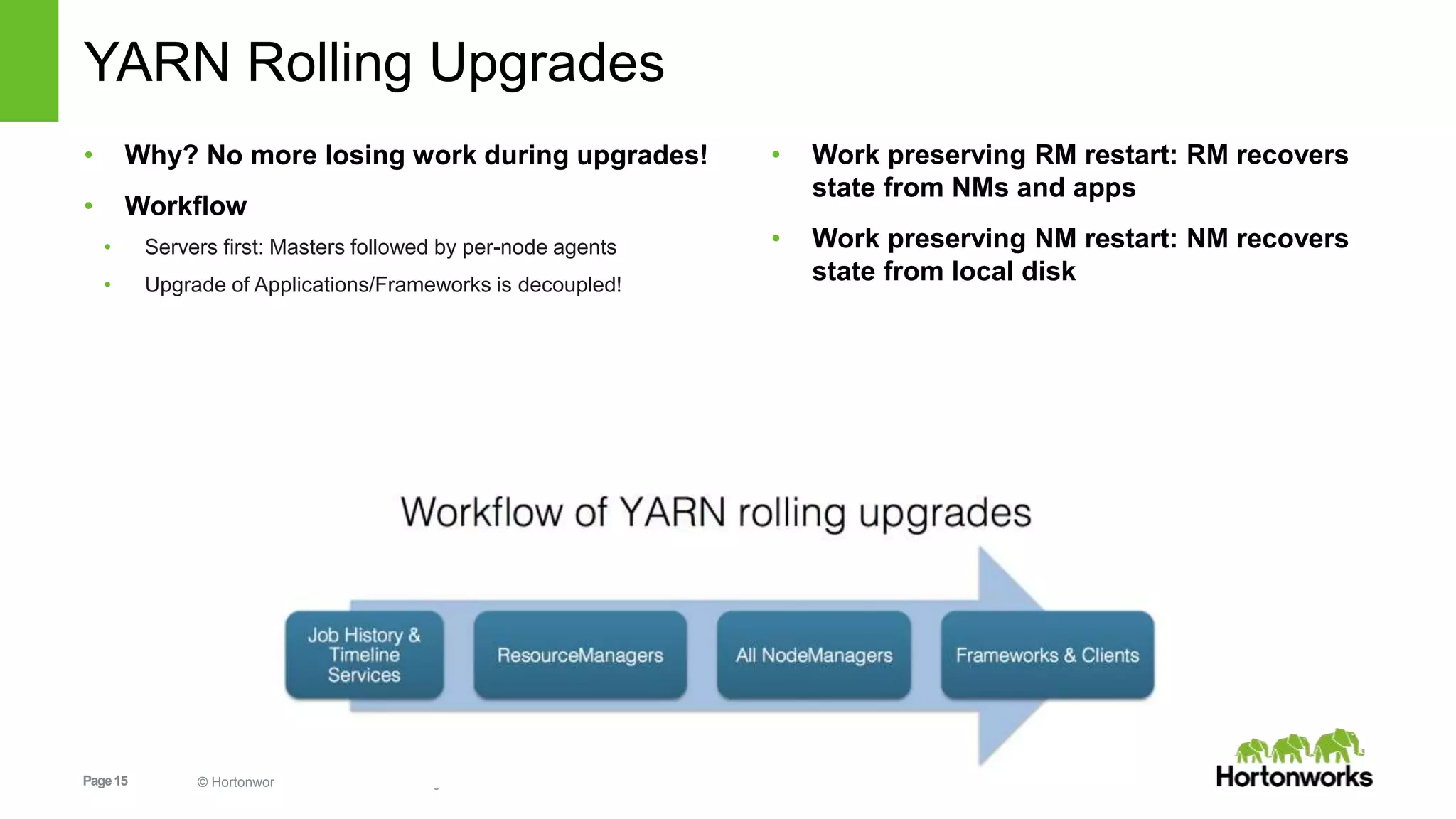
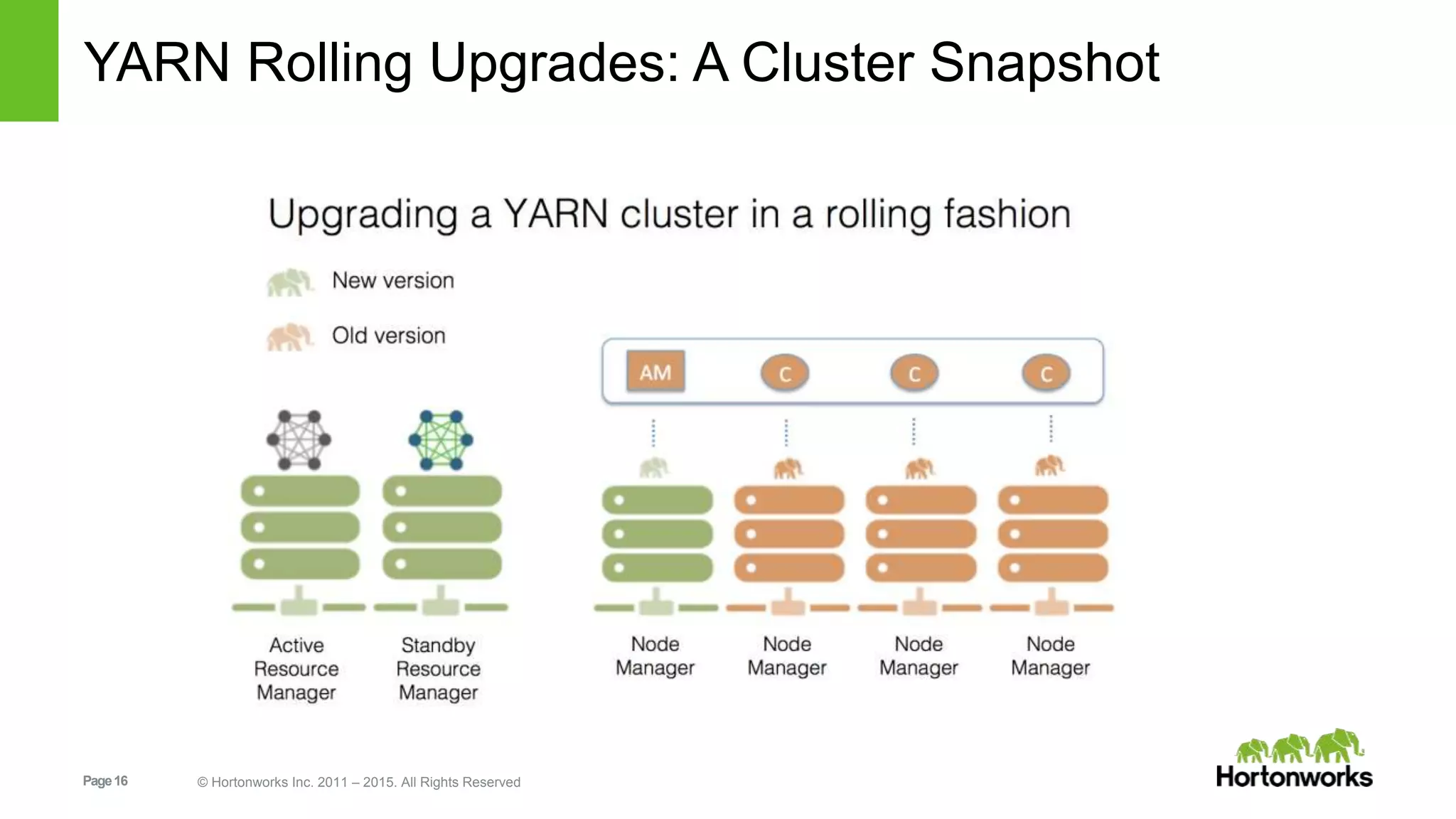
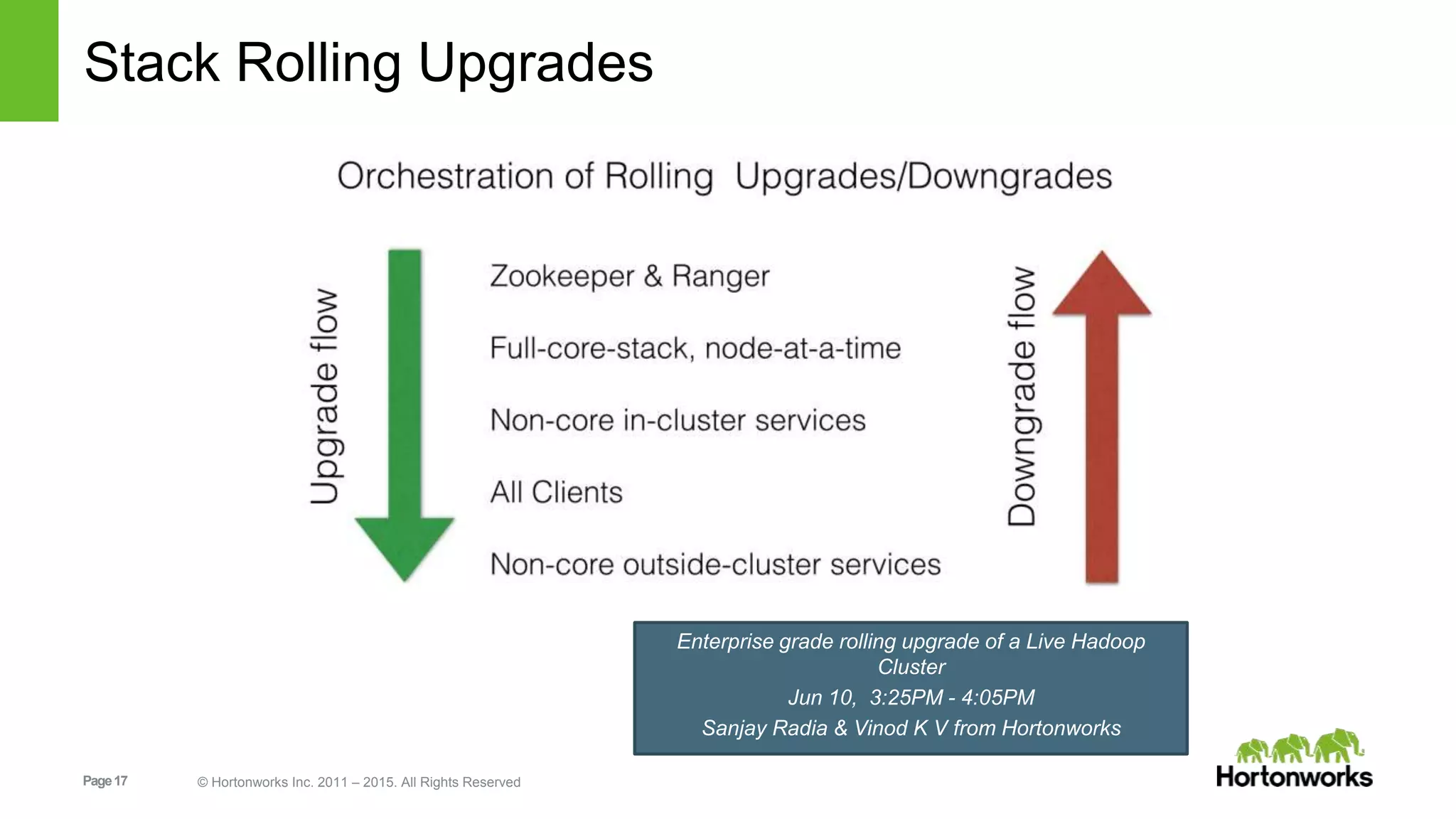
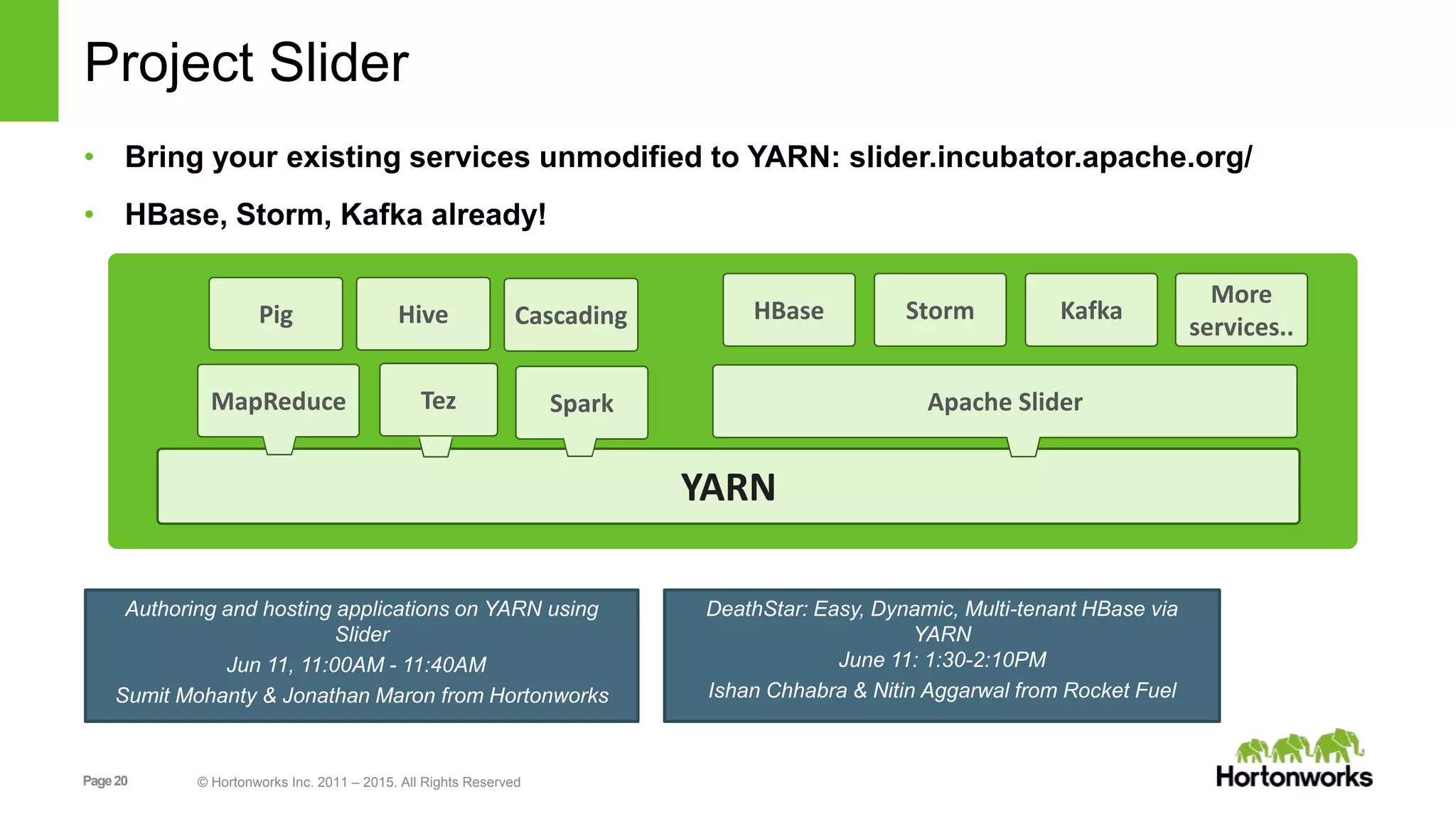
