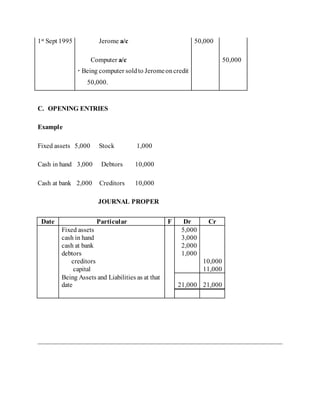
The journal proper is used to record transactions that cannot be entered in subsidiary books like sales returns, purchases returns, and cash books. It contains the date, account debited, account credited, amount, and narrative explaining the transaction. Examples of entries in the journal proper include purchases of fixed assets on credit, sales of fixed assets on credit, and opening entries to record assets, liabilities, and capital on the first day of business.