The document provides an overview of the key topics covered in the ITIL 4 Foundation exam preparation, including:
- Key concepts and definitions in ITIL 4 such as service, value, and customers
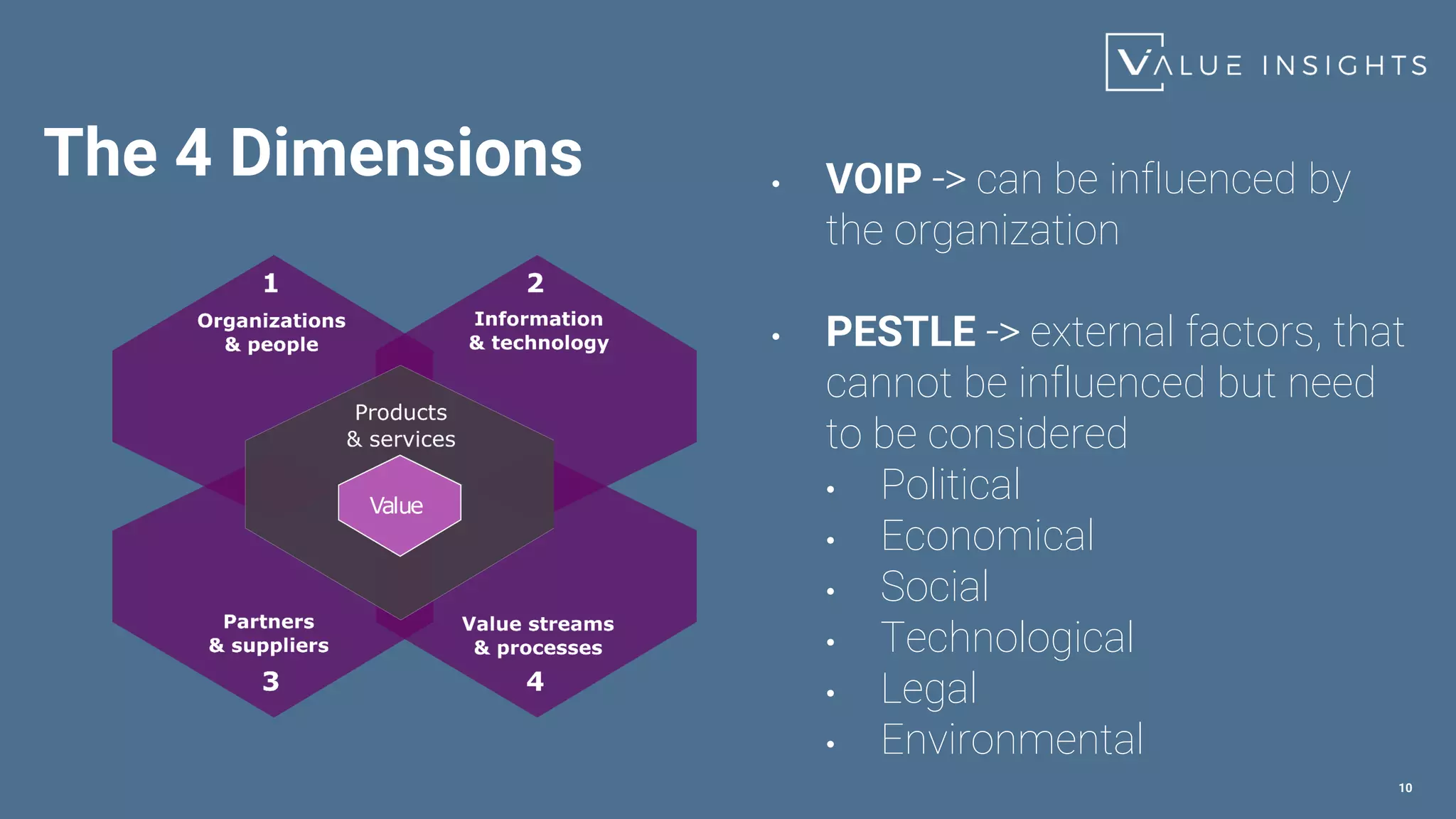
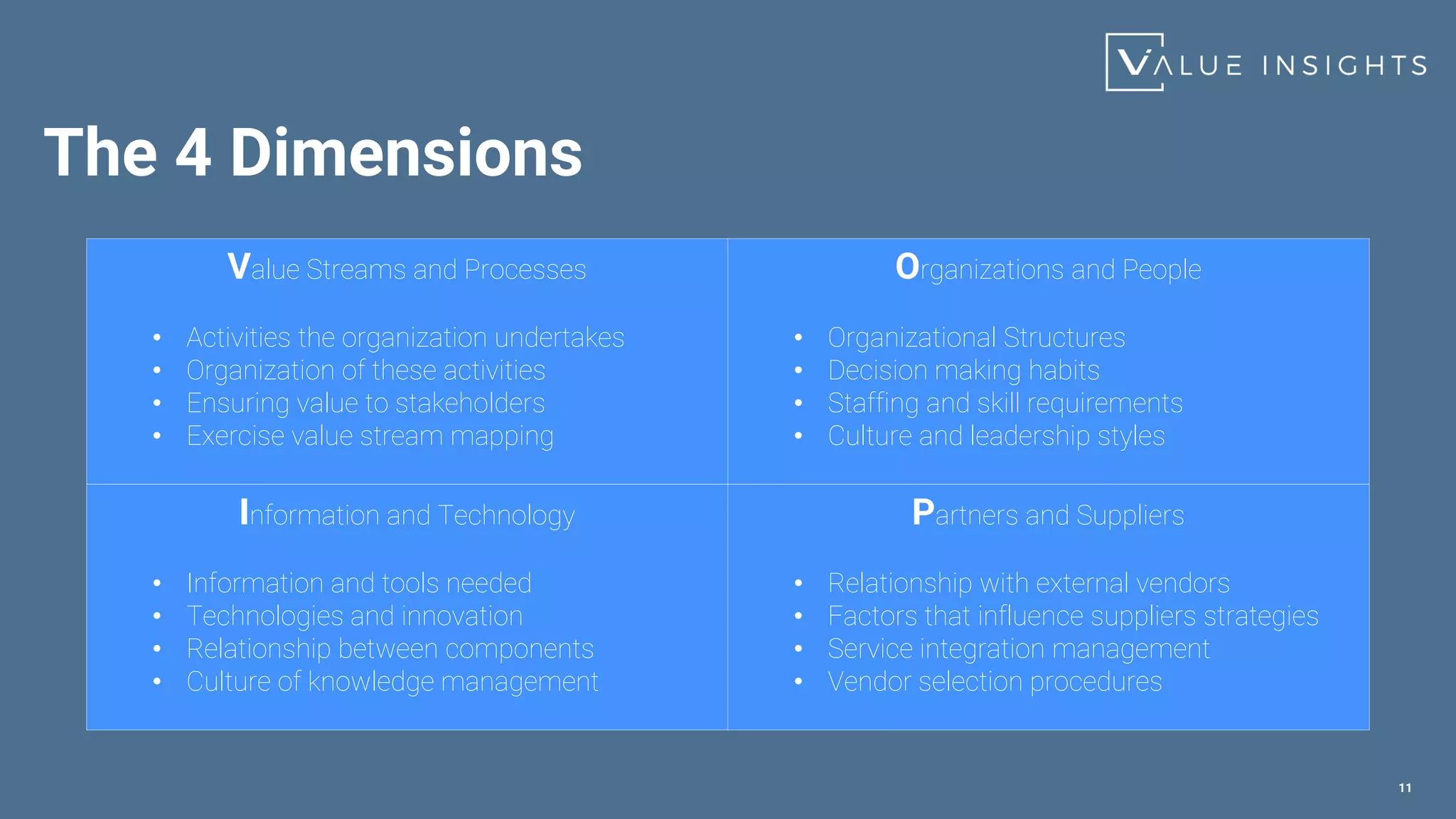
- The four dimensions of service management - value streams and processes, organizations