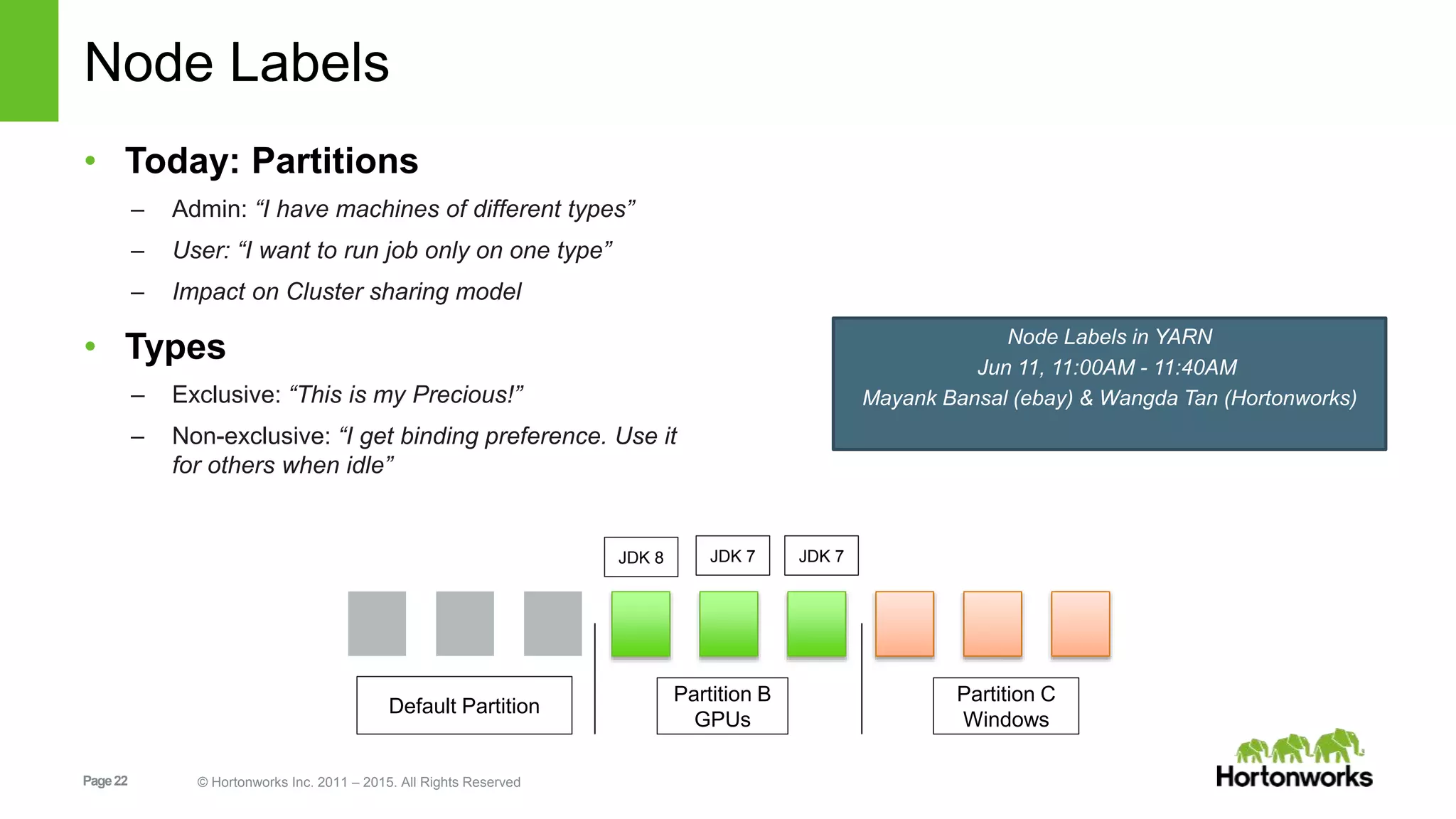
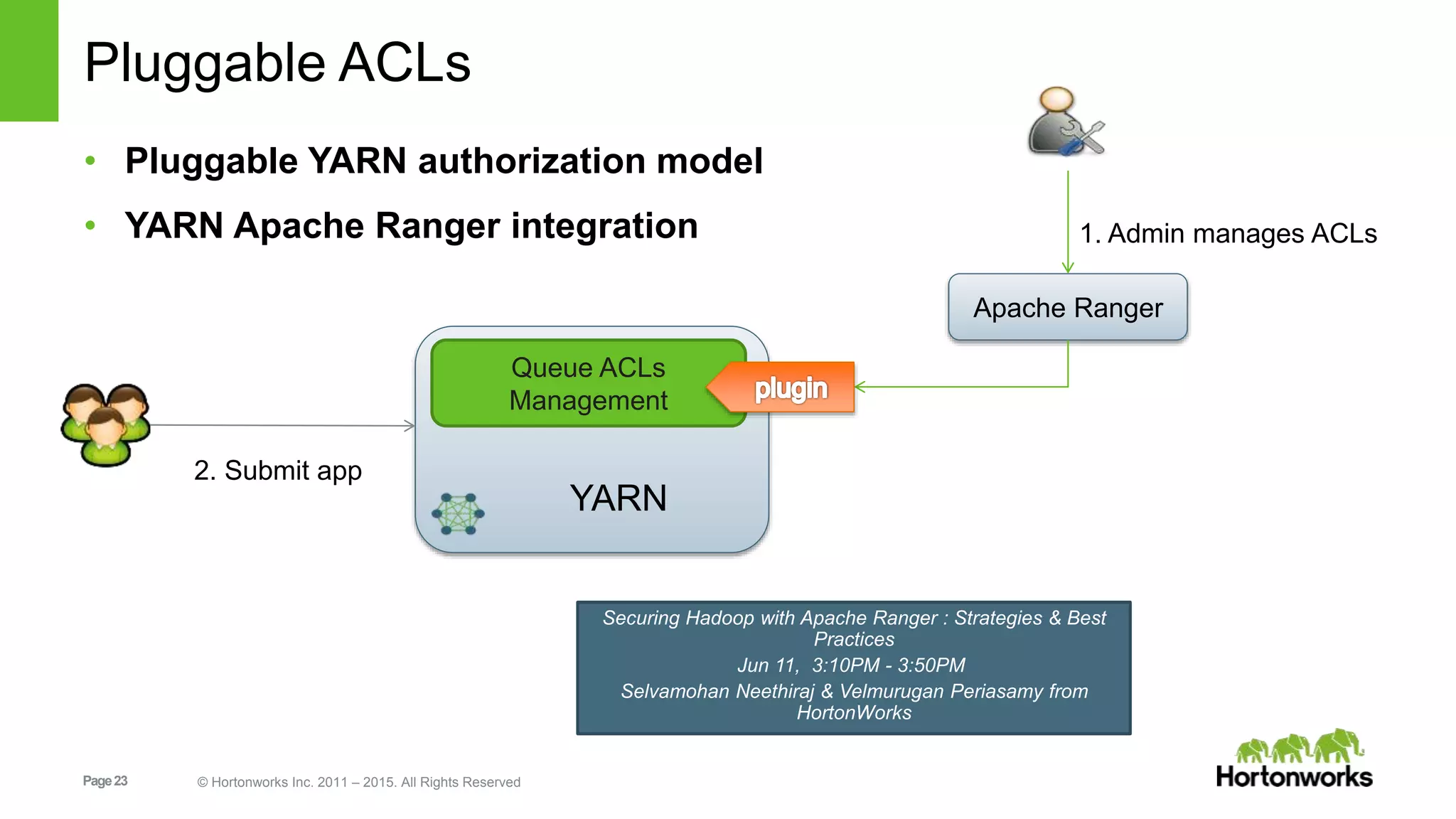
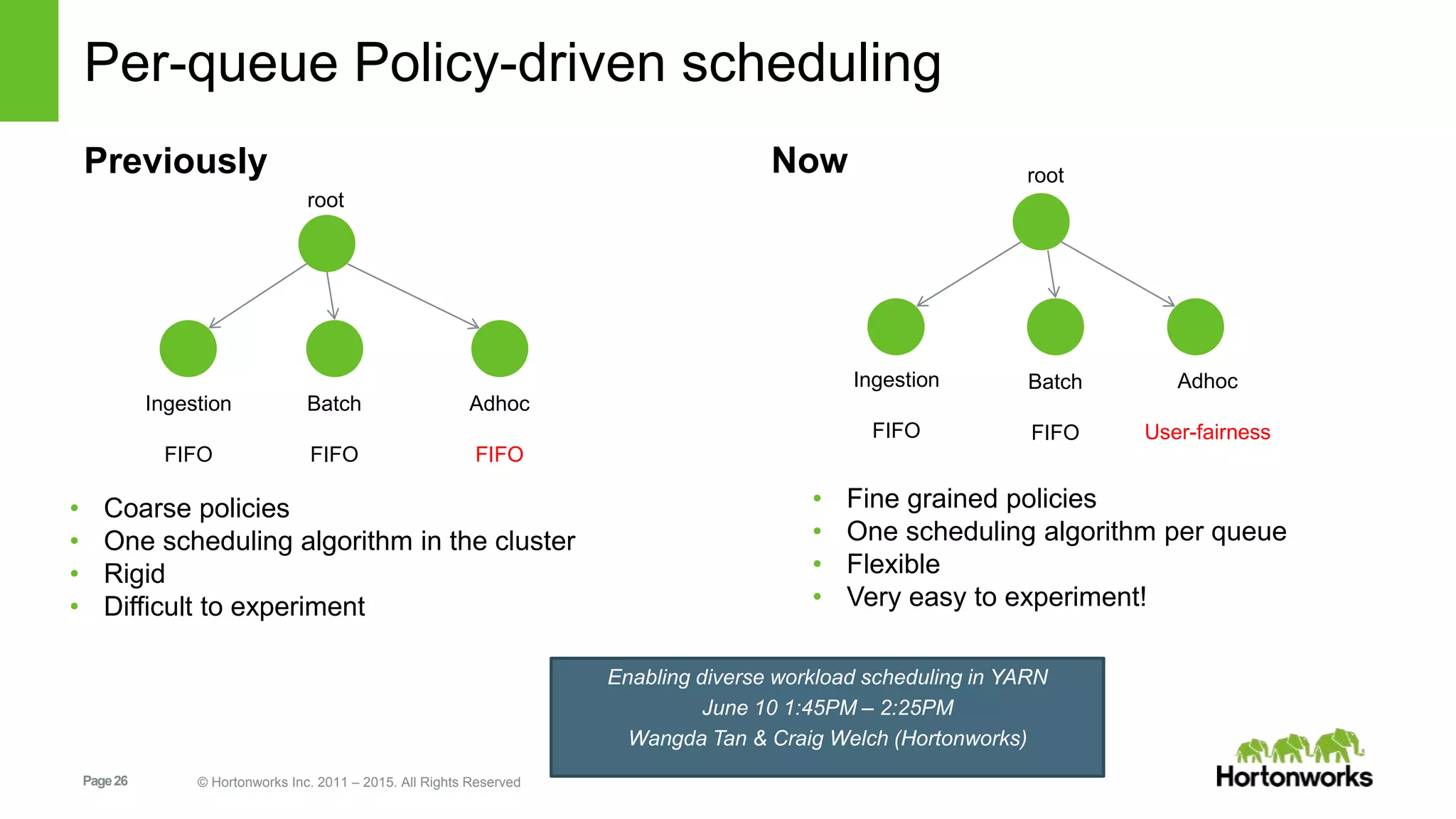
