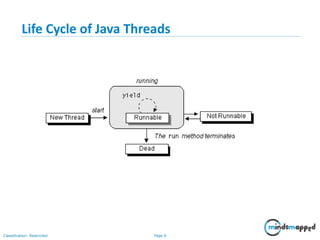
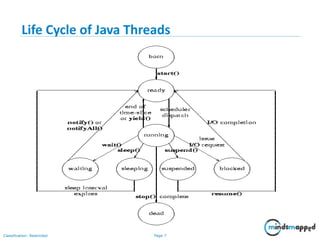
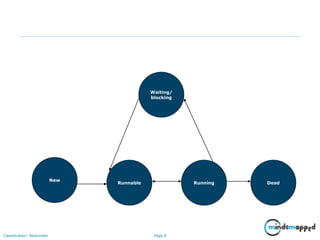
The document provides training on Java multithreading, covering the creation, management, and synchronization of threads using the java.lang.Thread class and the Runnable interface. Key concepts include the life cycle of threads, methods for starting and managing threads (like start(), join(), wait(), and notify()), and mechanisms for synchronizing access to shared resources. It also emphasizes the importance of using synchronized blocks and methods to prevent concurrent access issues.





![Page 5Classification: Restricted
Starting a Thread
• When start() method is called on a Thread object, the thread moves from
the new state to the runnable state
• When the Thread Scheduler gives the thread a chance to execute, the
run() method will be invoked
Eg:
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) System.out.println(“Running”); }
public static void main(String args[])
{
Thread t=new Thread(new MyRunnable());
t.start();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mindsmappedday6session9thread-180730215452/85/Java-Thread-6-320.jpg)







![Page 16Classification: Restricted
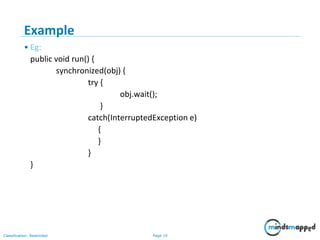
Example – synchronized method
• class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
• public void call(String msg) {
• Synchronized ( new ThreadTest()) {
• System.out.print("("+msg);
• }
• Synchronized ( new ThreadTest()) {
• System.out.print("("+msg);
• }
• try{ Thread.sleep(5000); }
• catch (InterruptedException e){}
• System.out.println(")");
• }
• public void run() {
• call(Thread.currentThread().getName());
• }
• public static void main(String args[]) {
• ThreadTest t=new ThreadTest();
• Thread t1=new Thread(t);
• t1.start();
• Thread t2=new Thread(t);
• t2.start(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mindsmappedday6session9thread-180730215452/85/Java-Thread-17-320.jpg)
![Page 17Classification: Restricted
Example – synchronized block
Eg: class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
• public void call(String msg) {
• System.out.print("("+msg);
• try{ Thread.sleep(5000); }
• catch (InterruptedException e){}
• System.out.println(")"); }
• public void run() {
synchronized(this) {call(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }
• }
• public static void main(String args[]) {
• ThreadTest t=new ThreadTest();
• Thread t1=new Thread(t); t1.start();
• Thread t2=new Thread(t); t2.start();
• } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mindsmappedday6session9thread-180730215452/85/Java-Thread-18-320.jpg)