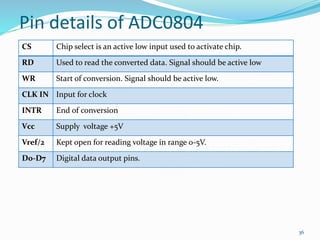
This document contains information about programming microcontrollers using C language including Keil and Proteus software. It provides examples of programs to generate square waves with varying frequency and duty cycle and sense analog signals using an ADC. The programs demonstrate using timers to create delays, interrupts for inputs, and reading analog sensor values to display on ports. The document discusses requirements for microcontroller applications and solutions for meeting needs like providing gate signals, sensing voltage, current, and speed.