and people, information and technology, and partners and suppliers
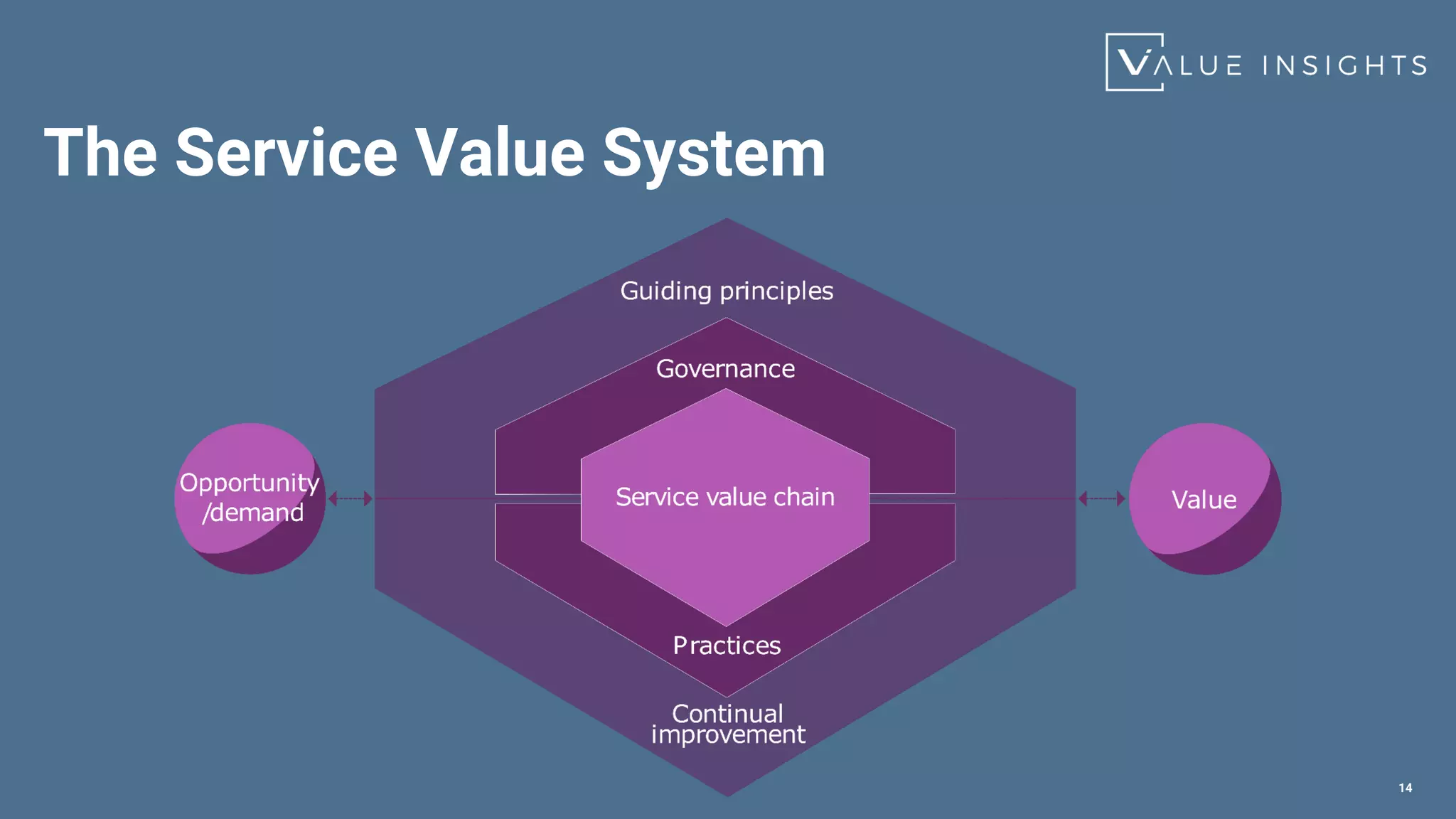
- The service value system that represents the flow of value