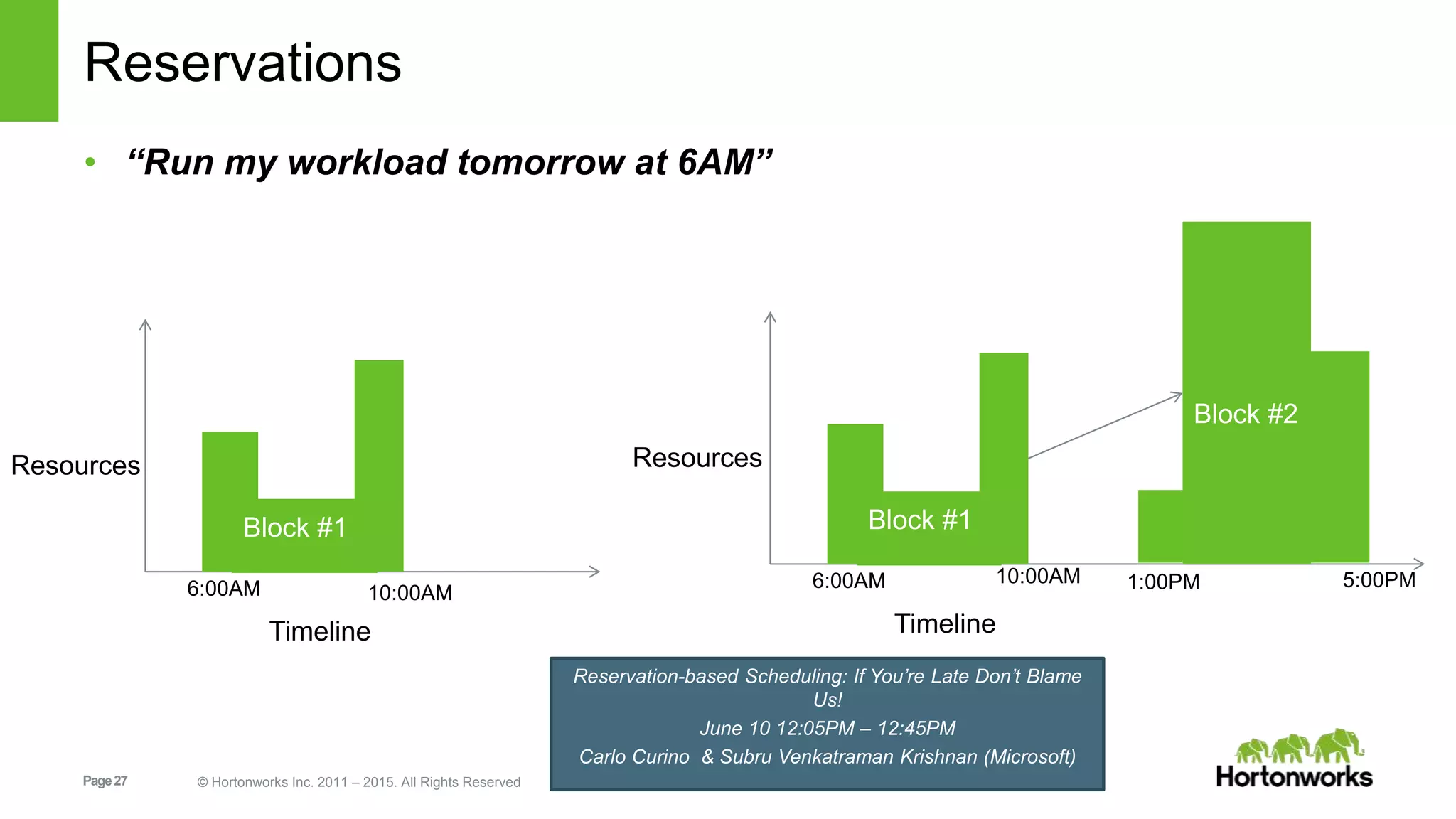
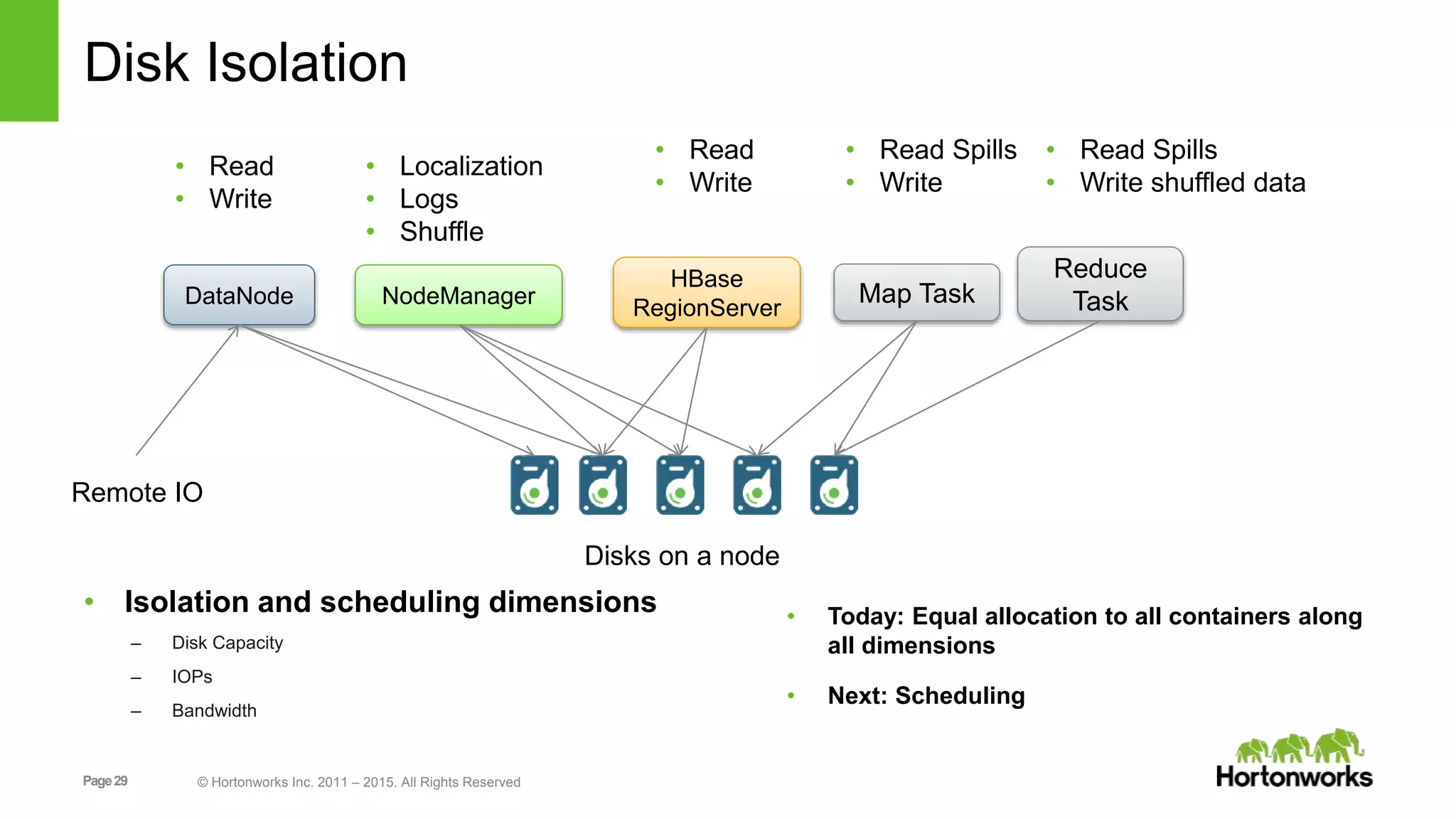
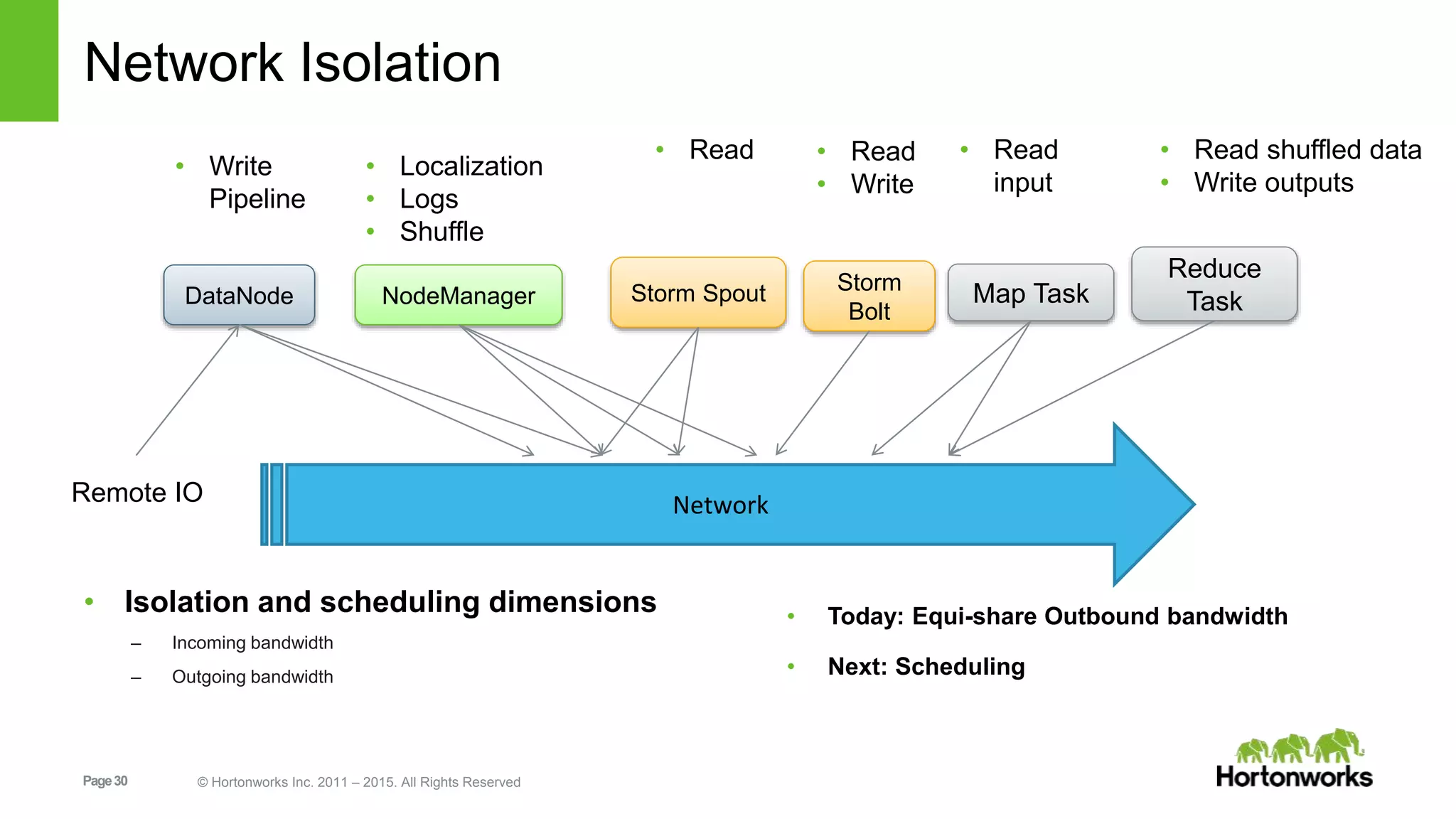
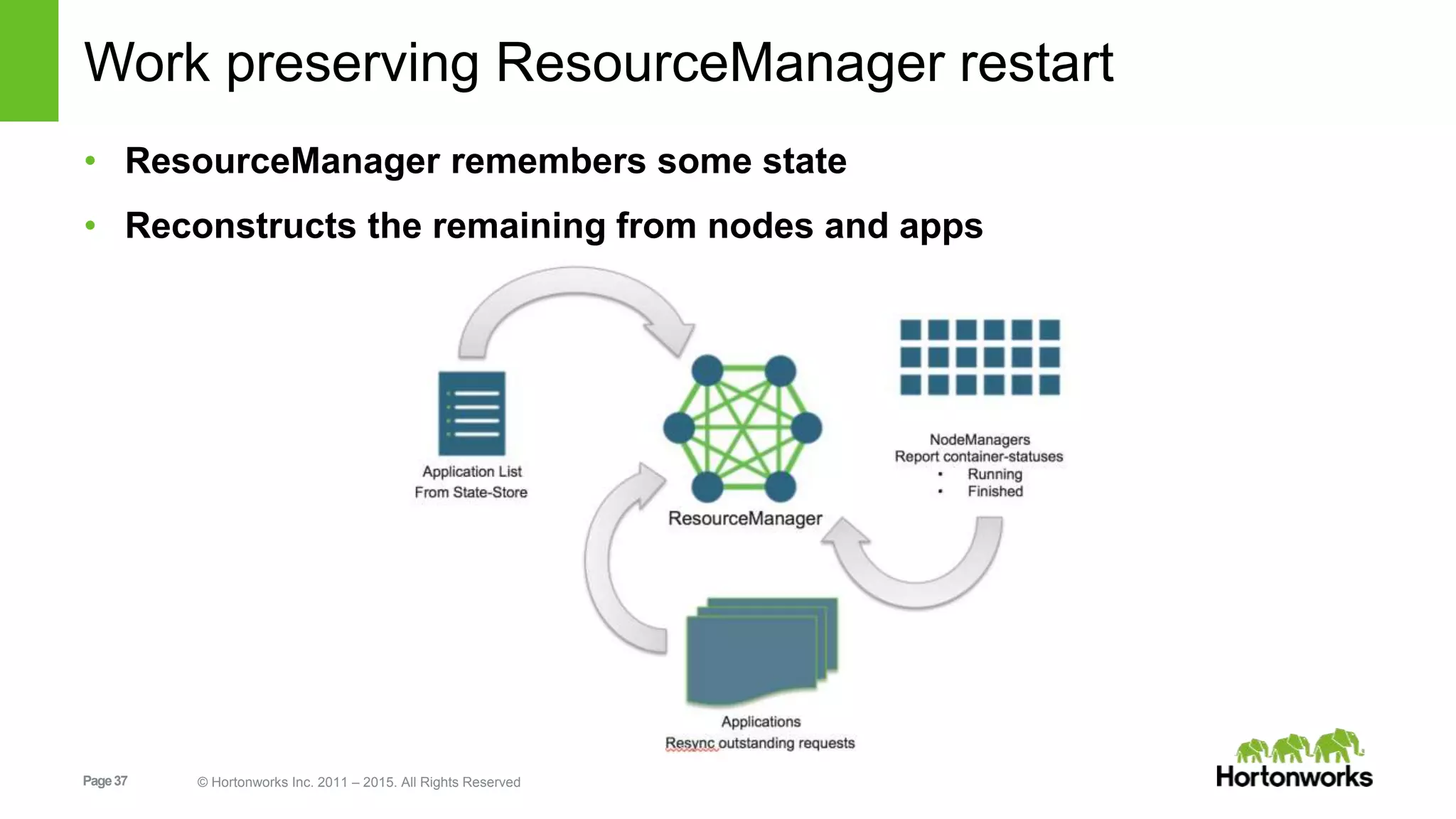
