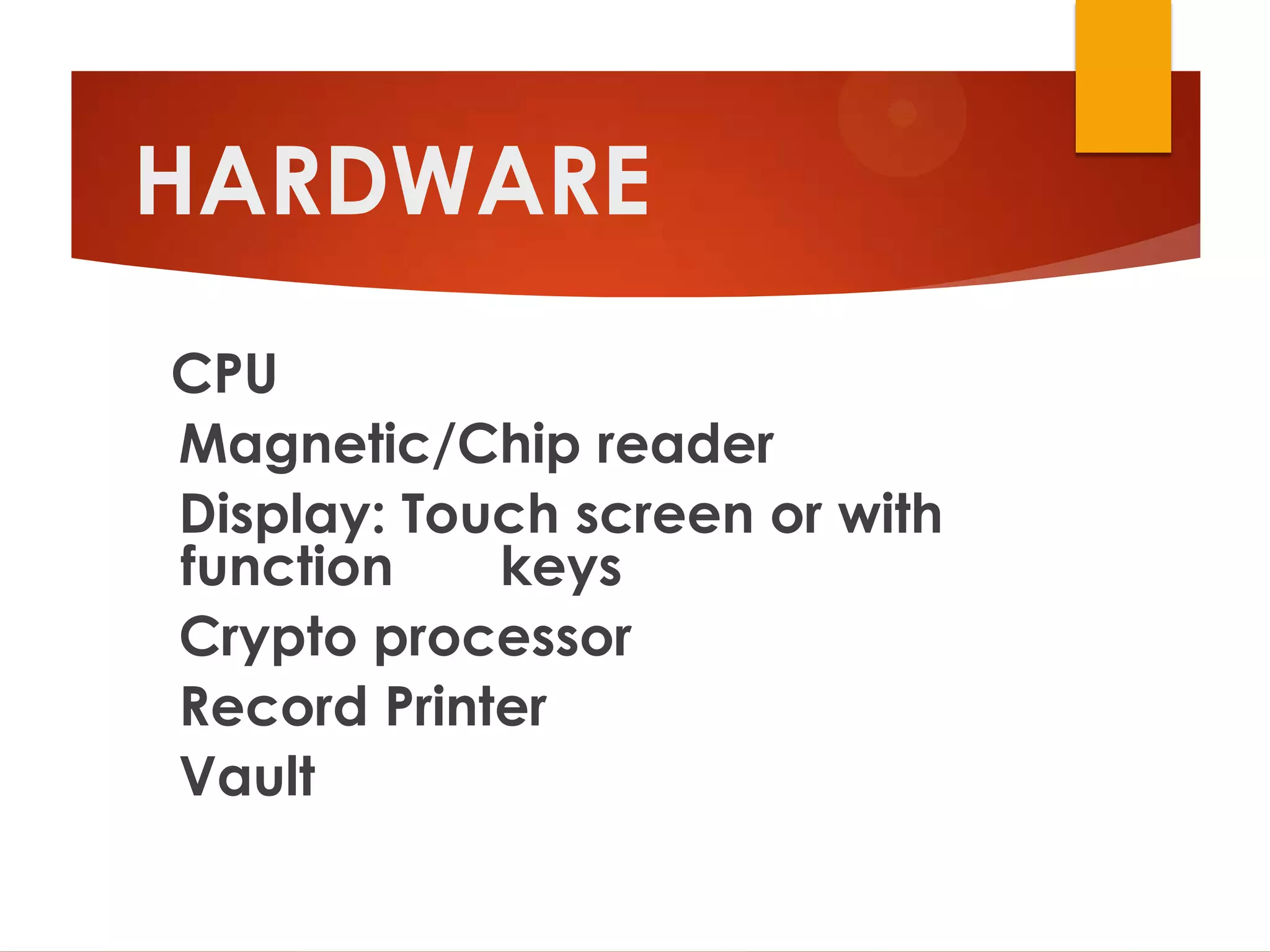
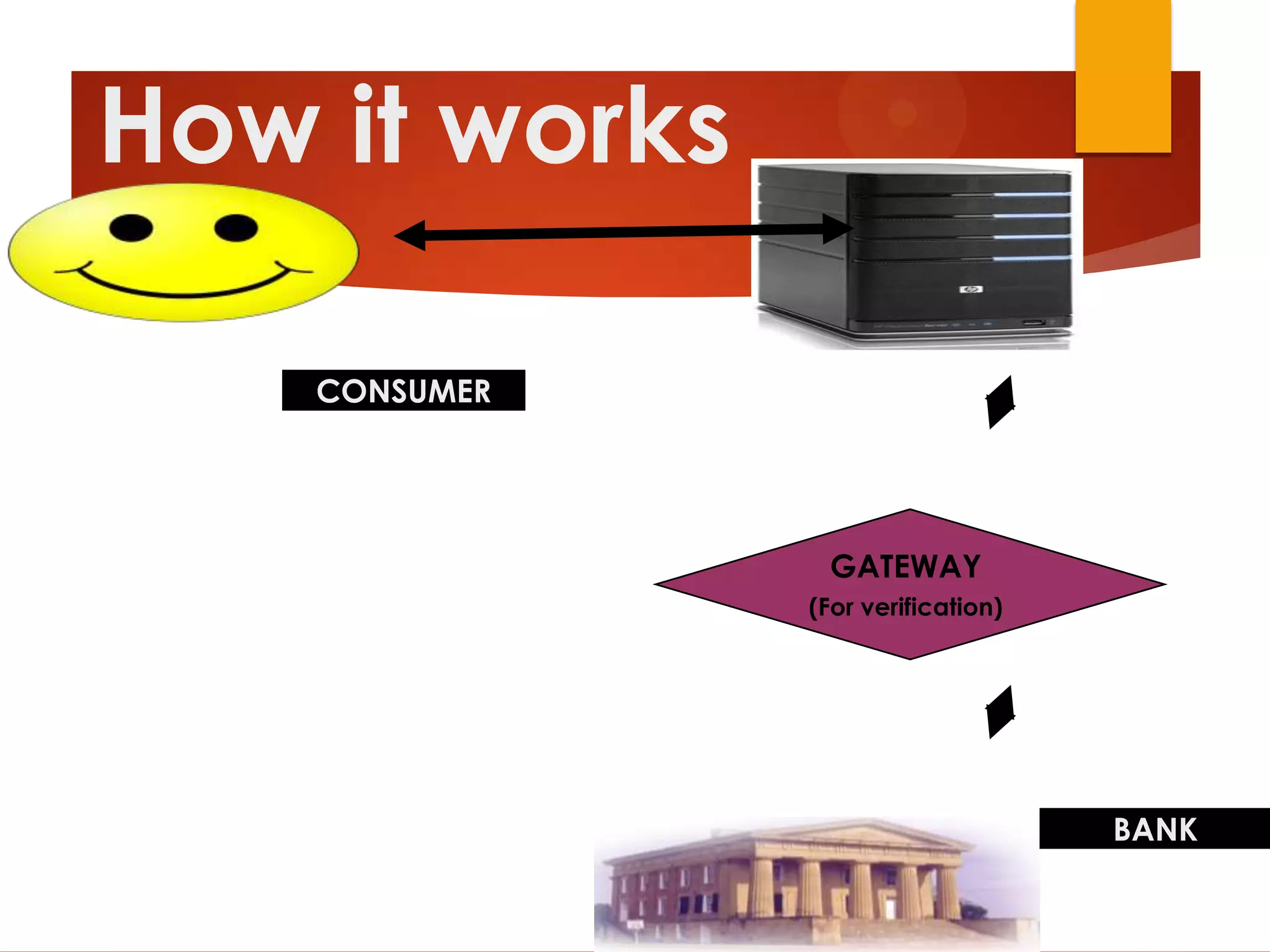
This document provides an overview of ATM components, security features, and operations. It discusses the hardware and software used in ATMs, including tangible security mechanisms like stainless steel housings and time-delay locks. Threats like worms and denial of service attacks are described along with prevention methods like firewalls and network separation. The document explains how ATM transactions work through the consumer, gateway, and bank network. It also covers functions, advantages, disadvantages, and common errors.