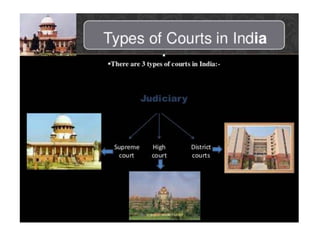
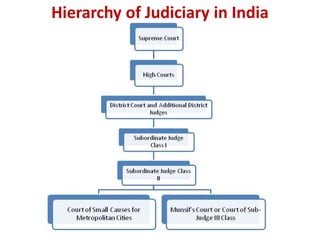
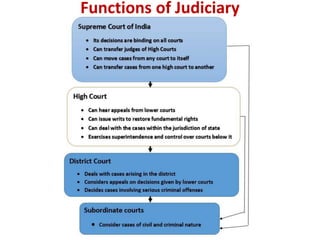
The Indian judicial system has a single integrated structure with the Supreme Court at the top, High Courts in each state, and subordinate courts below the High Courts. It ensures an independent judiciary through measures like secure appointment and salaries of judges. The Supreme Court acts as the final interpreter of the Constitution and has powers like judicial review to evaluate the constitutionality of laws. High Courts also exercise judicial review and help resolve disputes between states and between states and the central government. The judiciary acts as protector of fundamental rights and citizens can approach courts for constitutional remedies.