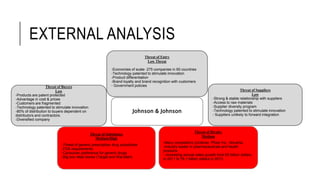
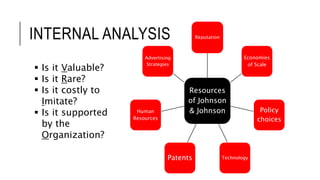
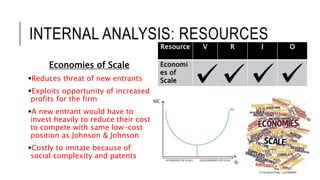
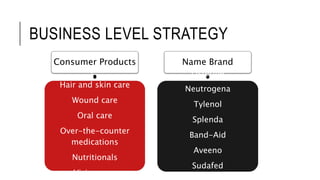
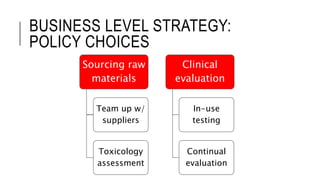
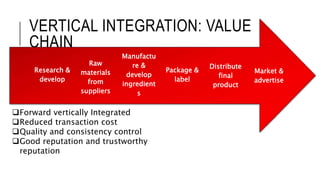
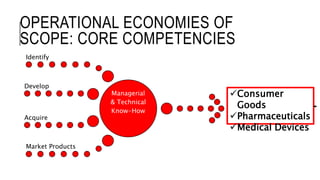
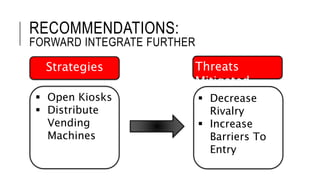
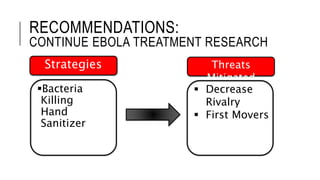
Johnson & Johnson pursues a business-level strategy that is 75% differentiation and 25% cost leadership. At the corporate level, its strategy focuses on vertical integration, product differentiation, and operational economies of scope across its consumer products, pharmaceutical, and medical devices segments. The presentation recommends Johnson & Johnson further integrate forward, continue ebola treatment research, and create a rewards program to mitigate threats from rivals.