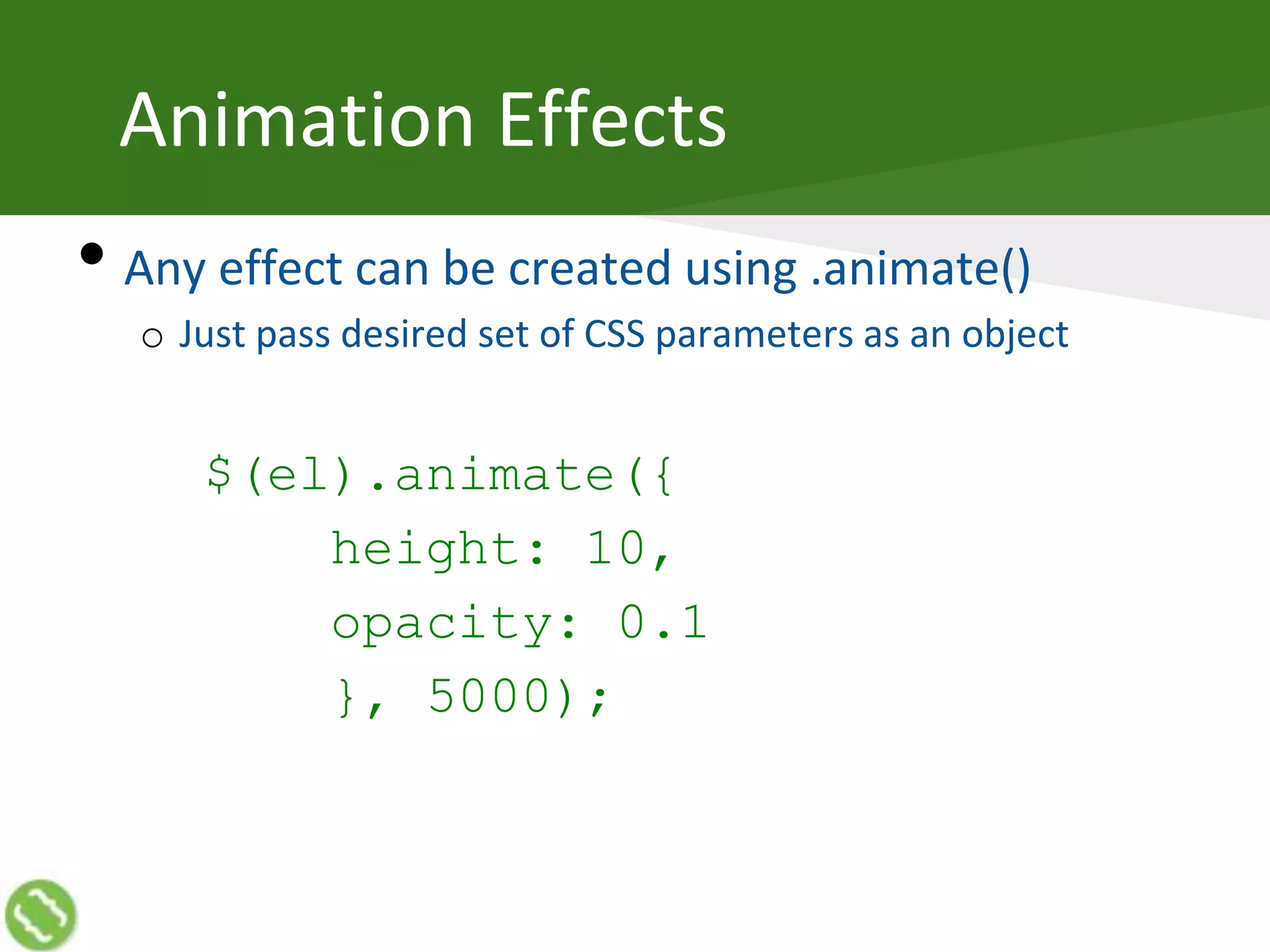
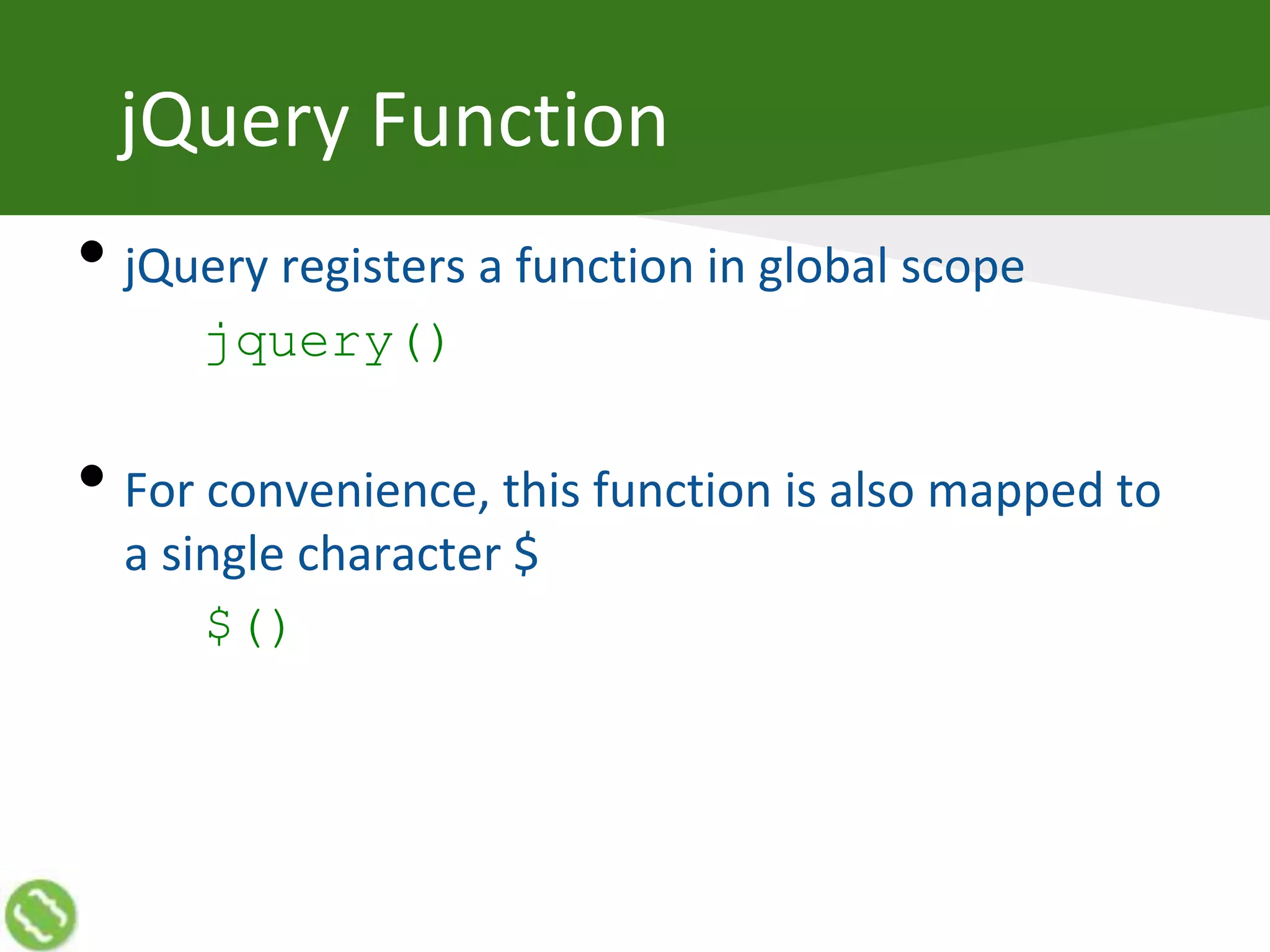
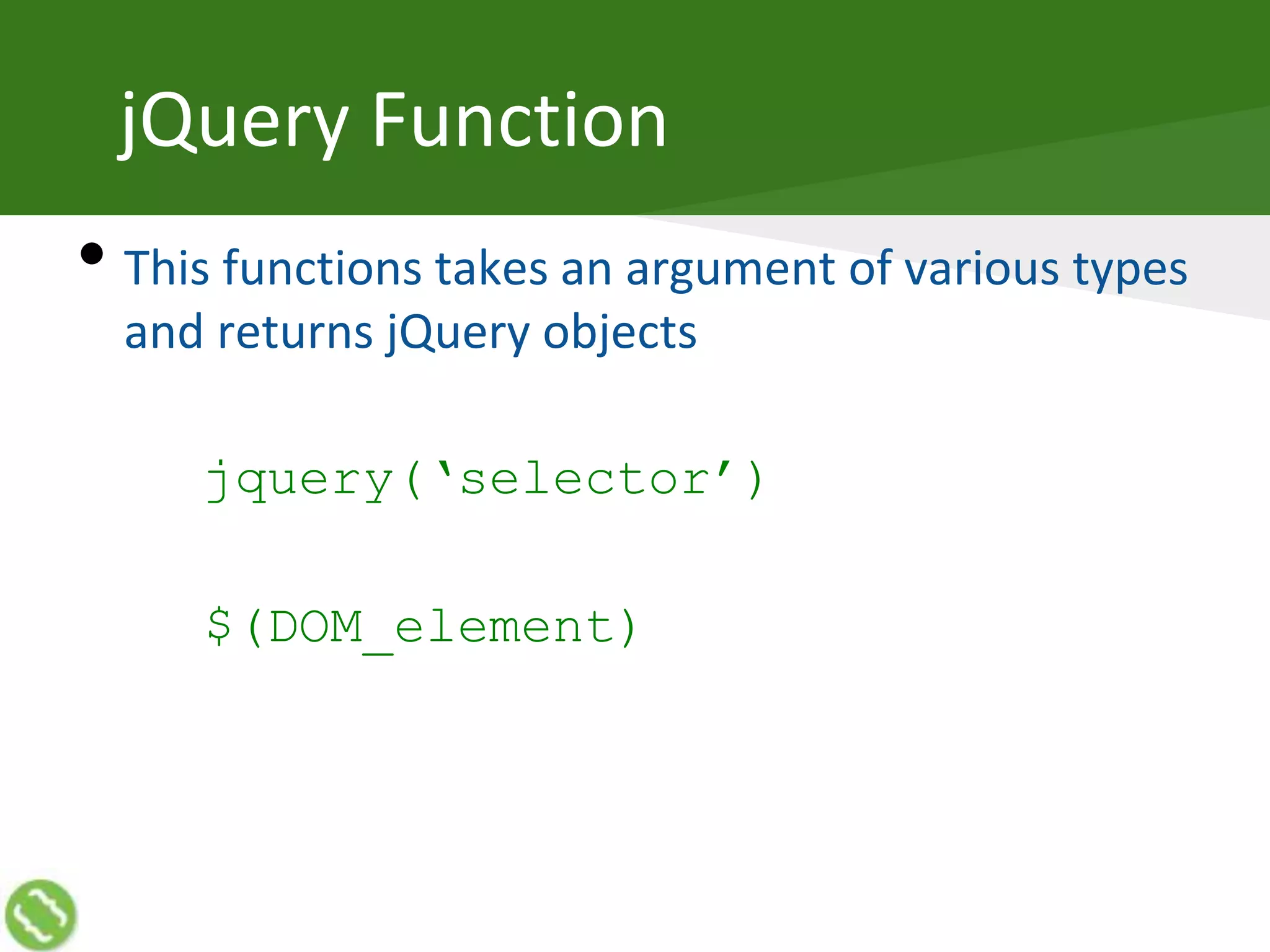
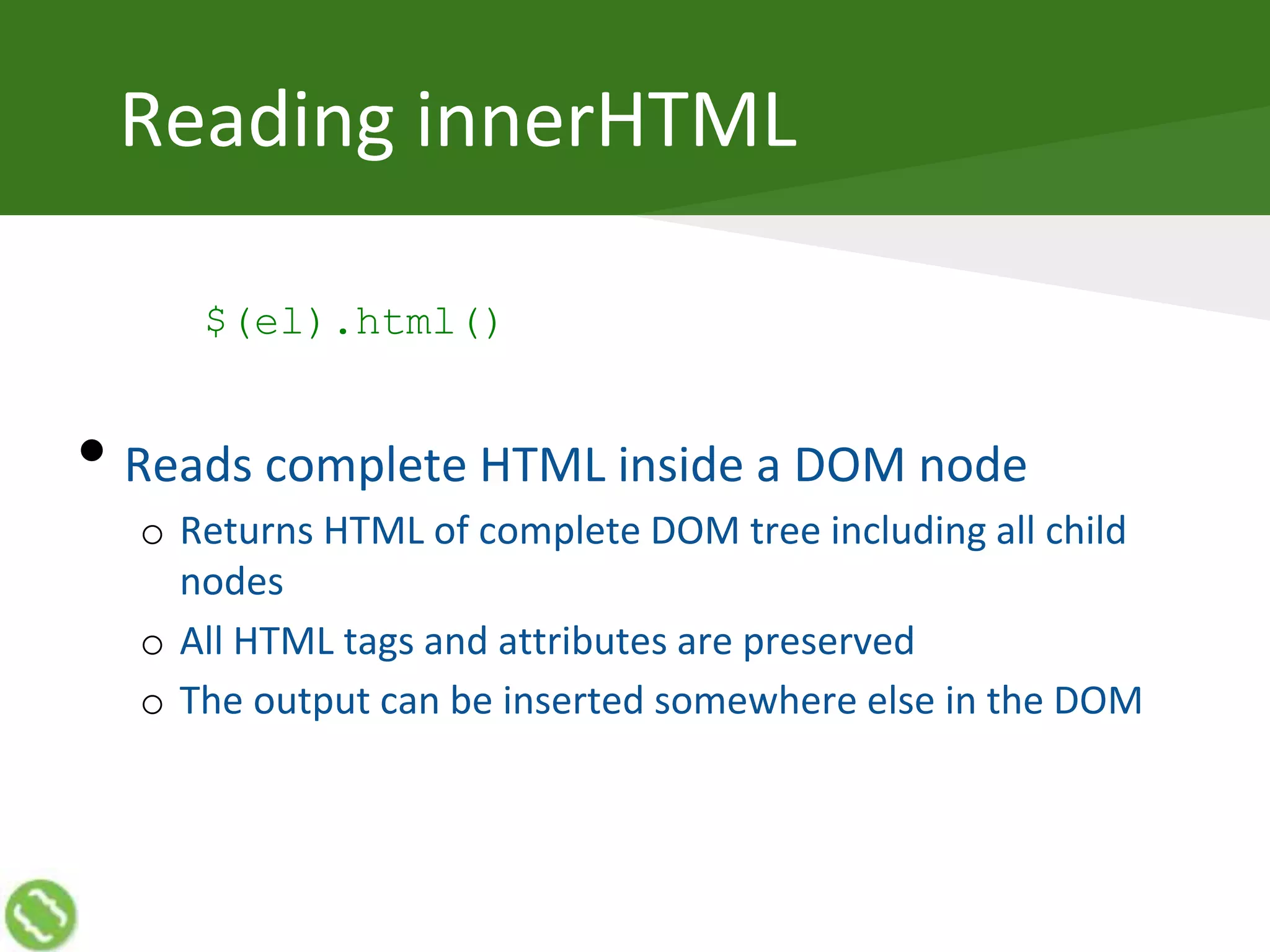