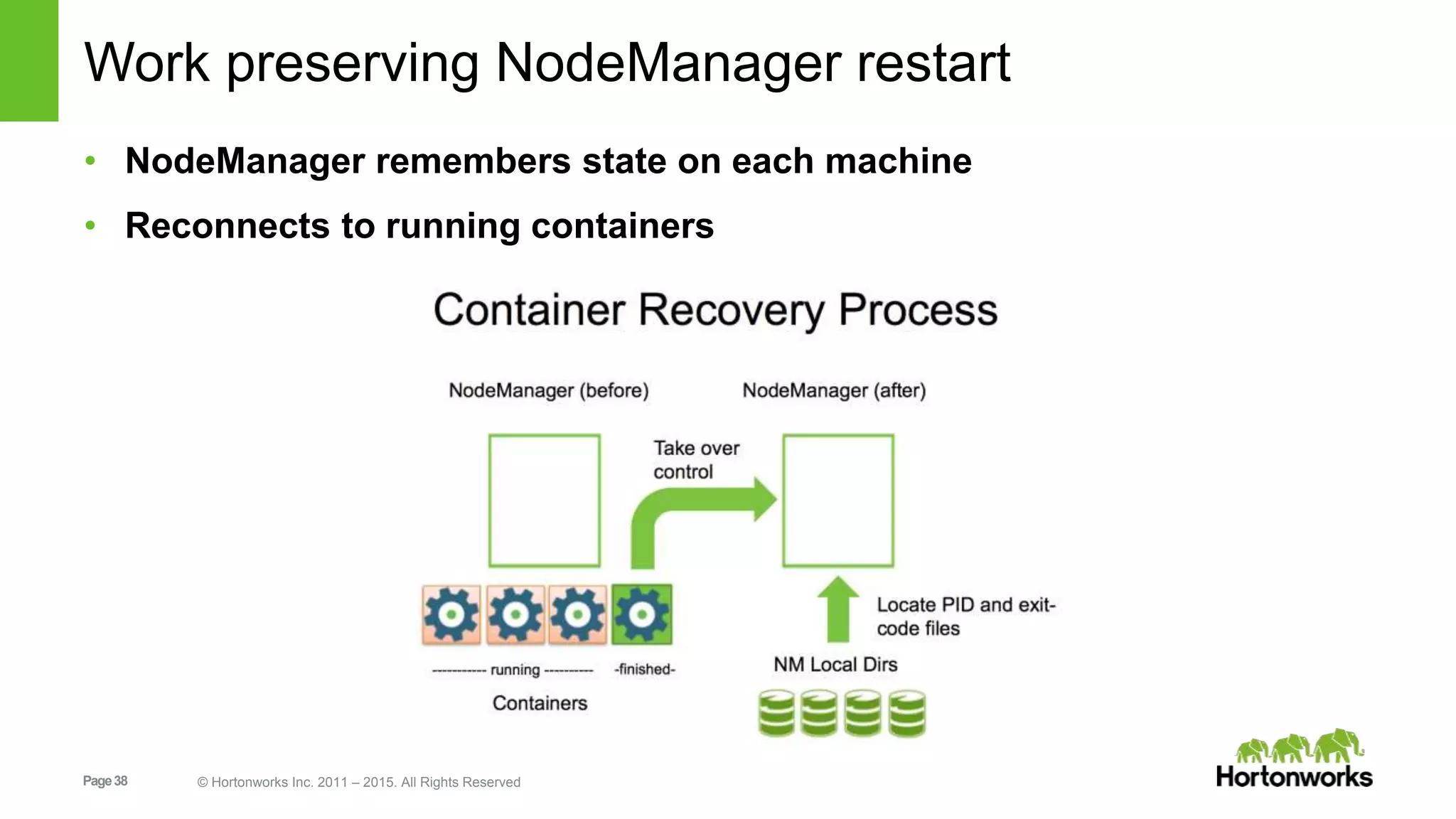
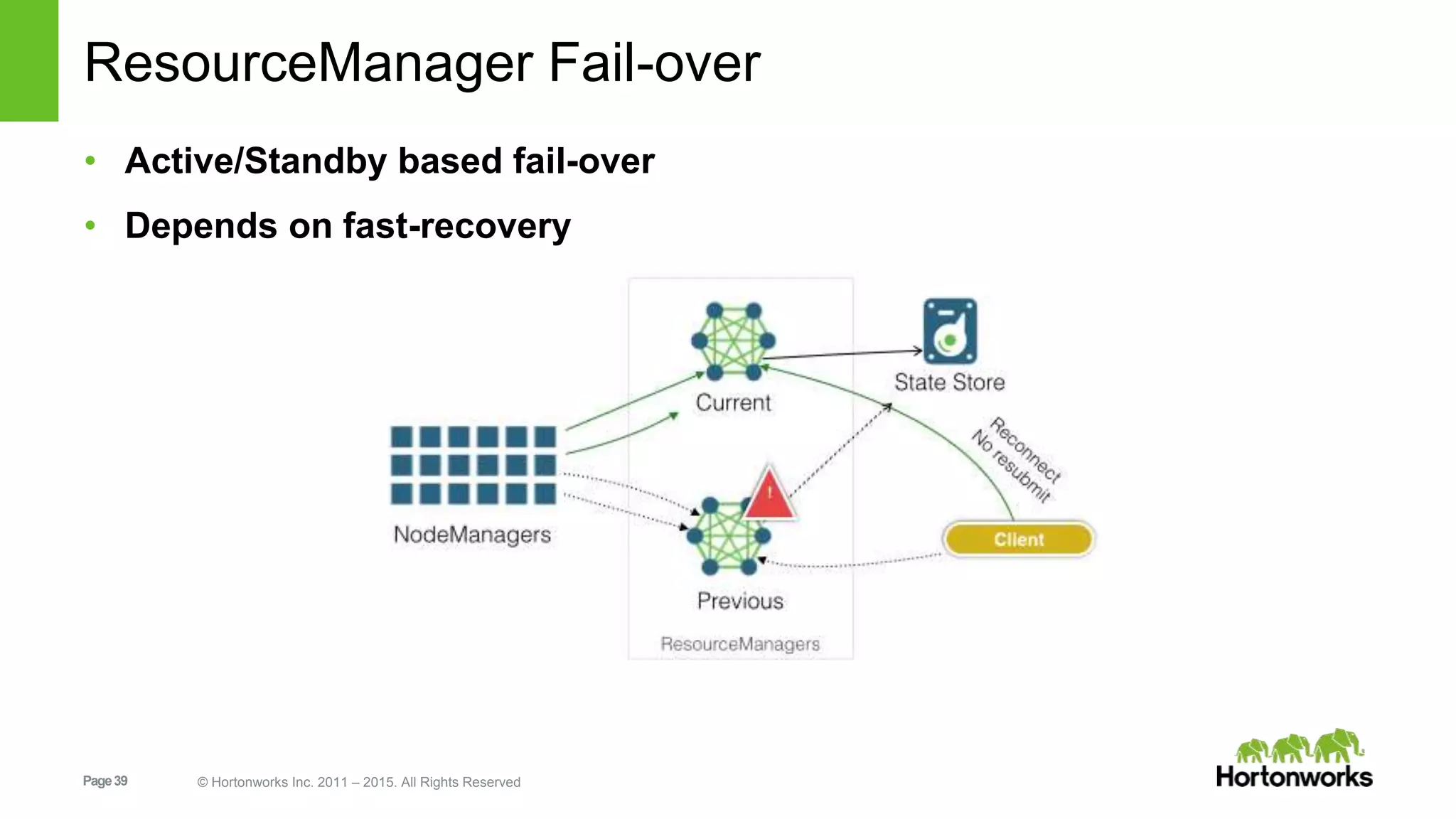
This document provides an overview of Apache Hadoop YARN, including its past, present, and future. In the past section, it discusses the early development of YARN as a sub-project of Hadoop starting in 2010, with its first code release in 2011 and general availability releases from 2013-2014. The present section outlines recent Hadoop releases from 2014-2015 that have incorporated YARN features like rolling upgrades and services on YARN. The future section describes planned improvements to YARN including per-queue policy-driven scheduling, reservations, containerized applications, disk and network isolation, and an improved timeline service.