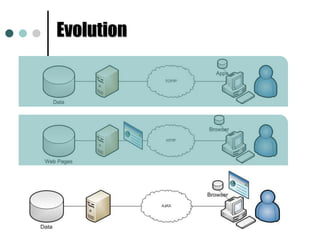
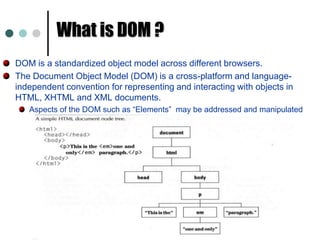
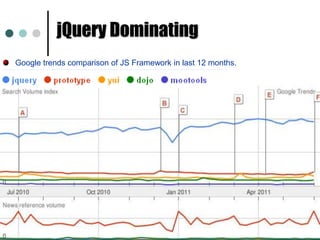
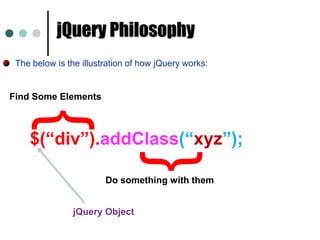
This document provides an introduction and overview of jQuery. It discusses how jQuery simplifies DOM navigation and manipulation, handles browser differences, and makes JavaScript coding easier. The document covers basic jQuery concepts like selectors, the jQuery function, attributes, and events. It also provides examples of common jQuery code.




















![jQuery SelectorsjQuery offers a set of tools for matching set of elements in a document.If you wish to use any of the meta-characters ( such as !"#$%&'()*+,./:; <=>? @[\]^`{|}~ ) as a literal part of a name, you must escape the character with two backslashes: \\.Ex: If you have an element with id="foo.bar", you can use selector $("#foo\\.bar").Some of the selector examples: $(“*”); //Selects all elements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-26-320.jpg)


![$(‘input[name=myName]’); //Selecting elements by attribute.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-29-320.jpg)
![$(‘input[name$=myName]’); //Selecting elements it attribute ends with myName. Choosing the good selector can improve the performance of your selector. To test whether the specified selection contain elements or not. if ($('div.foo').length) { ... } //If no elements it returns 0 and evaluates false.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-30-320.jpg)



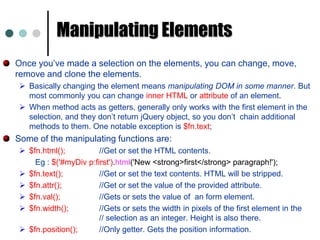
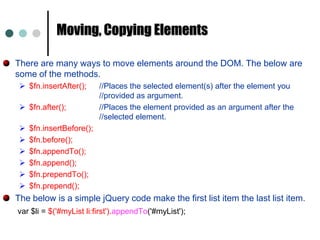
![$("input[type=text]"); // selects inputs that have specified type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-36-320.jpg)


















![$(‘p’)[1] gets the 2nd <p> element (0 based)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-55-320.jpg)







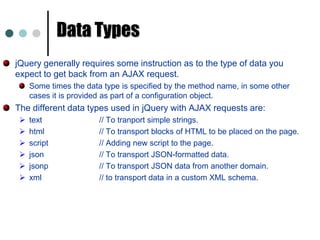


![$(‘img’[alt]) <img> elements having an alt attributeSelecting Elements Example cont..,The below are some more selectors examples:$(‘a’[href^=http://]) //Select <a> elmt with an href attribute starting with ‘http://’.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-66-320.jpg)
![$(‘a’[href$=pdf]) //Select <a> elmt with an href attribute ending with pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-67-320.jpg)
![$(‘a’[href*=ntpcug]) //Select <a> elmt with an href attribute containing ‘ntpcug”. Working with Attributes The $fn.attr method acts as both a getter and setter. The $.fn.attr as a setter can accept either a key and a value, or an object containing one or more key/value pairs.$('a').attr('href', 'allMyHrefsAreTheSameNow.html'); //single attribute.$('a').attr({ // Multiple attribues. 'title' : 'all titles are the same too!', 'href' : 'somethingNew.html' });The below example demonstrates the getting attribute href of the first <a> element in the document. $('a').attr('href');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jquery-111016203030-phpapp01/85/jQuery-68-320.jpg)