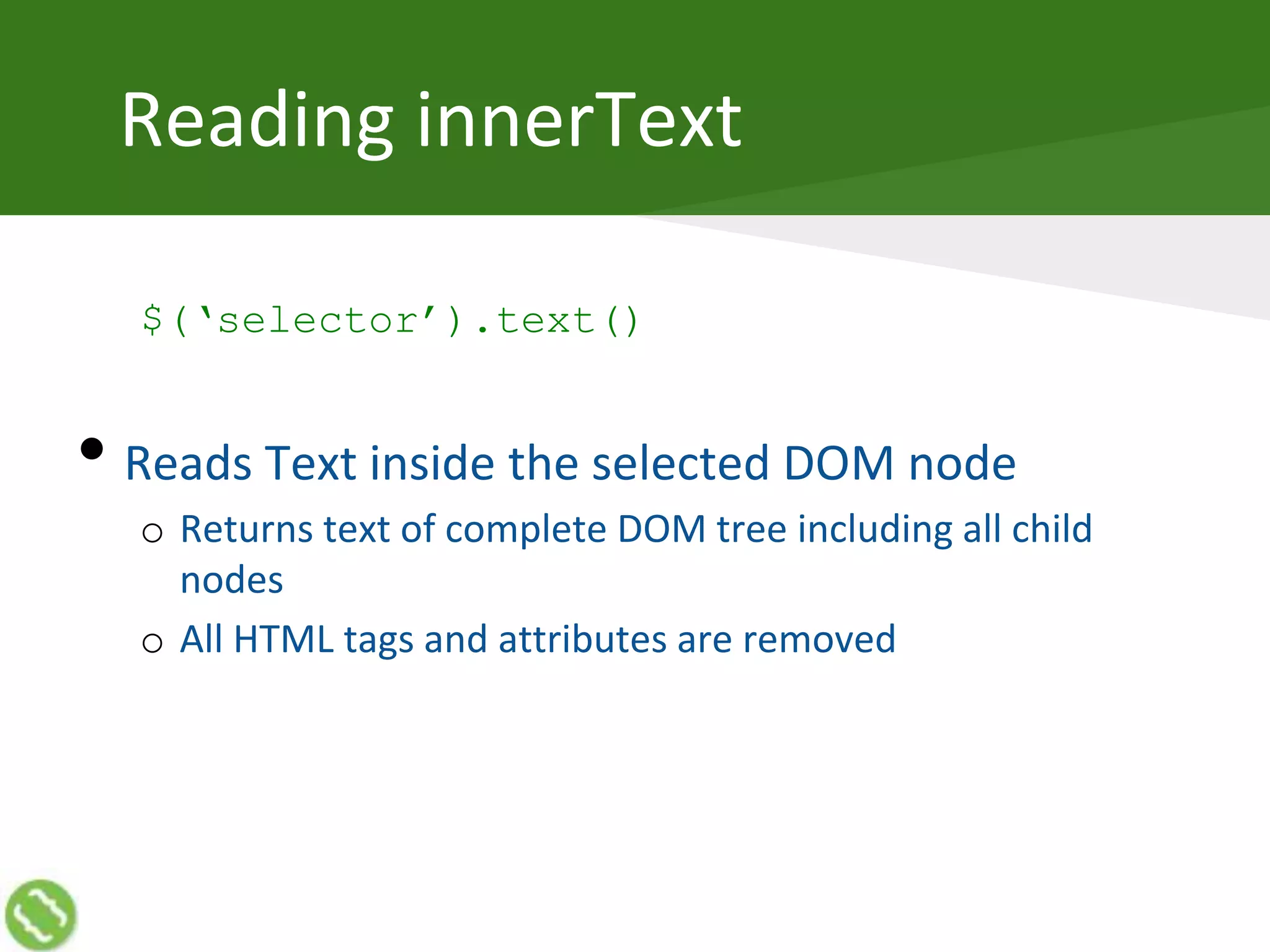
The document discusses creating web applications using jQuery. It begins with introductions and background on the speaker's experience. It then discusses how JavaScript can become complex when building real-world applications, but common requirements emerge a pattern. JavaScript frameworks help simplify coding through interfaces and syntactic sugar. jQuery is introduced as a popular framework that handles cross-browser compatibility issues and simplifies DOM manipulation through selectors and functions. The document then covers various jQuery topics like versions, objects, selectors, reading/manipulating the DOM, events, and communicating with servers.






