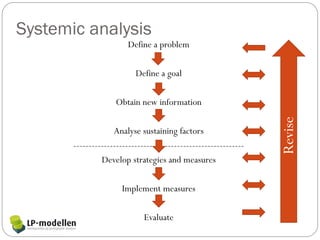
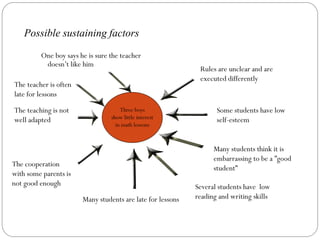
The LP-model is a strategy used in schools to improve the learning environment by having teachers collaborate to analyze challenges. It uses a systematic approach of analysis, reflection, developing measures, and evaluation. The goal is to establish a learning environment where all students can achieve social and academic success. Research shows factors like teacher skills, clear expectations, feedback, and student-teacher relationships impact learning. The LP-model takes a systemic approach, considering how individuals interact within a school's social system and how their actions shape its structures. Teachers analyze potential sustaining factors behind issues and develop strategies to create positive development. Evaluations found improved social skills, school enjoyment, relationships, and collaboration using this model.