- The guiding principles that should guide service management activities
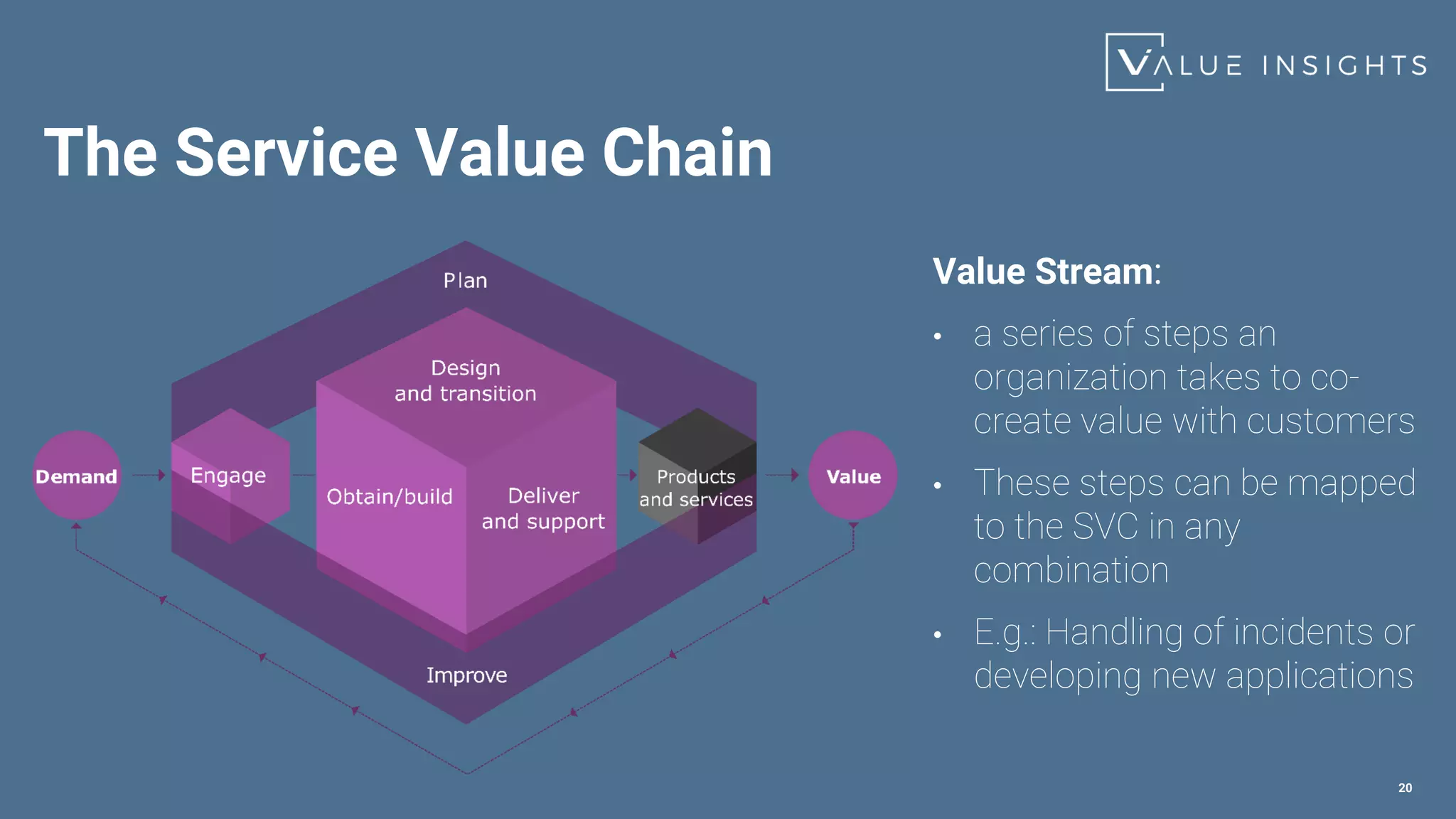
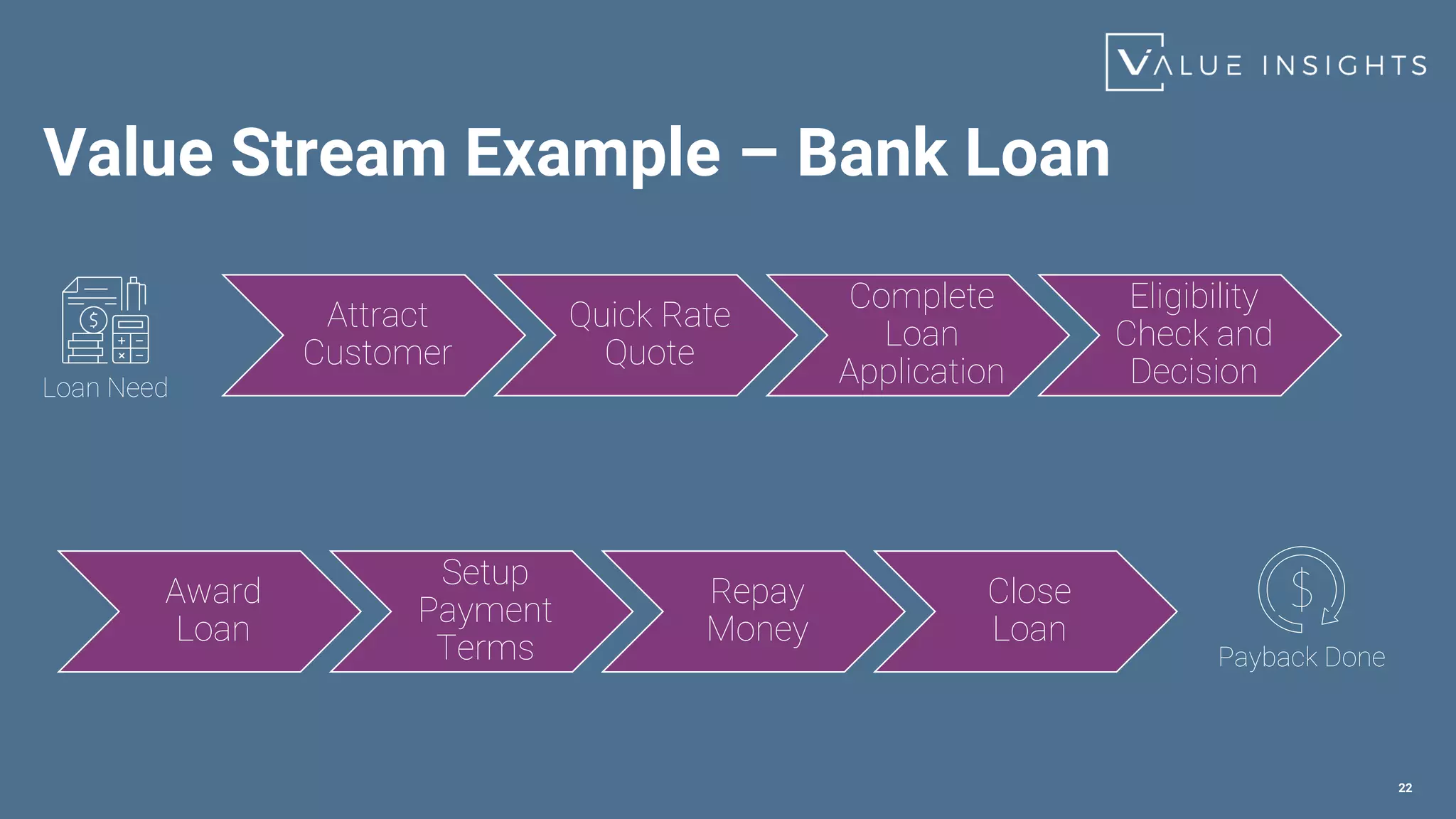
- The service value chain (PIEDOD) that outlines the activities needed to transform demand into value
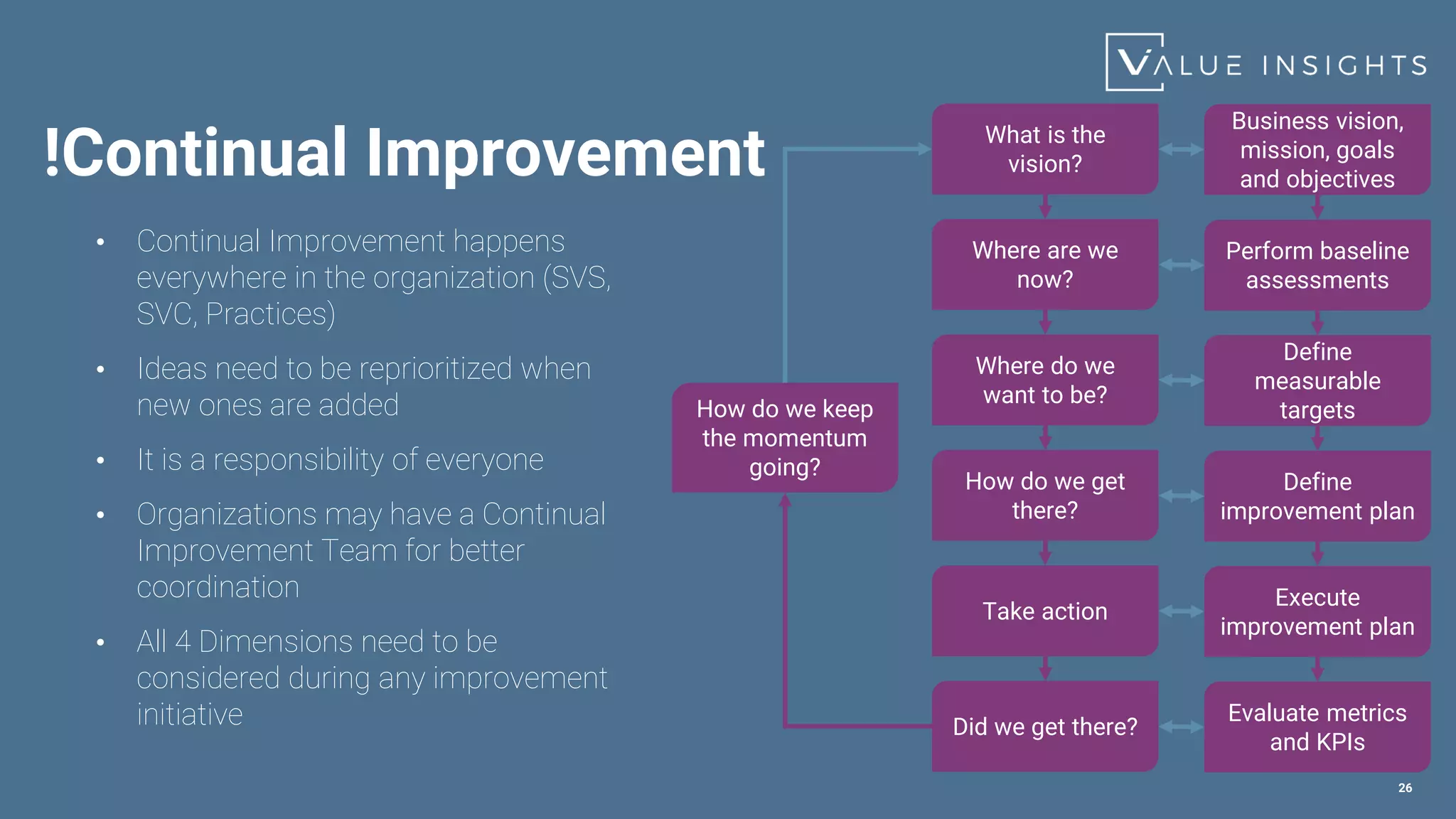
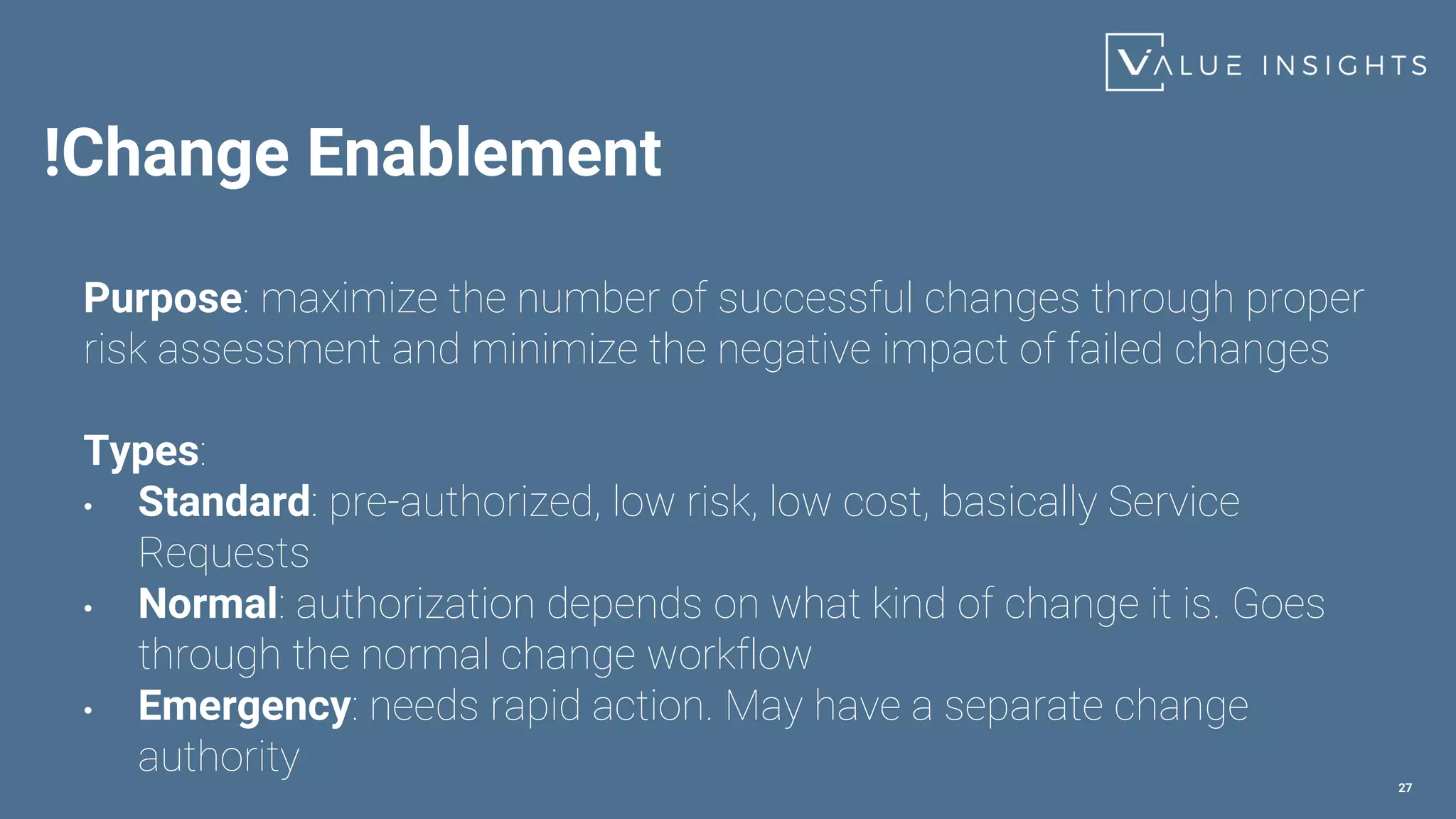
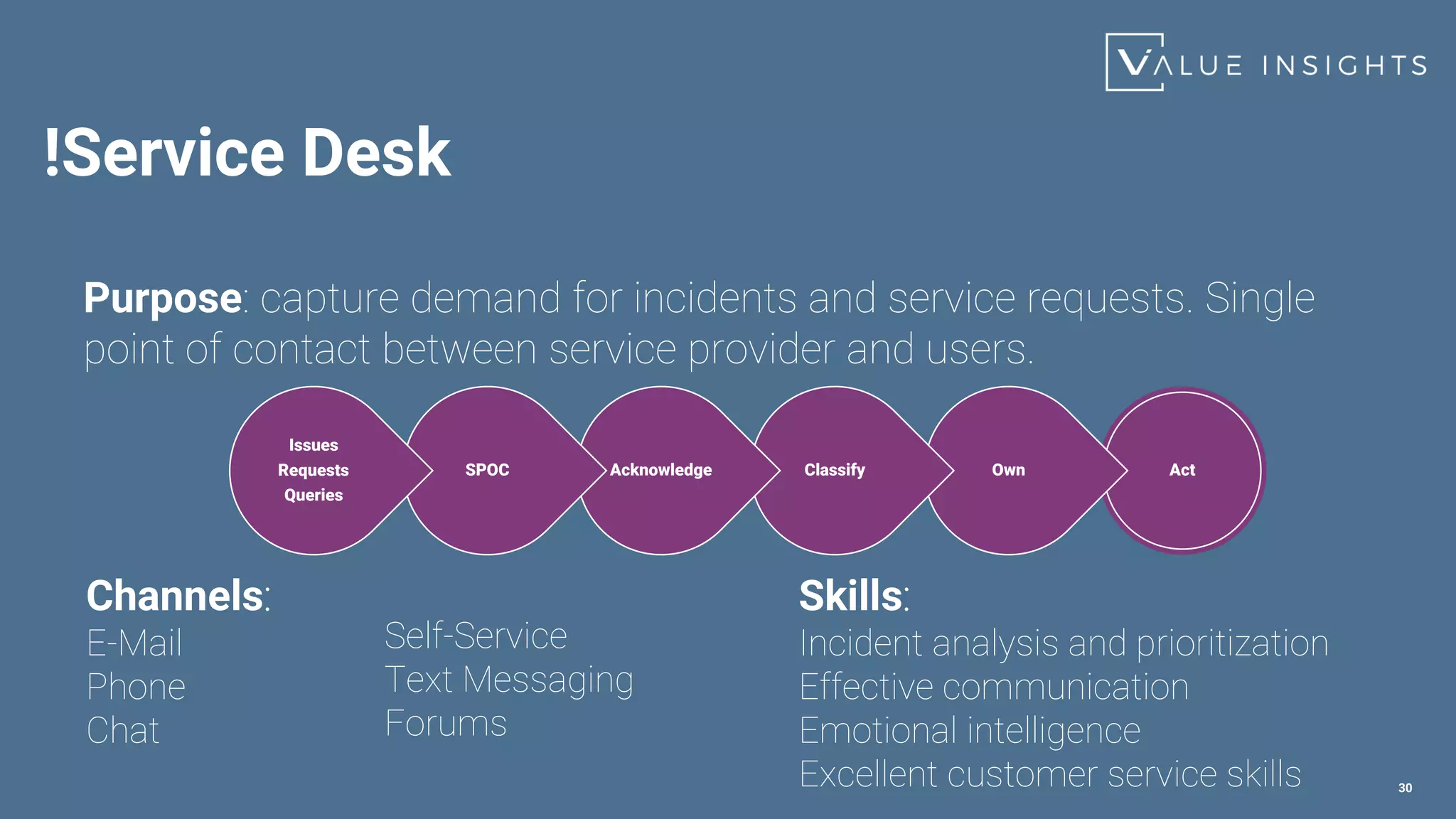
- An overview of the most important service management practices including continual improvement, change enablement, incident management, problem management, and service level management






















![GET IN TOUCH
WITH US
O U R C O M P A N Y
- [ ] -
https://valueinsights.ch info@valueinsights.ch
Value Insights GmbH
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valueinsights-itil4foundation-exampreparationv1-230320154557-73916b03/75/Value-Insights-ITIL-4-Foundation-exam-preparation-v1-0-1-pdf-39-2048.jpg)