![jQuery Object
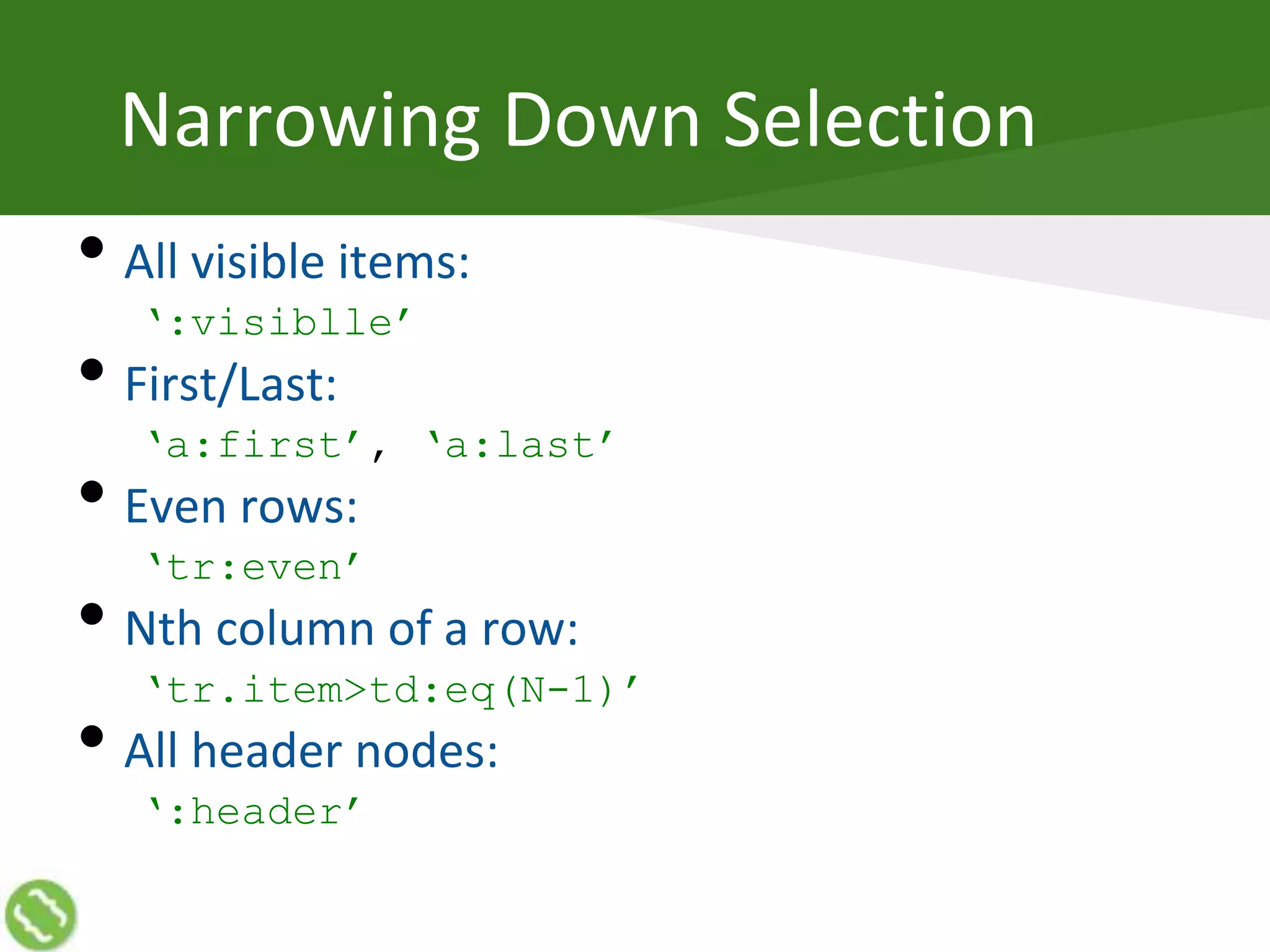
• Always a list (Array)
o Methods of Array work normally on jQuery object
$(‘’).length // 0
o Members of the list are DOM elements
o Empty list, if no element
• Native JavaScript methods and properties are
o NOT available on jQuery Objects
o Available on the members of the Array
$(‘img’)[0].src](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-140315120226-phpapp01/75/Getting-Started-with-jQuery-10-2048.jpg)









![Attribute Selectors
• Attribute selectors allow to create a selection
based on any attribute of a HTML node
o Attribute Equals: “div[el_id=‘my_id’]”
o Attribute Not Equals: “div[el_id!=‘my_id’]”
o Attribute Starts with: “div[el_id^=‘my_id’]”
o Attribute Ends with: “div[el_id$=‘my_id’]”
o Attribute Contains: “div[el_id*=‘my_id’]”
• These work on custom (non-standard) attributes
as well](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-140315120226-phpapp01/75/Getting-Started-with-jQuery-25-2048.jpg)