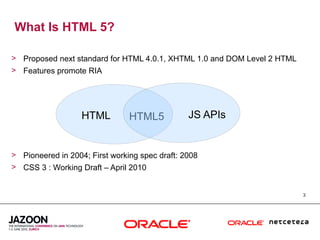
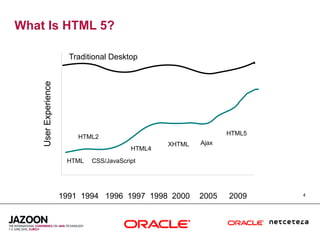
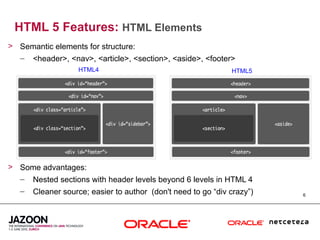
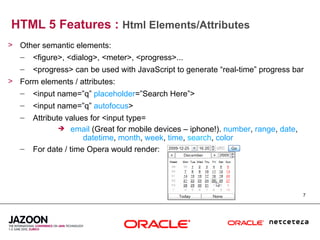
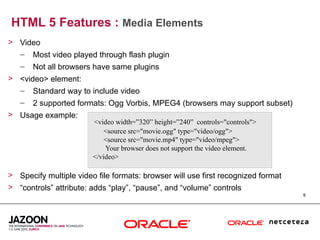
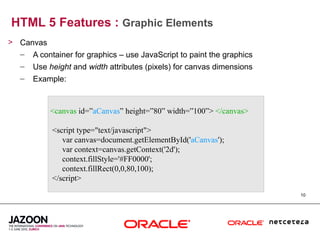
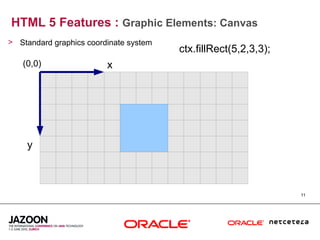
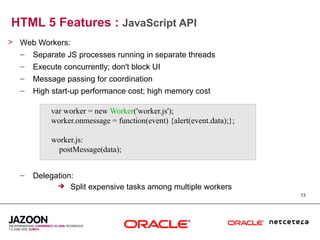
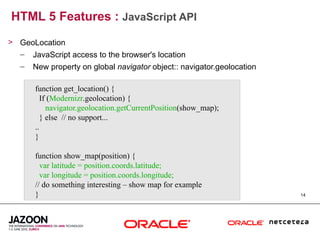
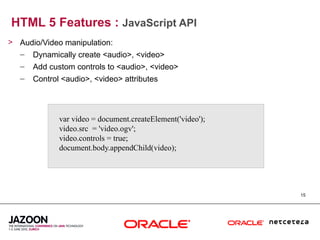
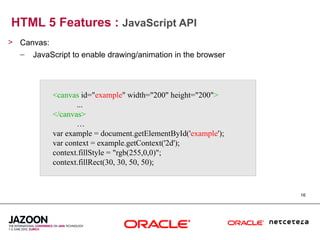
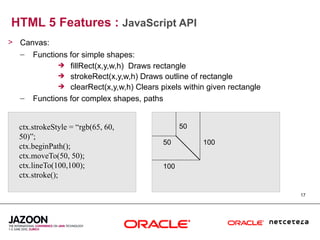
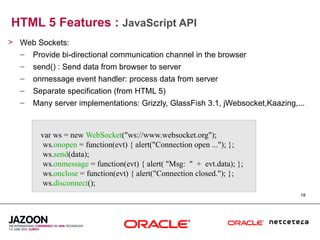
This document discusses HTML5 and how it can be used to enhance JavaServer Faces (JSF) 2.0 components. It provides an overview of HTML5 features such as new semantic elements, form controls, media elements, graphics with canvas, and JavaScript APIs. It also describes JSF 2.0's composite component model and how components can leverage HTML5 features like media playback and JavaScript integration. The document demonstrates a composite audio component that uses HTML5's audio element and JavaScript to control audio playback from JSF. It encourages leveraging HTML5 to promote rich user interfaces and future-proof JSF applications.












![Enhancing JSF 2.0 Components
With HTML 5
audio.js:
function play() {
var audio = document.getElementsByTagName("audio")[0];
audio.play();
var display = document.getElementsByTagName("input")[0];
display.value = audio.src;
}
function pause() {
var audio = document.getElementsByTagName("audio")[0];
audio.pause();
}
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsf2-html5-jazoon-100603141105-phpapp01/85/Jsf2-html5-jazoon-31-320.jpg)





